
In a groundbreaking development, astronomers have identified potential biosignatures on an exoplanet, a discovery that could suggest the presence of extraterrestrial life. This article delves into the specifics of this fascinating discovery and what it means for the scientific community and beyond.
The Discovery: Potential Biosignatures on K218b

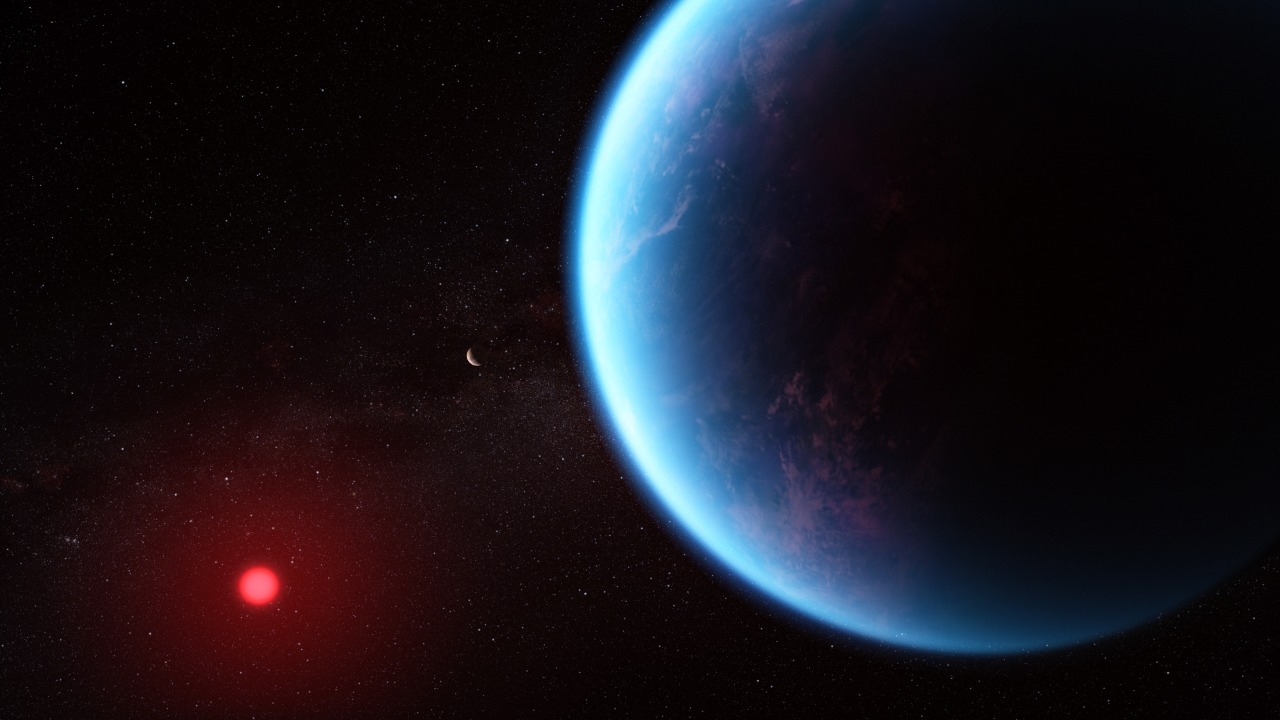
Utilizing advanced telescopes, astronomers have detected potential biosignatures on the exoplanet K218b. Located in the habitable zone of its host star, K218b is an exoplanet with conditions that may support life. Its size and composition are comparable to Earth, making it a significant focus in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Specifically, the potential biosignatures detected on K218b include chemicals that are often associated with the existence of life. Methane, water vapor, and oxygen – chemicals that on Earth are often produced by biological sources – were identified in the exoplanet’s atmosphere, sparking excitement and curiosity among the scientific community.
The Science Behind Biosignatures
Biosignatures are measurable substances or phenomena that provide evidence of past or present life. In astrobiology, the identification of biosignatures is critical for determining the potential habitability of other planets. The presence of chemicals associated with life, such as methane, water vapor, and oxygen, is often regarded as potential biosignatures.
