The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved lab-grown meat, heralding a new chapter in food production. This landmark decision could transform agriculture by offering a more sustainable and ethical way to consume meat. As the world faces growing environmental and ethical challenges, lab-grown meat presents a promising alternative.
The Science Behind Lab-Grown Meat
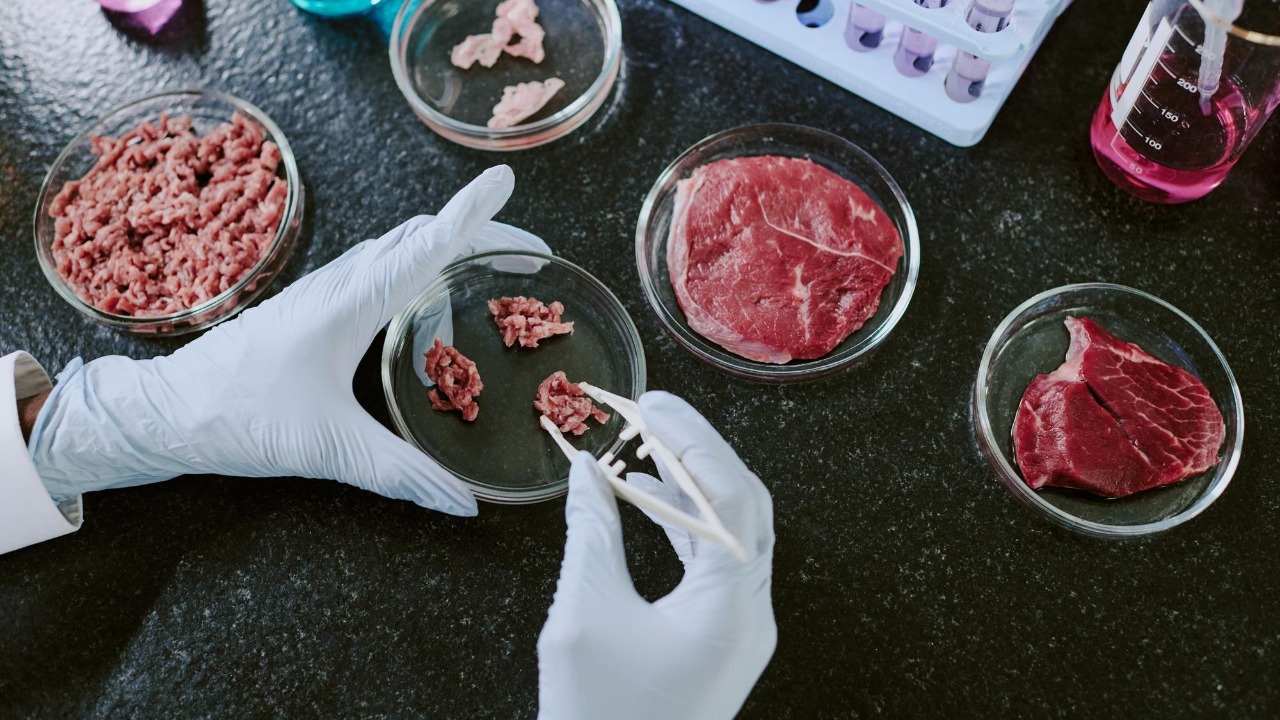
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cell-based meat, is produced through cellular agriculture. This cutting-edge process involves cultivating animal cells in controlled environments known as bioreactors. The journey begins with the extraction of a small sample of animal cells, which are then placed in a nutrient-rich culture medium that mimics the natural conditions found in an animal’s body. Over time, these cells multiply and differentiate, gradually forming muscle tissue that is virtually indistinguishable from conventional meat.
Technological advancements have played a crucial role in the development of lab-grown meat. Innovations such as improved bioreactor designs, optimized cell culture media, and advanced tissue engineering techniques have significantly accelerated production processes. These breakthroughs not only enhance the scalability of lab-grown meat but also ensure its safety and nutritional equivalence. Studies have shown that lab-grown meat can match the protein content and essential nutrients found in traditional meat, offering a viable alternative without compromising on nutrition.
Regulatory Landscape and FDA Approval

The approval of lab-grown meat by the FDA marks a significant milestone in the regulatory journey. The collaborative efforts between the FDA and USDA have been instrumental in establishing a robust framework for overseeing cell-based meat products. Both agencies have worked together to develop guidelines and standards that ensure the safety and quality of these innovative food products.
