The recent incident involving Boeing’s space capsule being hit by a micro-meteor has raised concerns within the aerospace community. This event underscores the vulnerabilities that spacecraft face in the harsh environment of space, where even tiny particles can cause significant damage. Understanding the implications of such incidents is crucial for future space missions and the safety of astronauts.
The Incident: A Closer Look
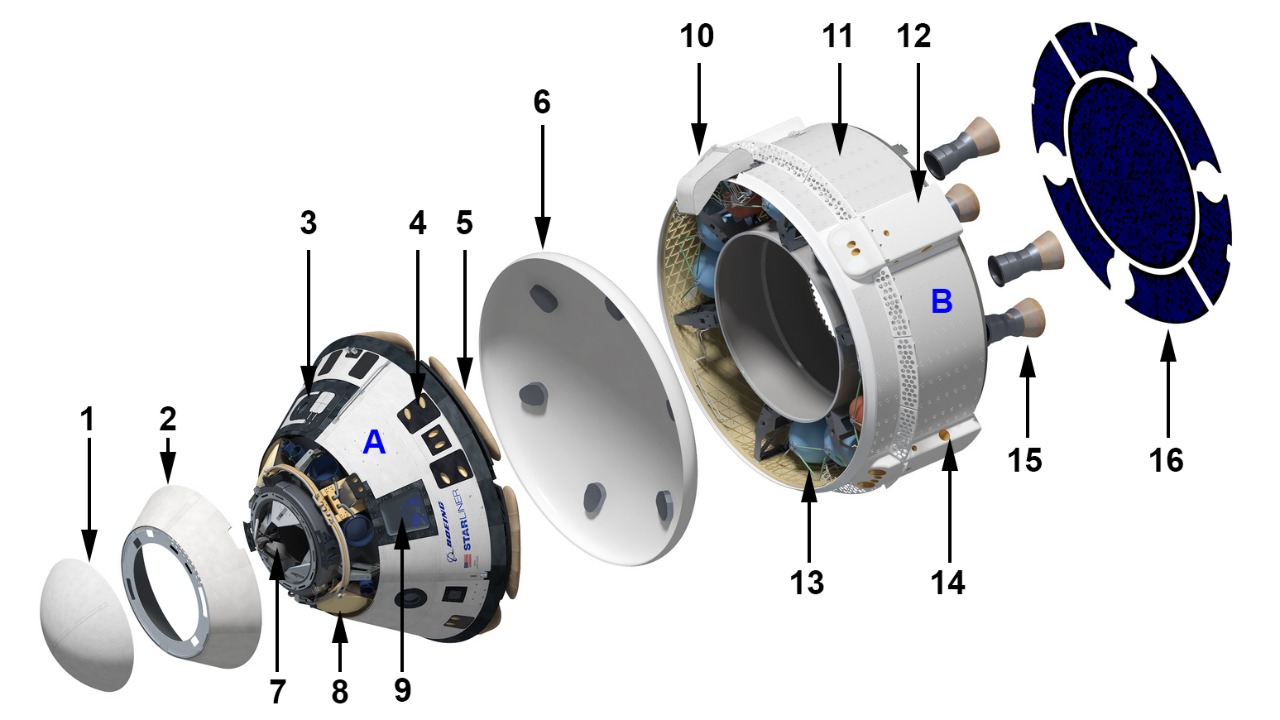
The impact event occurred when Boeing’s space capsule was on a routine mission, demonstrating just how unpredictable and hazardous the space environment can be. The incident took place at a time when the capsule was orbiting Earth at high speeds, a context in which even a small micro-meteor can penetrate the spacecraft’s exterior. Initial reports suggest the impact happened late at night, while the capsule was in a region known for a higher concentration of space debris.
Upon impact, there was immediate concern about the structural integrity of the capsule. Engineers feared that even minor breaches could lead to significant problems such as loss of pressure or damage to critical onboard systems. The initial response from Boeing and NASA was swift, involving the activation of emergency protocols designed to assess and mitigate the damage. Inspection procedures included remote diagnostics and, where possible, rerouting the capsule’s planned trajectory to minimize further risk.
Understanding Micro-Meteoroids and Space Debris

Micro-meteoroids are tiny particles, often no larger than a grain of sand, that travel through space at very high velocities. According to NASA’s research on micrometeoroids and orbital debris (MMOD), these particles are ubiquitous in space and pose a constant threat to spacecraft. Their prevalence makes them a significant concern for both current and future space missions.
