Despite the tense clashes between NASA and SpaceX’s Elon Musk, two NASA science missions were successfully launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on March 10, 2025. This event underscores the interdependence between the two entities, even as they maintain fundamentally different approaches to rocket development and operations. The question arises: why is NASA paying more for launches when reusable rockets, like those from SpaceX, are now a reality?
Design and Development Approaches

SpaceX, under the influence of Elon Musk, has adopted a strategy of rapid iteration and testing. This approach often results in frequent explosions during the development phase, which are considered part of the normal process according to The Verge. This innovative but risky prototyping starkly contrasts with NASA’s approach.
NASA, on the other hand, focuses on traditional, highly verified designs for its rockets. The agency prioritizes safety over speed in development, adhering to a more bureaucratic oversight process. This difference in approach is one of the key factors that distinguish SpaceX and NASA rockets.
Elon Musk’s philosophy of ‘fail fast, fail often’ is deeply ingrained in SpaceX’s culture. The company’s willingness to take calculated risks and learn from failures has led to breakthroughs that were previously thought impossible. This approach has allowed SpaceX to iterate quickly and bring new technologies to market faster than traditional aerospace companies. However, it also means that SpaceX’s development process can appear chaotic and unpredictable, especially when compared to NASA’s more conservative approach.
NASA’s development approach, while slower and more methodical, has a proven track record of success. The agency’s meticulous design and testing processes have resulted in some of the most reliable and successful spacecraft in history. However, this approach also tends to be more expensive and time-consuming, which can be a disadvantage in a rapidly evolving industry like space exploration. The contrast between these two approaches is a key factor in the ongoing debate about the future direction of space exploration.
Reusability Innovations
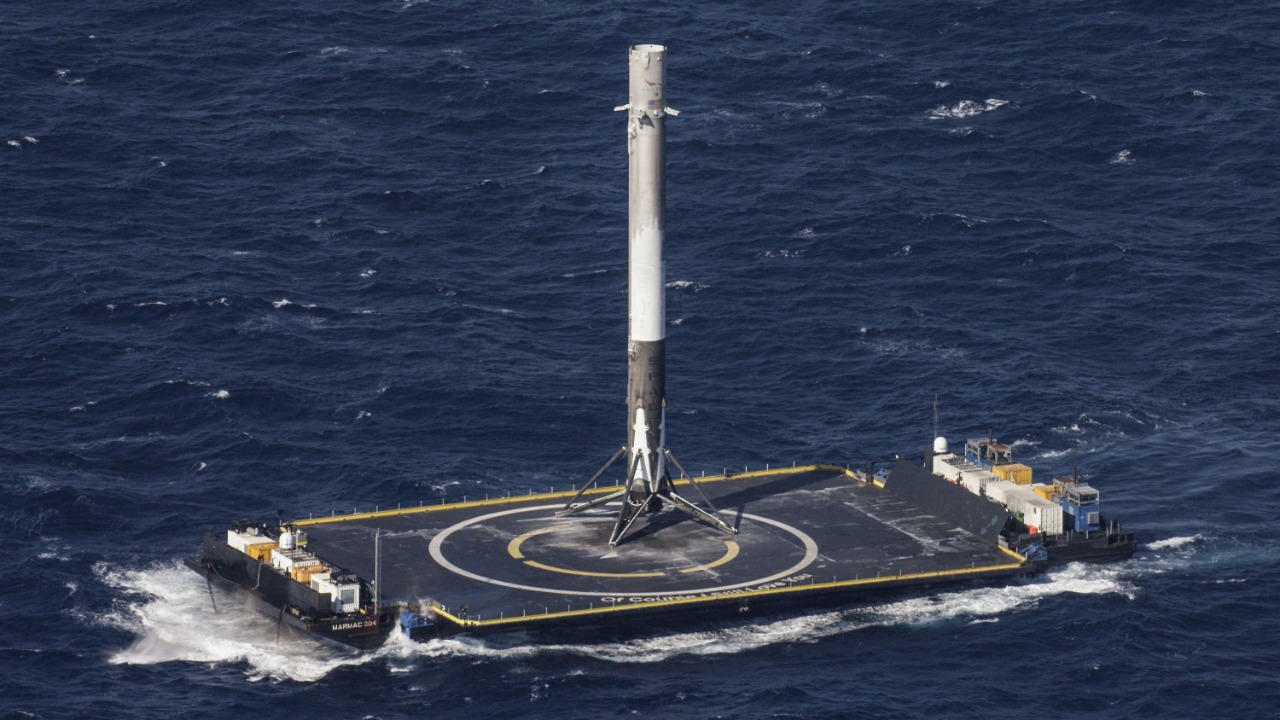

SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket is designed with reusability in mind. This feature allows for multiple launches from the same booster, reducing costs over time as reported by Ars Technica. This innovation is a significant departure from traditional rocket designs.
