Researchers at Rice University have pioneered a groundbreaking nasal spray that uses lithium-loaded gold nanoparticles to deliver the drug directly to the brain, bypassing the kidneys and thus avoiding toxicity. This innovative approach, demonstrated in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, not only improved memory function but also holds promise for treating various neuropsychiatric conditions. The study, published in October 2025, aims to enhance lithium’s therapeutic potential while minimizing systemic side effects.
The Science Behind Lithium and Gold Nanoparticles
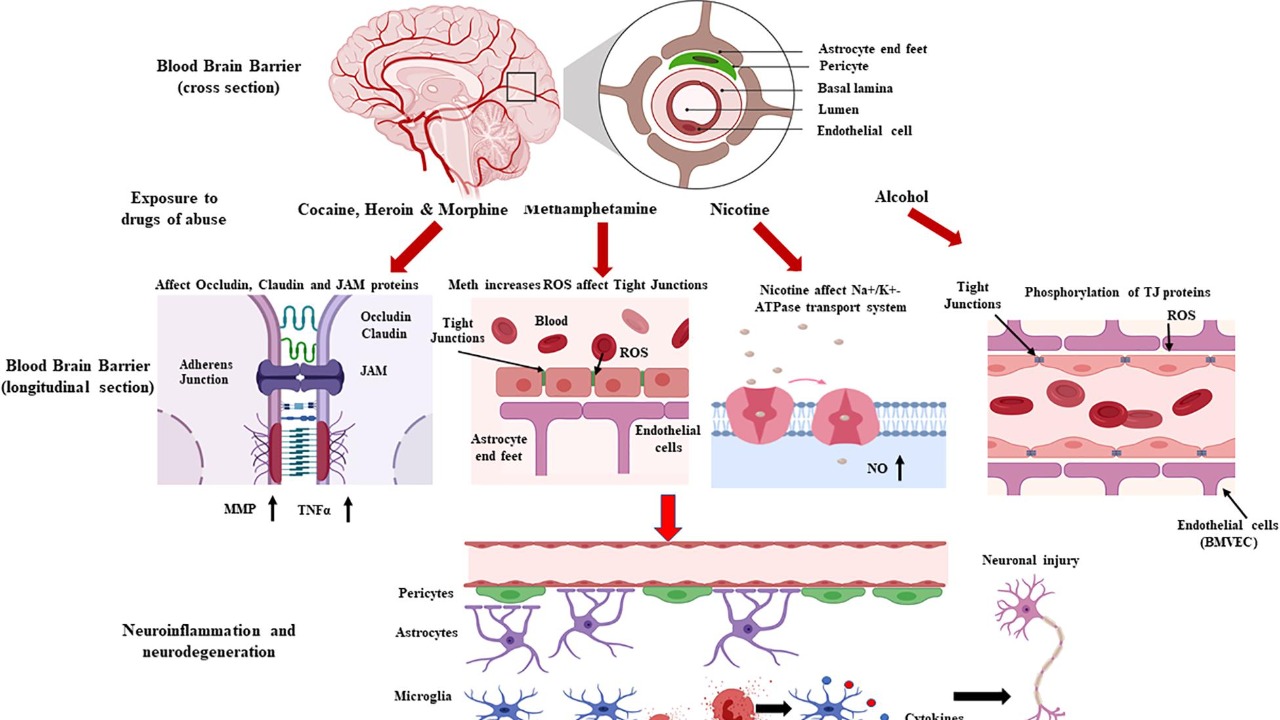
Traditional lithium therapy, commonly used for bipolar disorder and other neuropsychiatric diseases, often results in kidney damage due to the high systemic doses required. This new approach leverages gold nanoparticles as carriers, enabling targeted brain delivery via the nasal route. According to Psychiatric Times, these nanoparticles are designed to transport lithium directly to the brain, significantly reducing the risk of renal toxicity.
The design of these nanoparticles is crucial to their function. They are engineered to be small enough to pass through the blood-brain barrier after nasal administration. The lithium-loading mechanism ensures that the drug is delivered effectively to the brain without accumulating in peripheral organs. This innovative design was highlighted in a report by Interesting Engineering, which detailed how the nanoparticles achieve this targeted delivery.
Preclinical evidence from mouse studies further supports the safety of this method. As reported by Phys.org, even at doses equivalent to those used in humans, no renal toxicity was observed, marking a significant advancement in lithium therapy.
Delivery Mechanism and Brain Targeting
The administration of the nasal spray is straightforward, with nanoparticles traveling along the olfactory nerves directly to the brain. This method achieves higher lithium concentrations in neural tissue compared to traditional oral methods. A study covered by Study Finds confirmed that this route allows for more effective brain targeting, which is crucial for treating neuropsychiatric conditions.
Imaging and pharmacokinetic data from the Rice University study reveal that the brain uptake of lithium occurs rapidly, within hours of dosing, with minimal presence in the bloodstream. This rapid uptake is a significant advantage over oral or intravenous lithium, which often requires higher doses and can cause gastrointestinal side effects. The Interesting Engineering report emphasizes these benefits, noting the potential for reduced dosage needs.
By avoiding the gastrointestinal tract and systemic circulation, this nasal spray offers a more efficient and safer alternative to existing lithium therapies. This innovation could transform the treatment landscape for patients who are unable to tolerate traditional lithium formulations due to side effects.
Applications for Neuropsychiatric Diseases
The potential applications of this nasal spray extend beyond Alzheimer’s disease. In mouse models, repeated nasal dosing not only restored spatial memory but also reduced amyloid plaque formation, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s. This promising outcome was highlighted in a report by Study Finds, suggesting a new avenue for Alzheimer’s treatment.
Beyond Alzheimer’s, the implications for bipolar disorder and depression are significant. Lithium’s mood-stabilizing effects could be enhanced without the long-term risk of kidney damage, making it a more viable option for a broader range of patients. The Psychiatric Times article discusses these broader implications, noting the potential for improved patient outcomes.
Ongoing research is essential to validate these findings in human trials. The Rice University team plans to conduct clinical trials to confirm the efficacy and safety of this approach in humans, as reported by Phys.org. These trials will be crucial in determining the future of this promising treatment.
Safety Profile and Future Implications

The safety profile of this nasal spray is a key factor in its potential success. Toxicology findings from the study show no adverse effects on kidney function markers, such as creatinine levels, in treated mice over a 28-day period. This was reported by Interesting Engineering, underscoring the treatment’s safety.
Compared to existing lithium formulations, this approach could significantly expand patient eligibility by mitigating contraindications for those with renal issues. The Psychiatric Times article highlights how this could change the landscape of lithium therapy, offering new hope to patients previously unable to use lithium.
Looking ahead, the next steps include navigating FDA approval pathways and scaling up production for commercial use. The potential for this nasal spray to revolutionize treatment for neuropsychiatric diseases is immense, and its development will be closely watched by the medical community and patients alike. As noted by Phys.org, the scalability and regulatory approval will be critical in bringing this innovative treatment to market.