Space debris, including man-made fragments from previous missions, adds to this threat. The risks posed by these particles are well-documented, with past incidents highlighting the potential for severe damage. For example, the Soyuz spacecraft has previously encountered similar challenges, underscoring the frequency and severity of micro-meteoroid impacts. These events illustrate the ongoing challenges faced by spacecraft operating in such a hostile environment.
Impact on Current and Future Space Missions
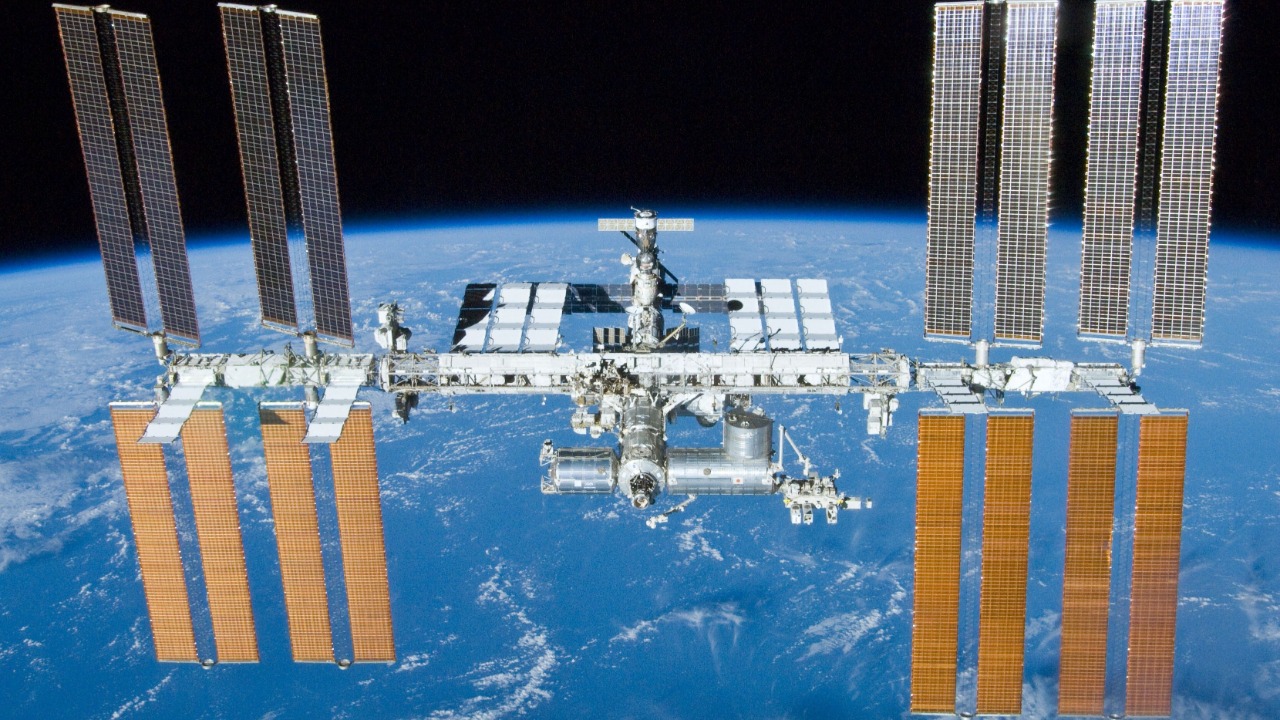
The Boeing capsule incident has immediate implications for current missions, particularly those involving the International Space Station (ISS). The safety and operational readiness of capsules tasked with ferrying astronauts to and from the ISS are paramount. Any compromise in the spacecraft’s integrity could have dire consequences for crew safety and mission success. As seen in past missions, such as the delay of Boeing’s Starliner program, these incidents can lead to significant operational disruptions.
Looking ahead, this event may influence future spacecraft design and the development of protective measures against micro-meteor impacts. Engineers are likely to explore advanced materials and innovative technologies aimed at enhancing the resilience of spacecraft. Moreover, collaborative efforts with NASA and other international agencies will be crucial in developing comprehensive strategies to mitigate these risks. Boeing’s challenges could also prompt a reevaluation of risk assessment protocols, potentially leading to delays in collaborative missions, as noted in the recent ISS mission adjustments.