Conversely, NASA’s rockets, such as those in the Space Launch System (SLS) program, remain largely expendable. Each mission requires a new build, which contributes to the higher costs. Despite the advent of reusable rockets, NASA’s launch expenses have not immediately decreased due to existing contract structures.
SpaceX’s focus on reusability is not just about reducing costs. It’s also about increasing the frequency of launches. By reusing rockets, SpaceX can launch more frequently, which allows it to gather more data and iterate on its designs more quickly. This approach has allowed SpaceX to make rapid advancements in rocket technology and has the potential to revolutionize the space industry.
On the other hand, NASA’s approach to rocket design has traditionally focused on reliability and safety, rather than reusability. This approach has resulted in some of the most successful and reliable rockets in history, but it also means that NASA’s rockets are typically more expensive to build and launch. However, NASA is not completely opposed to the idea of reusability. The agency has been exploring various concepts for reusable spacecraft, and it’s possible that we could see more reusable NASA rockets in the future.
Cost and Economic Models

Even with the advent of reusable rockets from SpaceX, NASA continues to pay more for launches according to Ars Technica. SpaceX’s commercial model allows for lower per-launch costs through reusability and high launch cadence, offering significant potential savings.
However, NASA’s government-funded approach involves fixed-price contracts that do not fully leverage SpaceX’s efficiencies yet. This economic model is a significant factor in the cost disparity between SpaceX and NASA launches.
SpaceX’s economic model is based on the idea of economies of scale. By launching more frequently and reusing rockets, SpaceX is able to spread its fixed costs over a larger number of launches, which reduces the cost per launch. This model has allowed SpaceX to offer launch services at prices that are significantly lower than those of traditional aerospace companies.
NASA’s economic model, on the other hand, is based on the idea of cost-plus contracting. This model allows NASA to cover its costs and ensure a reasonable profit, but it also tends to result in higher prices. However, NASA’s model also provides a higher level of certainty and stability, which can be a significant advantage in a high-risk industry like space exploration. The contrast between these two economic models is a key factor in the ongoing debate about the future direction of space exploration.
