Scientists have achieved a groundbreaking feat by capturing images of Neptune’s northern aurora for the first time. This remarkable discovery provides new insights into the dynamic atmospheric phenomena of the distant ice giant, offering a glimpse into the planet’s complex magnetic field and interaction with solar winds.
The Significance of Neptune’s Auroras
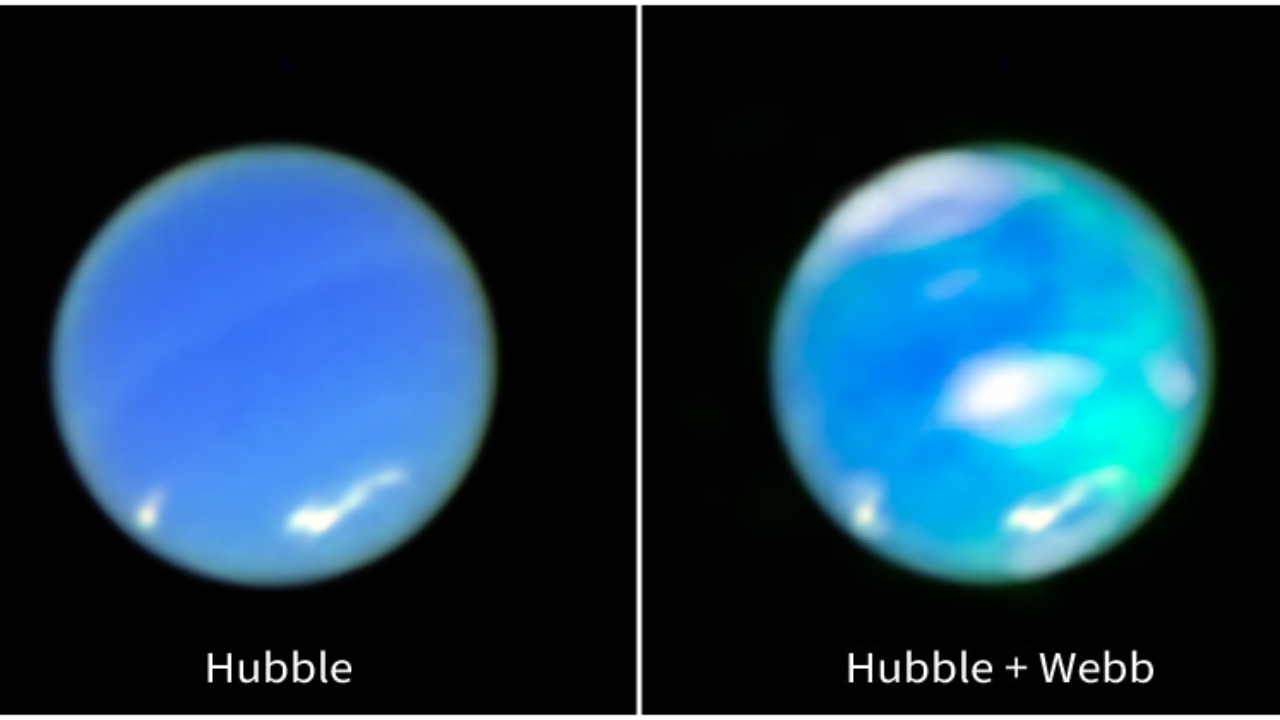
Auroras are dazzling natural light displays that occur when charged particles from the sun interact with a planet’s magnetic field. On Earth, these phenomena manifest as the northern and southern lights, captivating onlookers with their vibrant colors. The discovery of auroras on Neptune, a planet located nearly 4.5 billion kilometers from the sun, underscores the dynamic nature of its atmosphere. Unlike Earth, where auroras are largely confined to polar regions, Neptune’s magnetic axis is tilted relative to its rotational axis, resulting in auroral activity at more varied latitudes.
Studying auroras on Neptune provides valuable insights into planetary atmospheres beyond our own. Unlike the auroras on Jupiter and Saturn, which are influenced by volcanic activity on their moons, Neptune’s auroras are primarily driven by solar winds. This makes them an intriguing subject for scientists hoping to understand the magnetic environments of ice giants. By examining these celestial displays, researchers can unravel the mysteries of Neptune’s magnetosphere and its interactions with the solar system, offering clues to the planet’s internal structure and atmospheric dynamics.
Technological Advancements Enabling the Discovery
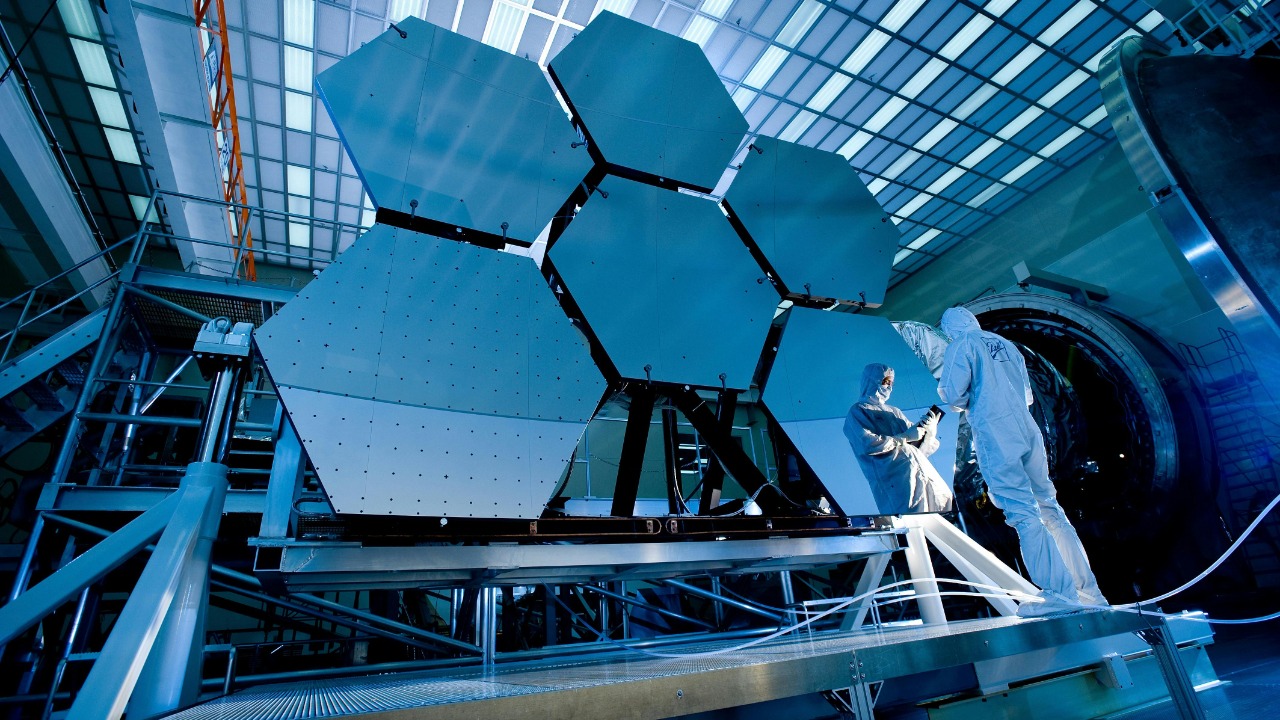