Boeing’s Response and Mitigation Measures
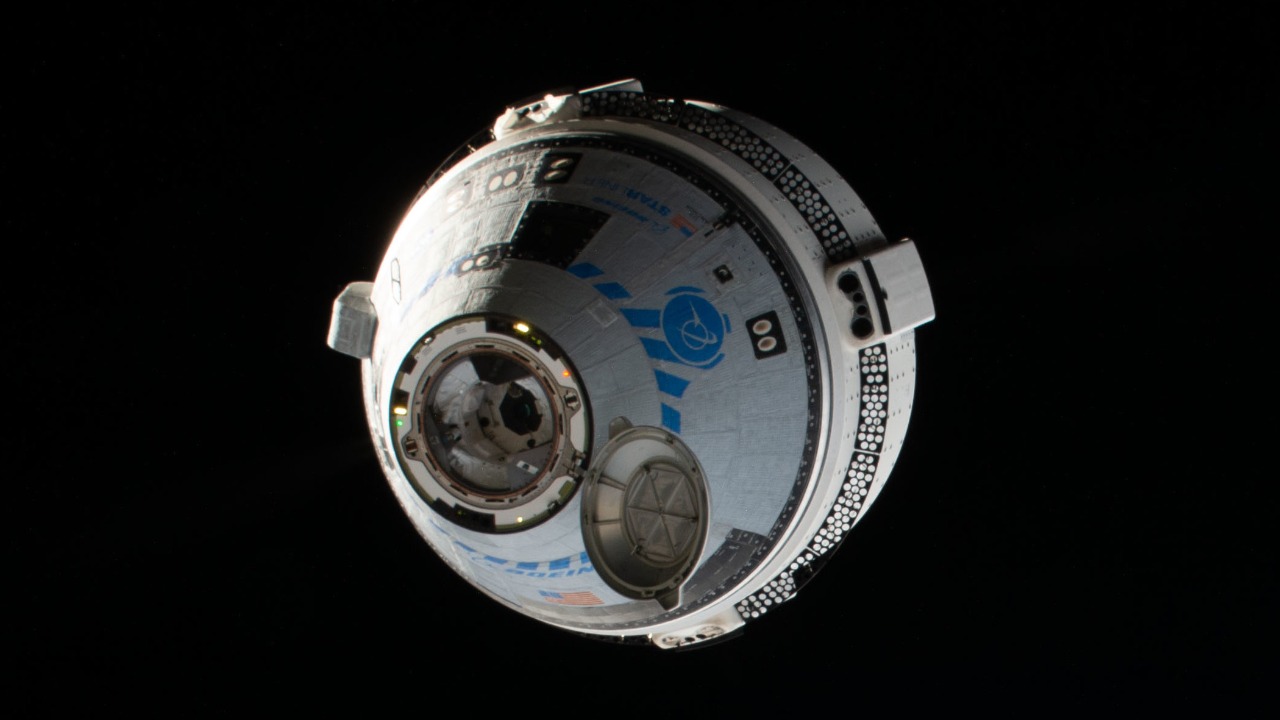

Boeing has issued an official response to the incident, emphasizing their commitment to safety and transparency. Public statements have reassured stakeholders and the general public about the ongoing efforts to understand and address the incident. Boeing’s technical assessments are focused on determining the extent of the damage and identifying any systemic vulnerabilities that could have contributed to the impact.
The company is collaborating with international partners to enhance the protective measures of their spacecraft. This includes exploring new shielding technologies and improving detection systems for micro-meteoroids. Furthermore, Boeing is part of a broader international effort to enhance spacecraft protection, as collaboration is essential in ensuring astronaut safety. These efforts are crucial in minimizing the impact of future incidents and safeguarding the progress of space exploration.
The Broader Context: Space Exploration and Safety

As human activity in space increases, the aerospace industry faces a growing set of safety challenges. The incident with Boeing’s space capsule highlights the importance of addressing these challenges head-on. Advancements in technology and international policies are critical in tackling the threats posed by space debris and micro-meteoroids. Organizations worldwide are investing in research to develop innovative solutions that can withstand the harsh conditions of space.
Continued research and investment in space safety are vital to support the future of space exploration. The collaboration between industry leaders, government agencies, and international partners is key to overcoming these challenges. As we expand our presence in space, ensuring the safety of spacecraft and astronauts will remain a top priority. The lessons learned from incidents like Boeing’s will contribute to a safer and more sustainable future for space exploration.