Reliability and Testing Regimes
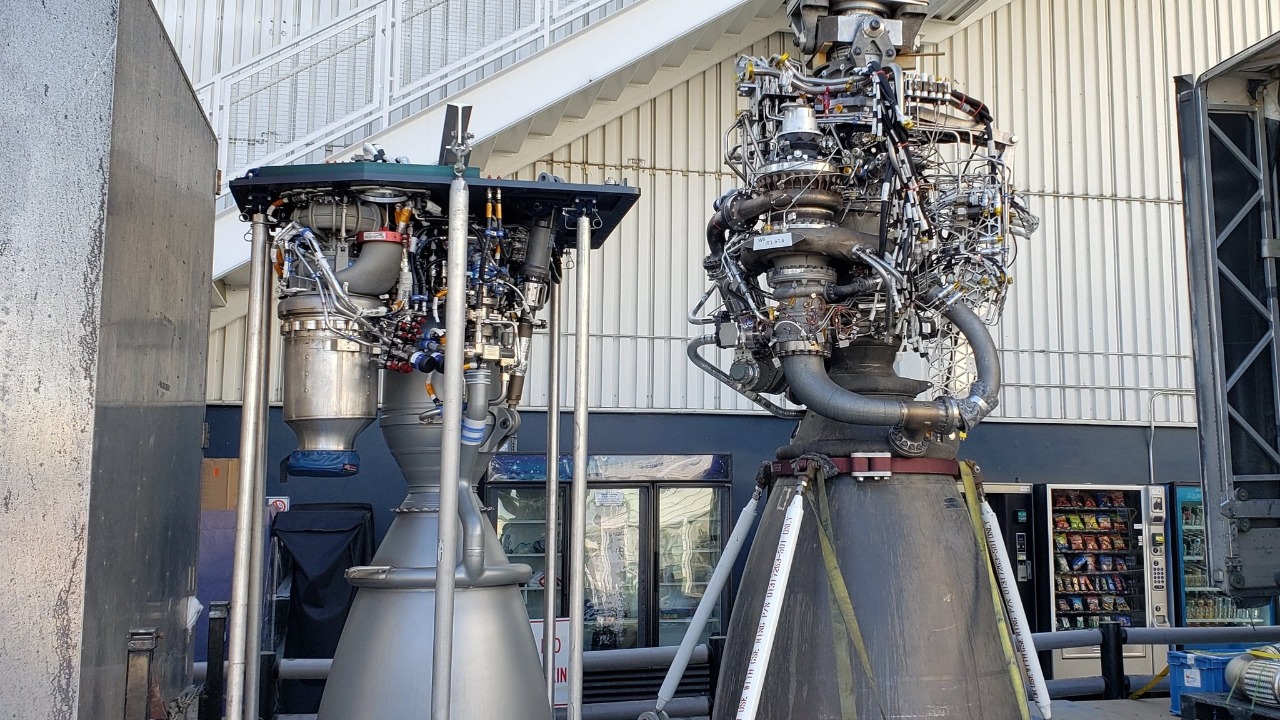
SpaceX’s approach to rocket development involves frequent testing, which often results in explosions. As of May 31, 2025, these explosions are viewed as a normal part of the iterative development process according to The Verge.
In contrast, NASA enforces stringent pre-launch verifications, resulting in fewer but more predictable failures. This conservative approach affects mission timelines and public perception, further distinguishing the two entities’ operational strategies.
SpaceX’s testing regime is characterized by its high frequency and high risk. The company’s philosophy of ‘fail fast, fail often’ means that it’s willing to take risks and learn from failures. This approach has allowed SpaceX to make rapid advancements in rocket technology, but it also means that the company’s testing process can be unpredictable and fraught with failures.
NASA’s testing regime, on the other hand, is characterized by its meticulousness and conservatism. The agency’s focus on safety and reliability means that it takes a more cautious approach to testing, which results in fewer failures but also longer development times. This approach has resulted in some of the most reliable and successful spacecraft in history, but it also means that NASA’s testing process can be slow and expensive.