While these chemicals can be produced by non-biological sources, their abundance in a planet’s atmosphere can suggest the presence of biological activity. However, it’s important to note that biosignatures are not definitive proof of life. They merely indicate conditions that may support life, and further investigation is needed to confirm the existence of extraterrestrial life.
The Role of James Webb Space Telescope
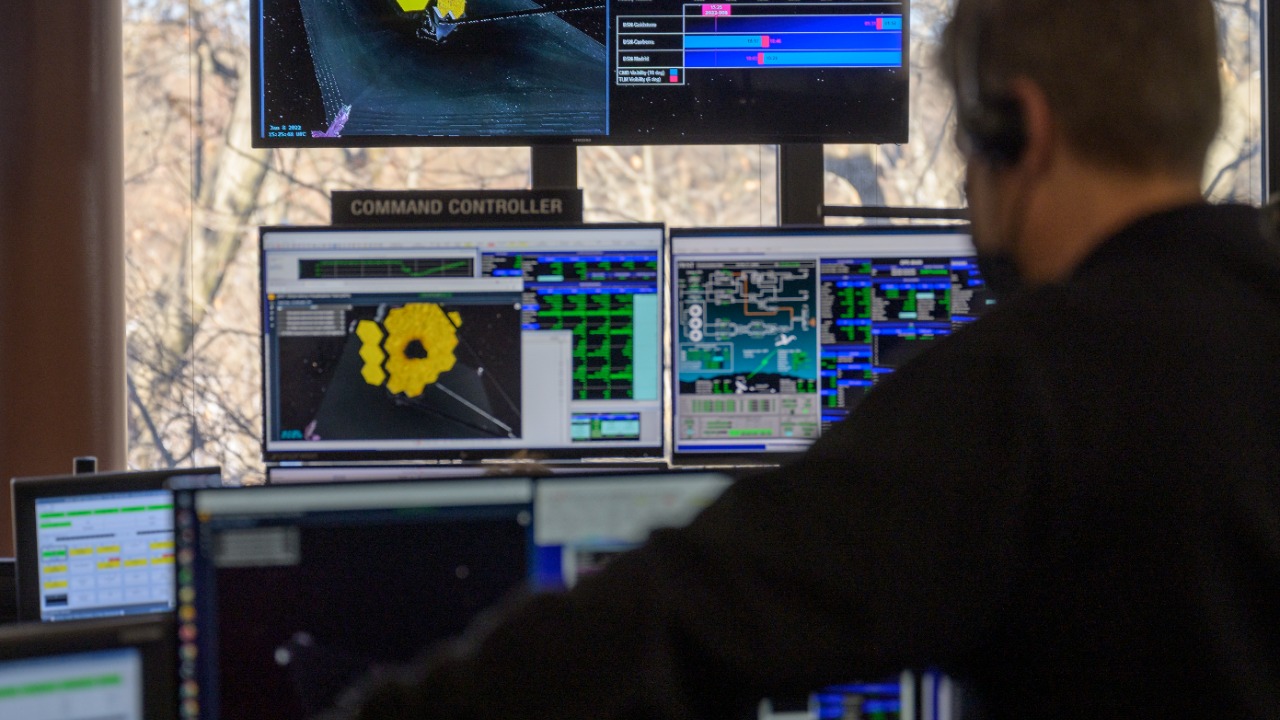

The recent detection of potential biosignatures on K218b was made possible, in part, by the James Webb Space Telescope. This telescope’s high sensitivity to infrared light allows it to detect the faint signals of chemicals in an exoplanet’s atmosphere. Moreover, it can analyze the light that passes through a planet’s atmosphere, providing valuable information about its composition.
Aside from the potential biosignatures on K218b, the James Webb Space Telescope has made other significant discoveries. Its ability to observe distant galaxies and their formation processes has provided unprecedented insight into the early universe, revolutionizing our understanding of space.