The approval process for lab-grown meat involves several rigorous steps. Companies must demonstrate the safety and nutritional equivalence of their products through comprehensive testing and data analysis. They must also adhere to stringent manufacturing practices to ensure consistency and quality. This regulatory approval sets a precedent for other countries, potentially inspiring them to develop their own frameworks for lab-grown meat, thereby influencing global markets and the future of food production.
Environmental and Ethical Implications
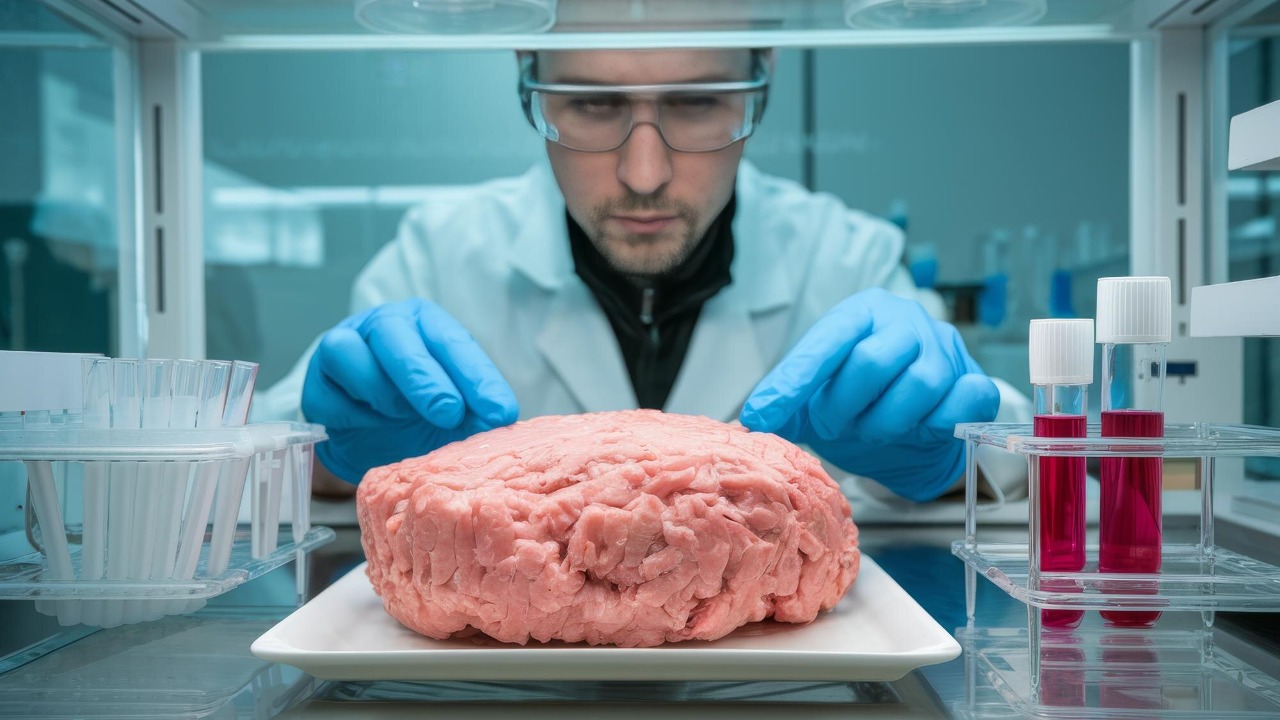

Lab-grown meat offers significant environmental benefits compared to traditional meat production. By reducing the reliance on livestock farming, cultured meat has the potential to significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption. According to some estimates, lab-grown meat could reduce emissions by up to 96% and land use by 99%. These reductions are crucial in the fight against climate change and could contribute to a more sustainable future.
From an ethical standpoint, lab-grown meat presents an opportunity to improve animal welfare. By eliminating the need for animal slaughter, it addresses concerns related to factory farming and the ethical treatment of animals. However, public perception and acceptance remain challenges. Consumer attitudes towards lab-grown meat vary, with some embracing it as a sustainable alternative and others expressing skepticism. Overcoming these hurdles will require transparent communication and education about the benefits and safety of cultured meat.
Economic and Market Potential

The economic potential of lab-grown meat is attracting significant attention from investors and major food corporations. Recent years have seen a surge in investments in lab-grown meat companies, with industry giants recognizing the transformative potential of this technology. Companies like Memphis Meats and Mosa Meat have secured substantial funding to scale their operations and bring lab-grown meat to market.