The successful capture of Neptune’s northern aurora was made possible through cutting-edge technology and international collaboration. Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope played a crucial role in this achievement. These telescopes, equipped with advanced imaging capabilities, allowed scientists to detect the faint glimmers of auroral activity on the distant planet. The James Webb Space Telescope, in particular, provided unparalleled clarity and resolution, enabling researchers to capture high-quality images despite the vast distances involved.
Photographing auroras on a distant planet like Neptune poses significant challenges. The planet’s faintness and distance from Earth make it difficult to capture detailed images. Additionally, its rapid rotation and dynamic atmosphere add complexity to the task. Overcoming these obstacles required precise coordination and expertise from scientists around the world, working together to push the boundaries of space observation technology. The success of this mission highlights the importance of international partnerships in advancing our understanding of the universe.
Scientific Insights from Neptune’s Auroras
The data obtained from the newly captured images of Neptune’s auroras have provided scientists with a wealth of information about the planet’s magnetosphere. The analysis of these images has revealed intriguing details about the strength and orientation of Neptune’s magnetic field. Unlike Earth’s relatively stable magnetic field, Neptune’s is highly dynamic and misaligned with its rotational poles. This misalignment results in unusual auroral patterns that offer valuable clues about the planet’s internal structure and the movement of charged particles within its atmosphere.
Understanding the connection between Neptune’s auroras and its atmospheric conditions is crucial for deciphering the planet’s climate and weather patterns. The interaction between the solar wind and Neptune’s magnetic field generates energy that influences the planet’s atmospheric dynamics. By studying these interactions, scientists can gain insights into the processes that drive weather systems on Neptune, such as its powerful storms and prevailing winds. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of Neptune itself but also provides a broader context for studying other ice giants in our solar system.
Implications for Future Space Exploration

The successful capture of Neptune’s northern aurora has significant implications for future space exploration missions. This discovery demonstrates the potential for new technology to enhance our ability to study distant planets. As scientists continue to refine their understanding of Neptune’s magnetosphere and atmospheric conditions, they can develop more targeted missions to explore the planet in greater detail. Future missions could involve sending probes equipped with advanced instruments to study Neptune’s auroras up close, providing unprecedented insights into its magnetic environment.
Furthermore, the techniques and technologies used in capturing Neptune’s auroras can be applied to the exploration of other outer planets in our solar system. By studying auroral phenomena on planets like Uranus, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the diversity and complexity of planetary magnetospheres. These discoveries contribute to the broader field of planetary science, helping scientists piece together the puzzle of how different planets interact with the solar wind and evolve over time.
Public and Academic Reactions

The discovery of Neptune’s northern aurora has sparked excitement and interest within the scientific community. Researchers worldwide have hailed this achievement as a significant milestone in planetary science. The data collected from these observations will be the subject of numerous studies, offering new avenues for research and exploration. The academic community recognizes the importance of these findings in advancing our understanding of planetary magnetospheres and atmospheric dynamics.
Public interest in the discovery has also been substantial, with media coverage highlighting the significance of this achievement. The captivating images of Neptune’s auroras have captured the imagination of people around the world, sparking curiosity about the mysteries of the outer planets. This increased public interest could lead to greater support for funding future missions to explore Neptune and other distant worlds. The discovery serves as a reminder of the enduring fascination with space exploration and the endless possibilities for discovery that lie beyond our planet.