Collaborative Mission Examples
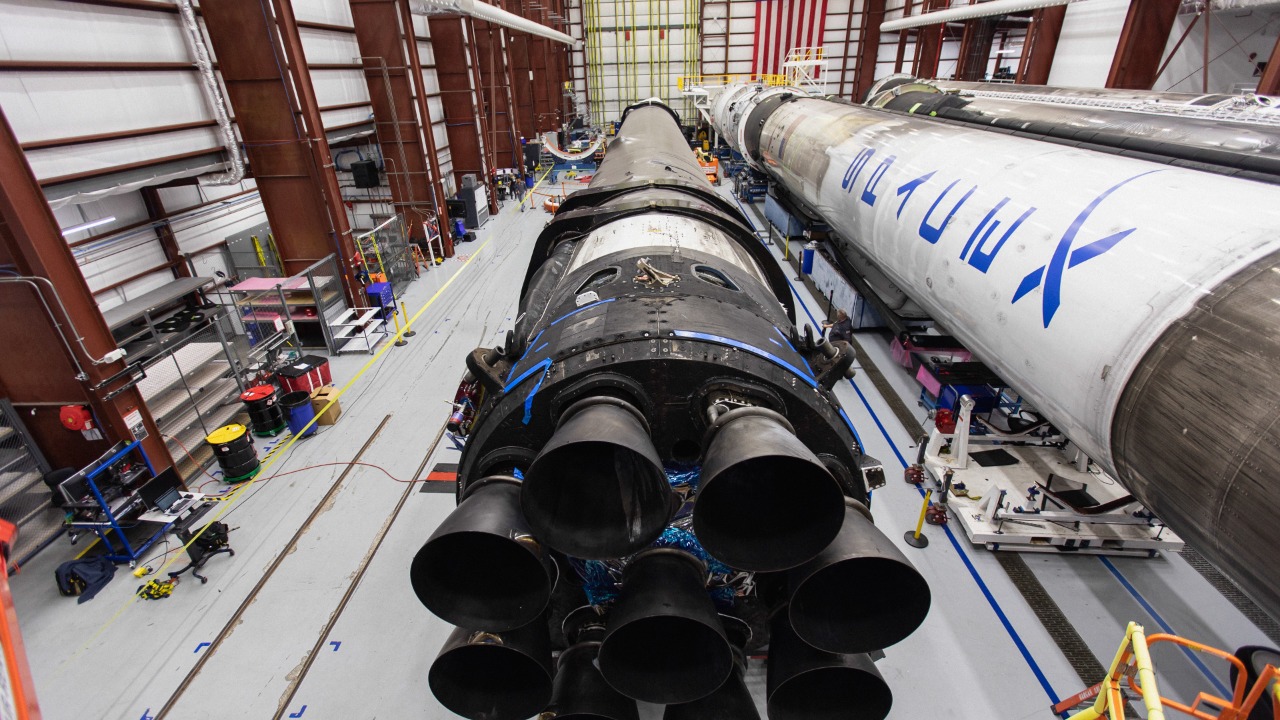

Despite their differences, SpaceX and NASA have successfully collaborated on several missions. For instance, on March 10, 2025, SpaceX launched NASA’s SPHEREx and PUNCH spacecraft on a Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg as reported by Spaceflight Now.
These missions, launched amid tense clashes between NASA and Musk, demonstrate the interdependence between the two entities according to Phys.org. SPHEREx, a mission to survey the sky in infrared, and PUNCH, a heliophysics probe, are just two examples of this ongoing collaboration.
Another example of successful collaboration between SpaceX and NASA is the Crew Dragon missions. These missions, which began in 2020, have allowed NASA to send astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) from American soil for the first time since the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011. The Crew Dragon missions have been a major success for both SpaceX and NASA, and they have demonstrated the potential benefits of public-private partnerships in space exploration.
Despite the differences in their approaches, SpaceX and NASA have found ways to work together effectively. Their collaborations have resulted in some of the most significant advancements in space exploration in recent years, and they have demonstrated the potential benefits of combining the strengths of public and private entities. However, these collaborations have also highlighted the challenges and tensions that can arise when two organizations with different cultures and philosophies work together.