Market readiness and scalability remain key challenges for the lab-grown meat industry. While pilot products have made their way into select markets, scaling production to meet global demand requires further advancements in technology and infrastructure. Additionally, pricing and accessibility are crucial factors in determining the widespread adoption of lab-grown meat. As production processes become more efficient, the cost of cultured meat is expected to decrease, making it more accessible to diverse consumer groups and potentially achieving price parity with traditional meat.
Future Outlook and Innovations
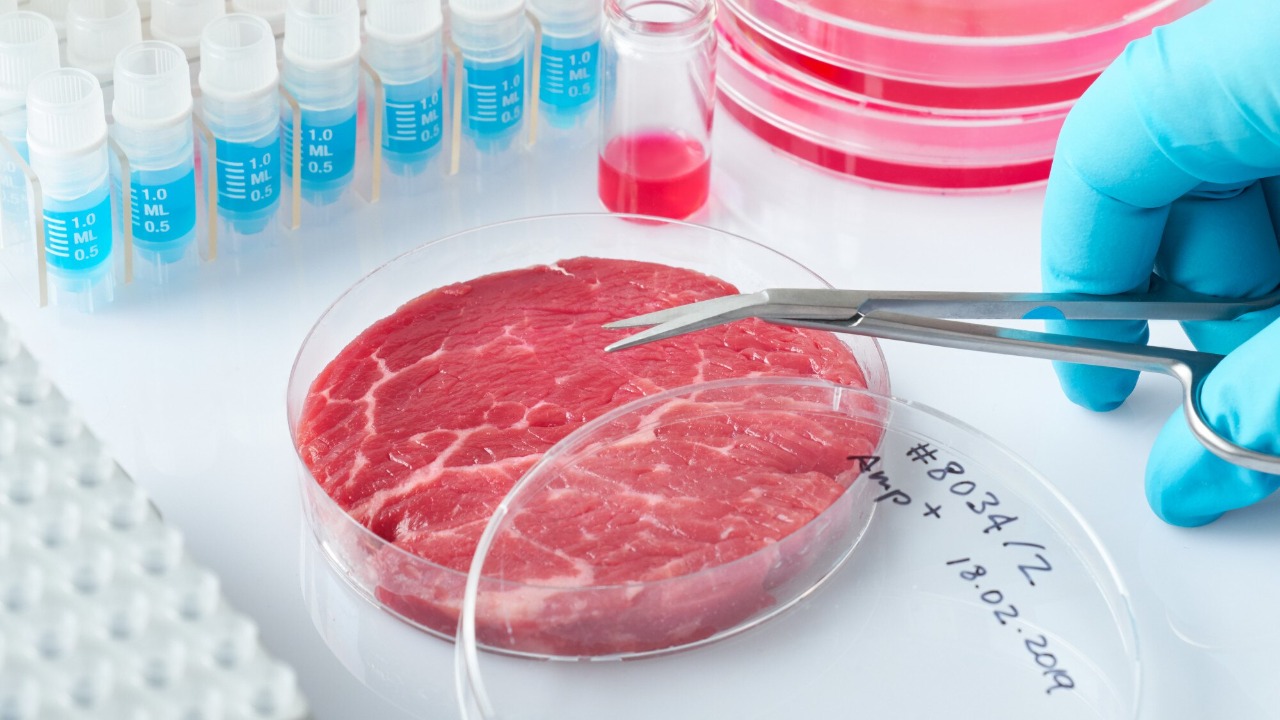
The future of lab-grown meat is rife with possibilities. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on creating new types of meat and improving production techniques. Innovations are not limited to traditional meat products; lab-grown seafood, such as lab-grown salmon, is also being explored, offering a sustainable alternative to overfishing and environmental degradation.
Integration with traditional agriculture presents an opportunity for synergy. Lab-grown meat can complement conventional farming practices, allowing farmers to diversify their products and adapt to changing consumer preferences. This integration could lead to a more resilient and sustainable food system that balances innovation with tradition.
The potential global impact of lab-grown meat extends beyond environmental and ethical considerations. By enhancing food security and sustainability, it has the potential to address pressing challenges such as population growth and resource scarcity. As research and development continue to advance, the vision of a future where lab-grown meat is an integral part of our diets becomes increasingly tangible. For a deeper dive into the role of regulators in this evolving landscape, you can explore insights in this journal article.