Properly destroying old data drives is crucial to protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. Various methods for securely disposing of data drives ensure that personal or business data remains confidential, safeguarding against potential breaches and identity theft.
Understanding the Importance of Data Destruction
The risks associated with data breaches and identity theft from discarded drives are significant. When data drives are improperly disposed of, the information they contain can be accessed by unauthorized individuals, leading to potential financial loss and privacy violations. It’s essential to understand that simply deleting files or formatting a drive doesn’t permanently erase data. Sensitive information can still be recovered using specialized software, making it imperative to employ more secure destruction methods.
Legal and compliance requirements further underscore the need for proper data destruction. Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate the secure disposal of data to protect consumer information. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines and legal action. Additionally, improper disposal of data drives can have detrimental environmental impacts. E-waste contains hazardous materials that can contaminate soil and water, contributing to pollution and harm to wildlife.
Physical Destruction Methods
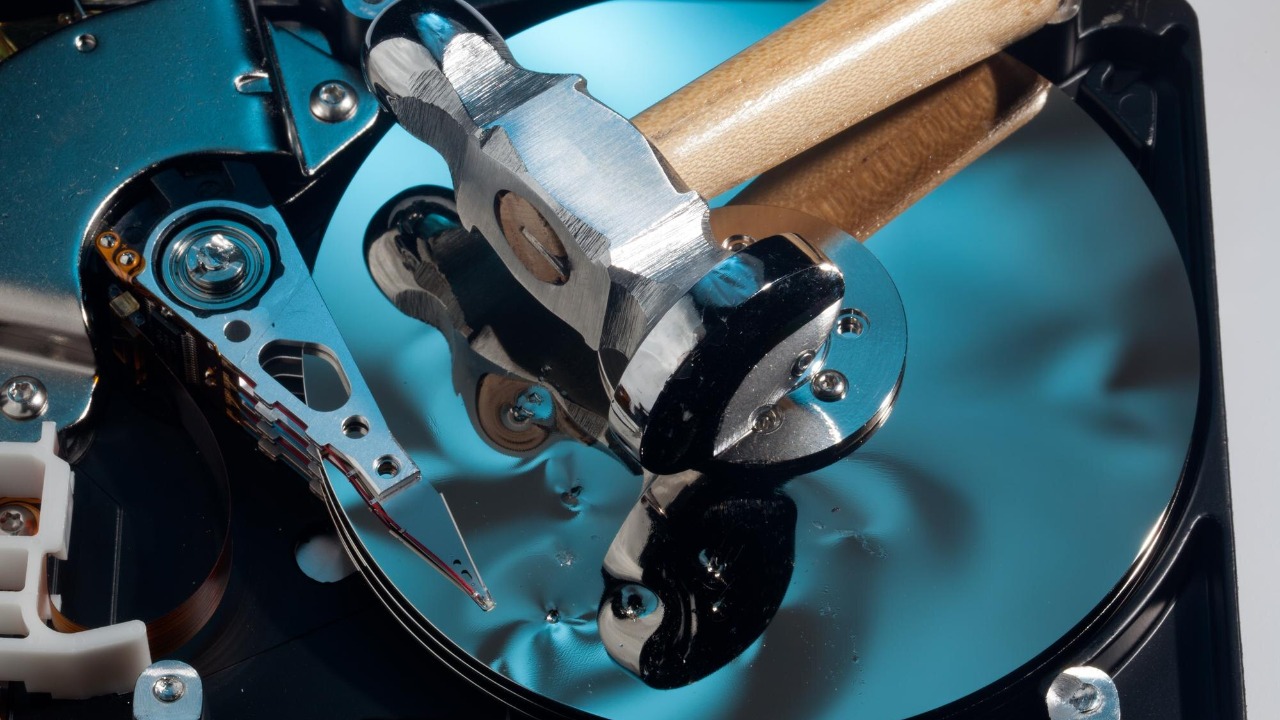
One of the most straightforward methods for destroying data drives is physical destruction. Using a hammer or drill to manually destroy a drive can be effective for personal use. By damaging the platters within a hard drive, you make data recovery extremely difficult, if not impossible. However, this method can be labor-intensive and may not be suitable for large quantities of drives.
For industrial-level destruction, employing a hard drive shredder is a more efficient option. These machines are designed to break down drives into small, unrecoverable pieces, ensuring comprehensive data destruction. Professional destruction services offer another viable option, particularly for businesses with large volumes of drives to dispose of. These services provide certification of destruction, which can be crucial for compliance with data protection regulations.
Software-Based Data Wiping

Software-based data wiping is a non-destructive method that involves overwriting data on a drive to prevent recovery. Data wiping software is available in various forms, ranging from free tools to comprehensive, paid solutions. These programs use algorithms to overwrite existing data multiple times, effectively erasing it.
Using data erasure programs is relatively straightforward. Typically, you would download and install the software, select the drive to be wiped, and choose the desired level of wiping security. It’s important to follow the software’s instructions carefully to ensure complete data erasure. When comparing free and paid options, consider factors such as ease of use, customer support, and the level of data security provided.
Degaussing: A Magnetic Approach

Degaussing is a data destruction method that uses a powerful magnetic field to erase data from magnetic storage devices. This process disrupts the magnetic domains on the drive, rendering the data unreadable. Degaussing is highly effective for hard drives and other magnetic media, but it renders the drive unusable afterward.
Despite its effectiveness, degaussing has certain drawbacks. It requires specialized equipment and may not be practical for home users. Additionally, degaussing doesn’t work on SSDs or flash drives, as these devices store data differently. However, in situations where rapid, secure disposal of large volumes of magnetic media is needed, degaussing can be an ideal solution.
Special Considerations for SSDs and Flash Drives

Traditional destruction methods often fall short when it comes to SSDs and flash drives. Unlike hard drives, SSDs store data in cells that can be more challenging to overwrite or physically destroy. As a result, securely erasing data from SSDs requires different techniques.
Best practices for erasing data from SSDs and flash drives include using specialized software designed for these types of drives. These tools implement secure erase commands that target the specific architecture of SSDs, ensuring data is irretrievable. It’s crucial to stay informed about the latest tools and techniques tailored for non-mechanical drives to maintain data security.
Ensuring Complete Data Security

Verifying data destruction is a critical step in ensuring complete security. Using data recovery tools, you can confirm that data has been effectively erased. If any data remains accessible, additional steps may be necessary to secure the drive.
Documenting the destruction process is essential for compliance and peace of mind. Maintaining records of how and when data was destroyed can protect against potential legal issues and provide evidence of compliance with data protection regulations. Establishing a data destruction policy can help ensure ongoing security needs are met, outlining procedures for the secure disposal of data drives as part of a broader data management strategy.