Interagency Reliance and Dependencies
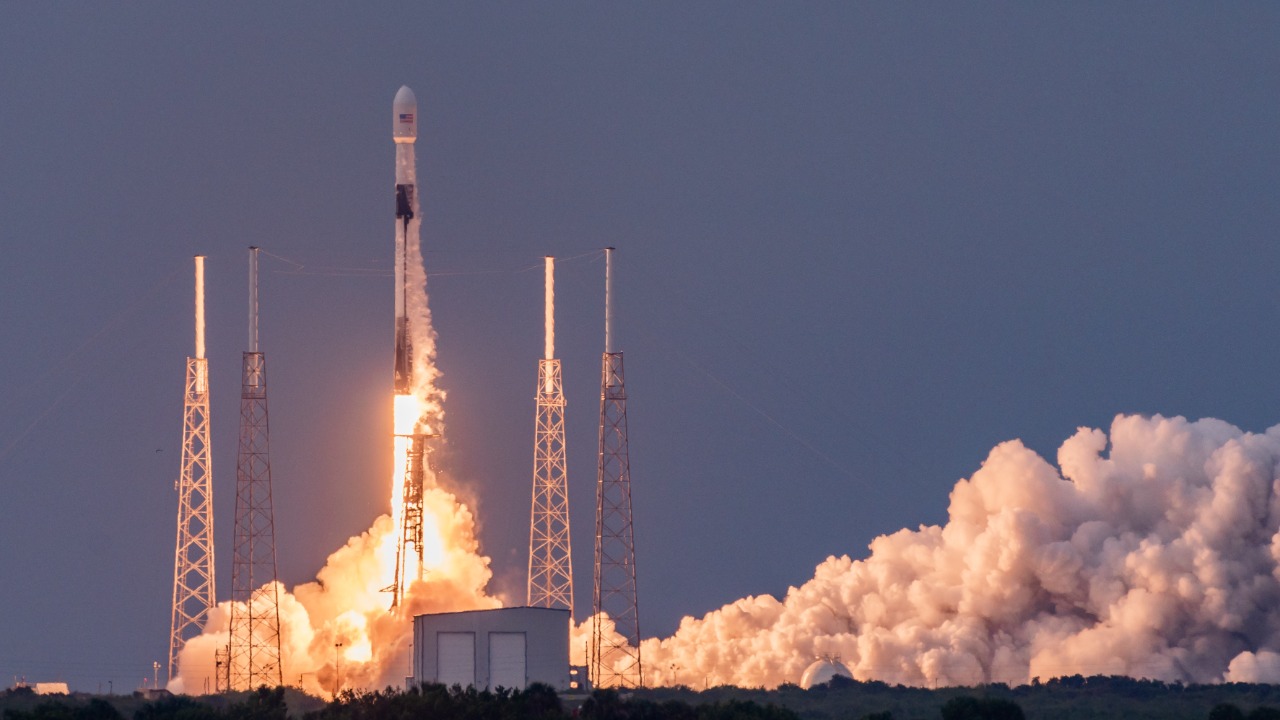

As of June 5, 2025, both NASA and the Defense Department rely heavily on SpaceX for critical launches and technology according to The New York Times. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 serves as a workhorse for NASA’s science missions, despite the philosophical differences between the two entities.
The Defense Department’s dependence on SpaceX extends to national security payloads, further amplifying NASA’s reliance on the private company. This interagency reliance underscores the integral role SpaceX plays in the U.S. space program.
SpaceX’s role in the U.S. space program extends beyond NASA. The company also provides launch services for a variety of other government agencies, including the Department of Defense, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). These agencies rely on SpaceX for a variety of critical missions, from launching weather satellites to sending spy satellites into orbit.
While NASA and the Defense Department are the most visible government customers for SpaceX, they are not the only ones. A variety of other government agencies also rely on SpaceX for launch services, including the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). These agencies rely on SpaceX for a variety of critical missions, from launching weather satellites to sending spy satellites into orbit.
Tensions in Partnership Dynamics

Despite the successful collaborations, tensions have arisen between NASA and Musk. These clashes, noted on March 13, 2025, have added a layer of complexity to the partnership according to Phys.org.
Musk’s role in SpaceX influences NASA relations, including potential impacts from political figures like President Trump as reported by The New York Times. Despite these tensions, NASA continues to proceed with SpaceX launches for missions like SPHEREx and PUNCH, balancing the risks and benefits of this unique partnership.
One of the main sources of tension between NASA and SpaceX is their different approaches to risk. SpaceX’s philosophy of ‘fail fast, fail often’ is at odds with NASA’s more conservative approach, which prioritizes safety and reliability. These differences in approach have led to clashes and misunderstandings, but they have also resulted in a productive tension that has pushed both organizations to innovate and improve.
Another source of tension is the difference in their organizational cultures. SpaceX, as a private company, is able to move quickly and take risks, while NASA, as a government agency, is subject to a higher level of scrutiny and bureaucracy. These differences in culture have led to clashes and misunderstandings, but they have also resulted in a productive tension that has pushed both organizations to innovate and improve.