In October 2017, a mysterious object named ‘Oumuamua was discovered passing through our solar system, marking the first known interstellar visitor. The prospect of reaching such an object has captivated scientists and sparked discussions on the feasibility of an interstellar mission. Humanity’s initial attempts to engage with this cosmic traveler highlight both the challenges and the technological advancements required for such an endeavor.
The Discovery of ‘Oumuamua
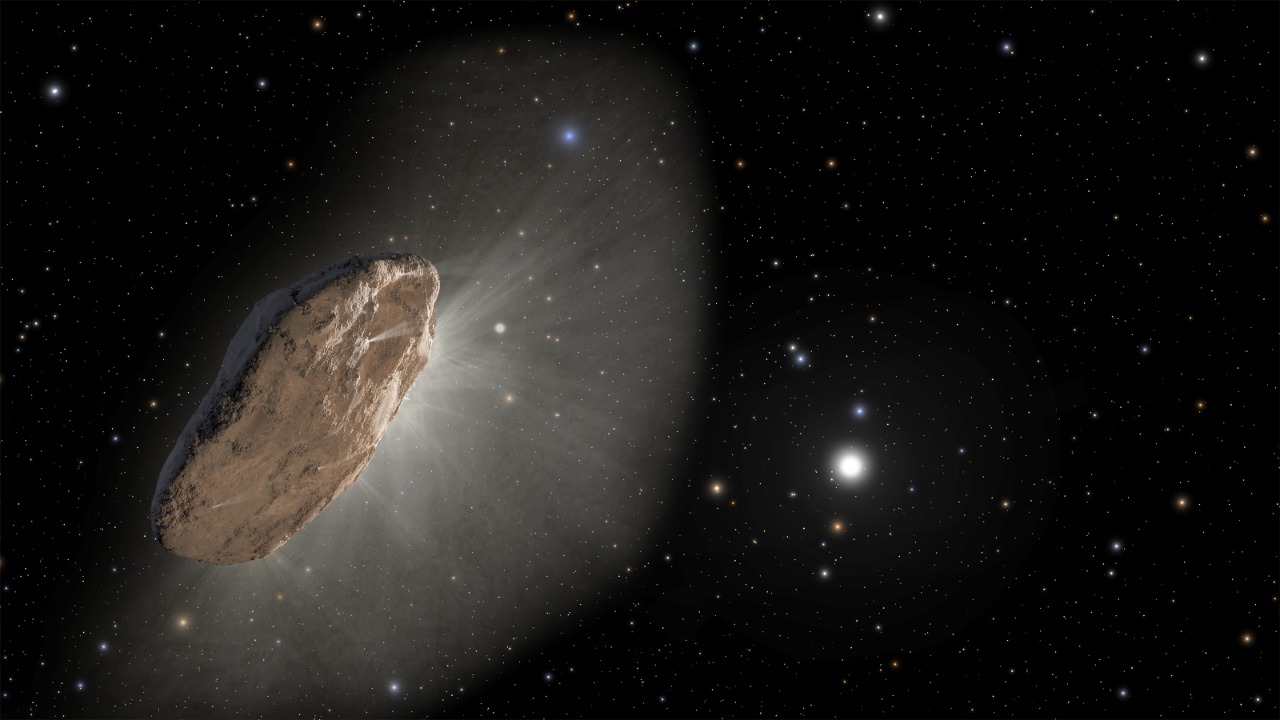

In the world of astronomy, the discovery of ‘Oumuamua by the Pan-STARRS telescope was groundbreaking. Located in Hawaii, the telescope detected the object as it zipped through our solar system at an unprecedented speed. Initial observations revealed an object with an unusual, elongated shape, unlike any comet or asteroid seen before. Its trajectory suggested it came from outside our solar system, making it the first known interstellar object to grace our cosmic neighborhood.
‘Oumuamua’s characteristics have been a source of fascination and controversy. Its speed, estimated to be around 315,000 km/h (196,000 mph), and hyperbolic trajectory indicated it wasn’t bound by the Sun’s gravity, confirming its interstellar origin. The object’s elongated, cigar-like shape and rapid tumbling motion added to its mystery, with scientists speculating about its composition and origin. Was it a fragment of a larger body, or something entirely different like a solar sail?
The scientific community has been abuzz with theories about ‘Oumuamua’s origins. Some suggest it could be a remnant of a planetesimal, the building blocks of planets, from another star system. Others propose more exotic origins, such as an artificial object sent by an extraterrestrial civilization. Despite the various hypotheses, what remains clear is that ‘Oumuamua has opened a new chapter in our understanding of the cosmos.
Technological Challenges and Innovations