Implications for the Search for Extraterrestrial Life
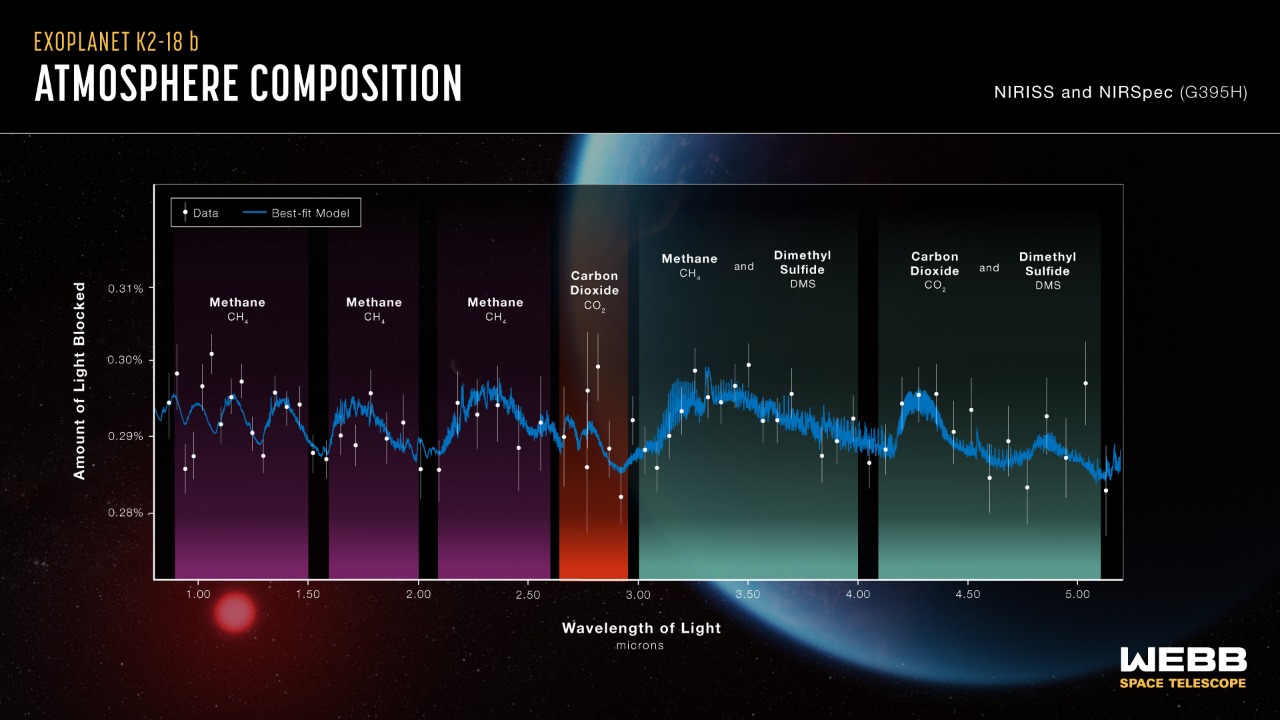
This discovery marks a significant advancement in the ongoing search for life beyond Earth. The detection of potential biosignatures on K218b adds another piece to the puzzle, stimulating further research and exploration of this and other similar exoplanets. Future missions may involve sending probes to collect more detailed data or even launching rovers to explore the surface.
Moreover, the broader implications of finding life beyond Earth are profound. The confirmation of extraterrestrial life would fundamentally alter our understanding of our place in the universe, challenging long-held perspectives and opening new avenues for exploration and discovery.
Future Directions in Exoplanet Research

Looking forward, the search for life on exoplanets continues to be a primary focus in space research. With improved technology, the detection of biosignatures will likely become more precise and reliable. Several future missions and research projects, such as the PLATO mission, are already in the works, aimed at uncovering more about the potential for life on exoplanets.
However, confirming the existence of extraterrestrial life presents significant challenges. It requires not only the detection of potential biosignatures but also the elimination of non-biological sources for these signatures. Despite these challenges, the potential rewards – the knowledge and understanding gained from discovering life beyond Earth – are immeasurable.