Recent groundbreaking studies have uncovered that sonic waves can induce vivid hallucinations when applied in controlled lab environments. This surprising discovery opens new avenues for understanding brain function and presents potential therapeutic applications for neurological disorders.
Understanding Sonic Waves and Their Interaction with the Brain
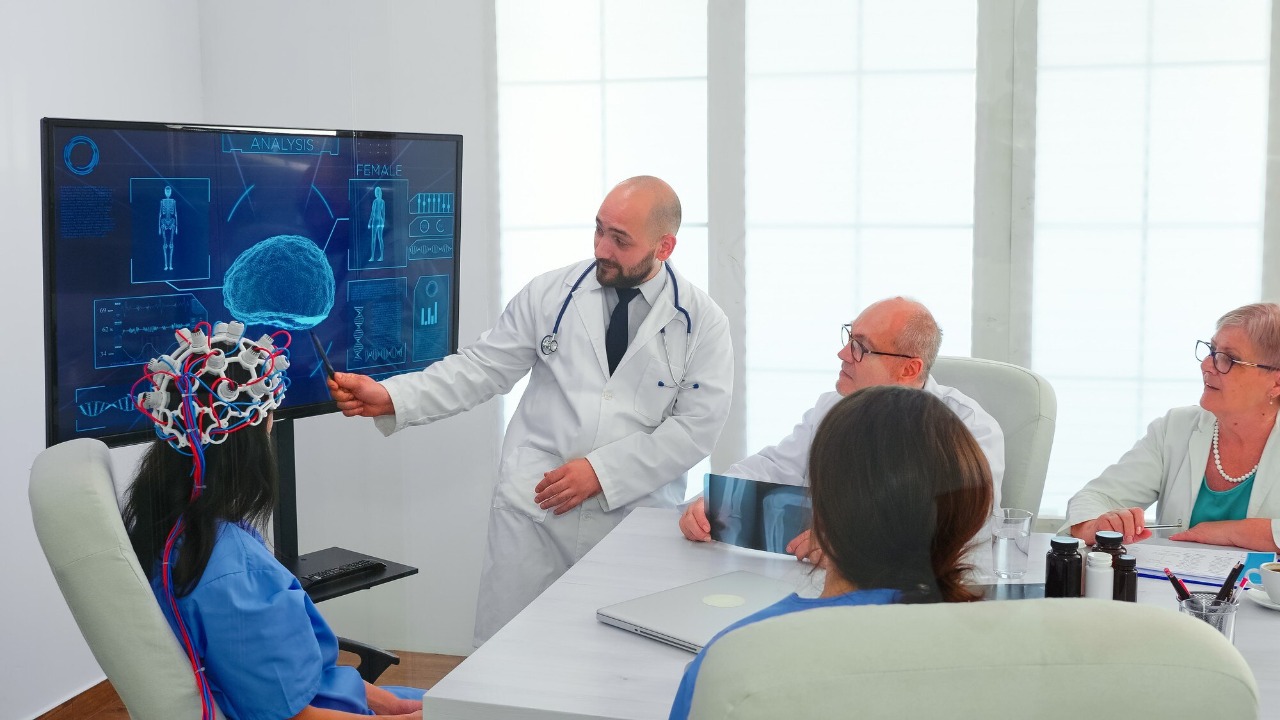

Sonic waves, essentially sound waves, are vibrations that travel through the air or another medium. These waves have varying frequencies, which can interact with brain tissues in unique ways. The use of focused sound waves presents a fascinating method to penetrate the skull non-invasively, allowing researchers to target specific brain areas without surgical intervention. This method could potentially revolutionize how we approach brain research and treatment.
Historically, sonic waves have been explored in various contexts, especially in medical imaging and therapy. For instance, ultrasound technology has long been used to visualize internal organs. In recent years, researchers have extended this concept by using sound waves to influence brain activity, as seen in studies involving transcranial ultrasound stimulation. These studies laid the groundwork for the current research, which aims to uncover the full potential of sound waves in affecting brain functions.
Lab Tests and Methodology
The experimental setup for the current studies involves a highly controlled lab environment equipped with advanced technology to direct sonic waves precisely. A significant breakthrough in this field is the use of holographic techniques to focus sound waves on specific brain circuits. This precision targeting is crucial for observing direct effects and minimizing unintended consequences.
When it comes to subject selection, researchers adhere to strict ethical guidelines to ensure the safety and well-being of participants. Volunteers undergo thorough screening to meet criteria related to health status and psychological stability. During the tests, subjects are exposed to varying frequencies and intensities of sonic waves while researchers monitor their brain activity and subjective experiences. This step-by-step approach allows for careful observation of hallucinations and other neurological responses.
Results: Vivid Hallucinations Induced by Sonic Waves
The results of these experiments are both intriguing and enlightening. Subjects reported experiencing a range of hallucinations, including visual phenomena like seeing colors and shapes, as well as auditory hallucinations such as hearing music or voices. One participant described the experience as “a vivid dream while being fully awake,” highlighting the profound impact of the sonic stimulation.
Data analysis from these experiments reveals statistically significant findings. The intensity and duration of hallucinations varied based on the frequency and focus of the sound waves applied. For instance, higher frequency waves tended to induce more intense visual hallucinations, while lower frequencies were more likely to trigger auditory experiences. These findings underline the complex relationship between sound waves and brain activity, suggesting that different areas of the brain may respond uniquely to sonic stimulation.
Implications for Neuroscience and Therapeutic Applications

These groundbreaking findings offer substantial advancements in our understanding of brain function. By manipulating sensory processing through sonic waves, researchers gain deeper insights into how the brain constructs reality and perception. This research also contributes to broader discussions on consciousness and the subjective nature of experience, potentially offering clues to some of neuroscience’s most enduring questions.
From a therapeutic perspective, the ability to induce controlled hallucinations opens up new possibilities for treating mental health disorders. Disorders such as depression and schizophrenia, where perception and reality are often distorted, could benefit from non-invasive brain stimulation techniques. The potential for using sonic waves as a therapeutic tool is vast, offering a non-pharmaceutical approach to mental health treatment that could reduce reliance on medication and its associated side effects.
Future Research Directions and Ethical Considerations
The promising results of these studies pave the way for future research that could further expand our understanding of sonic wave-induced hallucinations. Areas for further study include the long-term effects of repeated sonic wave exposure, as well as testing on a more diverse group of subjects to ensure the generalizability of findings. Collaboration between neuroscientists and technologists will be vital in pushing the boundaries of this research, potentially leading to new technological advancements.
However, with these exciting possibilities come ethical and safety concerns that must be addressed. The idea of manipulating brain activity using sound waves raises questions about consent and the potential for misuse. Ensuring informed consent is paramount, and safety protocols must be rigorously followed to protect participants. As research progresses, maintaining ethical standards will be crucial in harnessing the positive potential of sonic wave technology while safeguarding against its risks.