Reaching an object like ‘Oumuamua presents significant technological challenges. The main hurdle is its immense speed and the vast distance it covers. Current space travel technologies, such as chemical rockets, are inadequate for catching up with such fast-moving targets. To overcome this, scientists are exploring innovative propulsion methods that could potentially enable us to reach future interstellar visitors.
Among the proposed methods, solar sails and nuclear propulsion stand out. Solar sails use the pressure of sunlight for propulsion, a concept that offers continuous acceleration without the need for fuel. This technology is being tested by missions like NASA’s NEA Scout. Meanwhile, nuclear propulsion, which utilizes nuclear reactions to generate thrust, promises a more powerful alternative capable of reaching higher speeds.
However, both methods face significant engineering and safety challenges before they can be realized.
Advancements in imaging technology are also pivotal in the pursuit of interstellar exploration. The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, with its cutting-edge camera, is set to revolutionize our ability to detect and track fast-moving objects like ‘Oumuamua. Its wide-field survey capabilities will enhance our chances of spotting interstellar visitors earlier, providing more time to plan and execute missions.
Proposed Missions and Theoretical Concepts
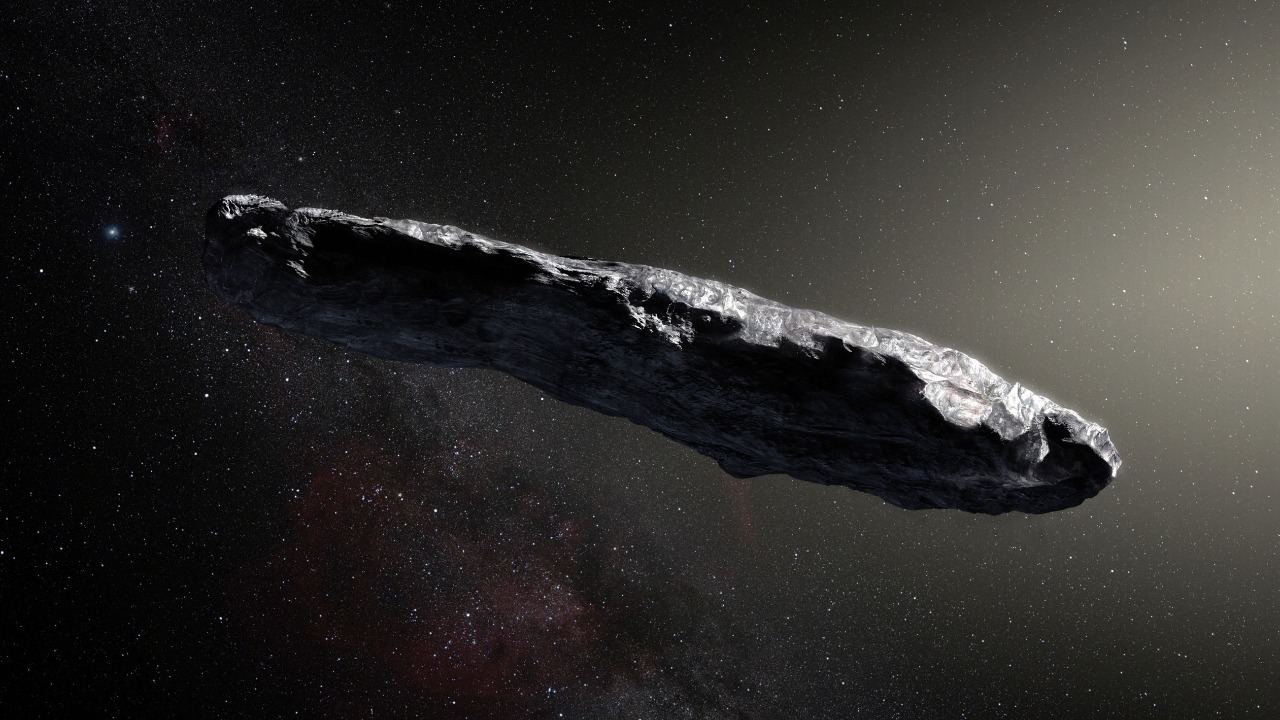

The fascination with ‘Oumuamua has spurred the development of several mission concepts aimed at reaching interstellar visitors. One prominent initiative is the Breakthrough Starshot project, which envisions sending small, light-propelled spacecraft to nearby star systems. While primarily focused on stars like Alpha Centauri, the technology developed could potentially be adapted for missions to interstellar objects passing through our solar system.
Other theoretical proposals include deploying fast-response missions equipped with high-velocity propulsion systems to intercept objects upon detection. These concepts, while promising, face significant logistical and financial challenges. The cost of developing and launching such missions is immense, requiring substantial investment and international collaboration.
Despite these challenges, the potential scientific rewards are immense. Successfully intercepting an interstellar visitor could provide unprecedented insights into the building blocks of other star systems. Analyzing the composition and structure of such objects might reveal new information about the processes that govern planet formation and the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
International Collaboration and Policy Considerations

Embarking on a mission to an interstellar object requires global cooperation. The financial and logistical demands are too great for any single nation to bear. International partnerships, similar to those seen in the International Space Station, would be essential to pool resources and expertise. Collaborative efforts could also streamline the development of new technologies necessary for interstellar exploration.
Moreover, the pursuit of interstellar missions raises important policy considerations. International space policies would need to address the legal implications of reaching and studying objects from beyond our solar system. These include questions of ownership, scientific sharing, and the ethical responsibilities of interacting with potential extraterrestrial materials.
Private space companies could play a crucial role in advancing these efforts. Their involvement in developing innovative technologies and reducing launch costs could accelerate the timeline for interstellar missions. Partnerships between governmental space agencies and private enterprises could pave the way for a new era of exploration, expanding humanity’s reach beyond our solar system.
The Future of Interstellar Exploration
The pursuit of interstellar visitors like ‘Oumuamua has the potential to redefine our understanding of the universe. By studying these objects, we could unlock secrets about the formation of solar systems and the distribution of organic materials across the cosmos. The implications extend beyond science, potentially impacting our search for life and our understanding of our place in the universe.
Discovering evidence of life or other civilizations through interstellar exploration could have profound implications for humanity. It would challenge our perceptions of life’s uniqueness and inspire new questions about the nature of intelligence and communication across vast distances. The technological advancements required for such missions could also drive innovation in other fields, from materials science to artificial intelligence.
As we look to the future, the pursuit of interstellar exploration represents one of humanity’s most ambitious endeavors. It challenges us to push the boundaries of what is possible and to collaborate on a global scale. The journey to reach and study interstellar visitors is not just about exploring distant objects; it’s about expanding the horizons of human knowledge and imagination.