NASA’s Opportunity rover reshaped our understanding of Mars by uncovering evidence of water, opening new avenues in the search for life beyond Earth. Through its groundbreaking discoveries, Opportunity has illuminated the Martian landscape in ways previously unimagined, marking a pivotal moment in space exploration history.
The Journey of Opportunity: A Mission Overview
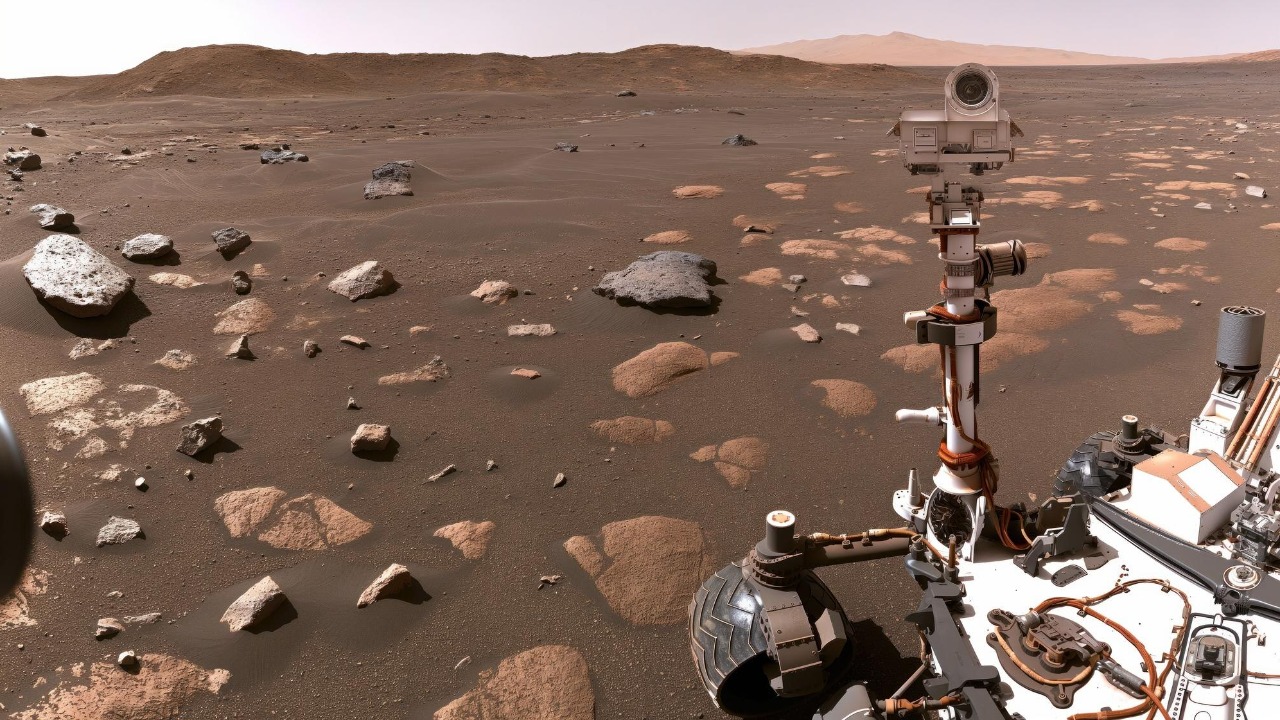

Launched on July 7, 2003, NASA’s Opportunity rover embarked on a journey that would redefine our knowledge of Mars. It landed on the Martian surface on January 25, 2004, in a region known as Meridiani Planum. This meticulously chosen landing site was selected due to its unique geological features that hinted at the presence of water in the planet’s past. The mission was initially slated to last just 90 Martian days (sols), yet Opportunity defied expectations, exploring the Martian terrain for nearly 15 years.
The primary objectives of Opportunity were ambitious and clear: to uncover signs of past water activity and to assess the planet’s potential to harbor life. By analyzing the surface composition and geological formations, the rover aimed to piece together Mars’ climatic history. Technological innovations were at the core of Opportunity’s extended mission. Its solar panels, designed to power the rover, and the advanced onboard system allowed it to communicate with Earth, even as it faced the harsh Martian environment.
Unveiling the Martian Surface: Opportunity’s Discoveries

One of Opportunity’s most significant discoveries was the identification of hematite spheres, affectionately dubbed “blueberries.” These small, spherical formations were found scattered across the Martian soil and were pivotal in suggesting the presence of water in Mars’ past. Hematite is a mineral that typically forms in water, thus providing direct evidence that liquid water once existed on the planet’s surface. This find was crucial in reshaping our understanding of Mars as a once potentially habitable environment.
Opportunity also uncovered sedimentary rock formations that further supported the theory of historical water activity. These formations indicated that the region had undergone processes typically associated with water, such as erosion and sediment deposition. Another key discovery was the identification of sulfate-rich soils. These soils are known to form in the presence of water, indicating that Mars had a wet environment long ago. These geological findings have had a lasting impact on planetary science, deepening our understanding of Mars’ complex history.
The Science of Water Detection on Mars
The detection of water on Mars was made possible through a combination of sophisticated tools and techniques. Opportunity was equipped with an array of scientific instruments, including spectrometers that analyzed the chemical composition of Martian rocks and soil. These instruments played a crucial role in identifying minerals that form in the presence of water, such as sulfates and clays.
Opportunity’s spectrometers were particularly instrumental in identifying chemical evidence of past water activity. By examining the spectra of light reflected from the Martian surface, scientists were able to detect minerals that form in watery environments. This process of data interpretation was complex and required careful analysis to confirm the presence of water on Mars. The rover’s findings have provided a wealth of information that continues to inform current and future Mars missions.
Implications of Water on Mars: Future Exploration and Research

The discovery of water on Mars has profound implications for the search for life beyond Earth. Water is a fundamental requirement for life as we know it, and its presence on Mars suggests that the planet may have once been capable of supporting life. This revelation has fueled renewed interest in the potential habitability of Mars and has become a key focus of ongoing research.
Opportunity’s findings have significantly influenced subsequent Mars missions. The data collected by the rover has helped shape the objectives of missions like the Mars Science Laboratory and the Perseverance rover, which continue to explore the Martian surface in search of signs of past life. Additionally, the technological advancements developed for Opportunity’s mission have paved the way for new innovations in space exploration, ensuring that future missions are even more capable of unlocking Mars’ secrets.
The Legacy of Opportunity: A Lasting Impact

Reflecting on Opportunity’s mission, it is clear that its achievements were nothing short of extraordinary. The rover’s resilience in overcoming technical challenges, such as dust storms and mechanical failures, speaks to the robustness of its design. Despite these challenges, Opportunity continued to make groundbreaking discoveries until its final communication with Earth in 2018.
Opportunity’s contributions to planetary science are immeasurable. The rover’s discoveries have provided invaluable insights into Mars’ geological history and have expanded our understanding of the planet’s potential to support life. By uncovering evidence of water, Opportunity has opened new avenues for exploration and research, inspiring future generations of scientists and space enthusiasts. Its mission is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
For more in-depth information on Opportunity’s discoveries and their implications, consider exploring additional resources such as scientific articles and news updates on Mars exploration. Opportunity’s legacy will undoubtedly continue to inspire and guide future missions to the Red Planet, as we strive to uncover the mysteries of our neighboring world.