Antarctica’s ice caves have long intrigued scientists with the potential to uncover hidden life forms and extinct species. Recent discoveries suggest that these subterranean chambers might hold the remnants of megafauna that once roamed the Earth. The significance of these findings could reshape our understanding of prehistoric life and the environmental conditions that sustained such creatures.
The Mysteries of Antarctica’s Ice Caves
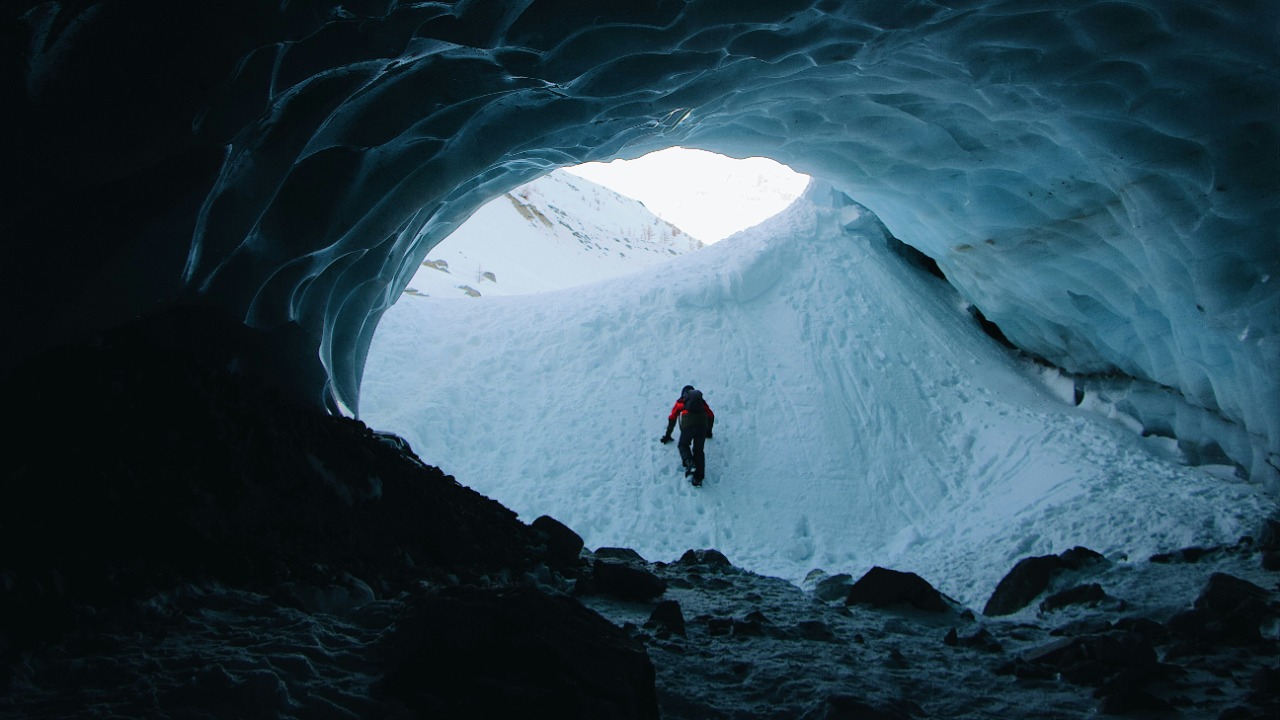

Antarctica’s ice caves are a geological marvel, formed by volcanic activity beneath the ice sheet. These caves are created when heat from volcanic vents melts the ice, resulting in vast underground networks. The unique conditions within these chambers, including stable temperatures and protection from external elements, create an environment that might preserve organic material for millennia. Scientists are particularly interested in these caves because they offer a rare glimpse into a world that remains largely untouched by modern human activity.
Historically, the exploration of these subterranean environments has sparked significant scientific interest. Researchers have discovered microbial life forms adapted to extreme conditions, suggesting the potential for more complex organisms. The possibility that these caves might harbor undiscovered life forms or even extinct species like megafauna adds a layer of excitement to current and future explorations. The allure of finding new species or ancient remnants fuels ongoing research and expeditions.
Evidence of Megafauna in Antarctica
Fossil discoveries in Antarctica have provided tantalizing hints of its prehistoric inhabitants. For instance, researchers have uncovered fossils of ancient creatures, such as a duck-like bird that might be the oldest modern bird ever discovered. While these findings are significant, the potential discovery of megafauna remains could offer new insights into the types of large creatures that once roamed the continent.
Megafauna, such as woolly mammoths and giant ground sloths, are well-documented in other regions, notably the Americas and Eurasia. However, the prospect of identifying similar species in Antarctica would be groundbreaking. Techniques such as radiocarbon dating and DNA analysis are crucial in identifying and dating megafauna remains. These methods allow scientists to establish timelines and draw connections between species found in different parts of the world.
Scientific Implications and Challenges
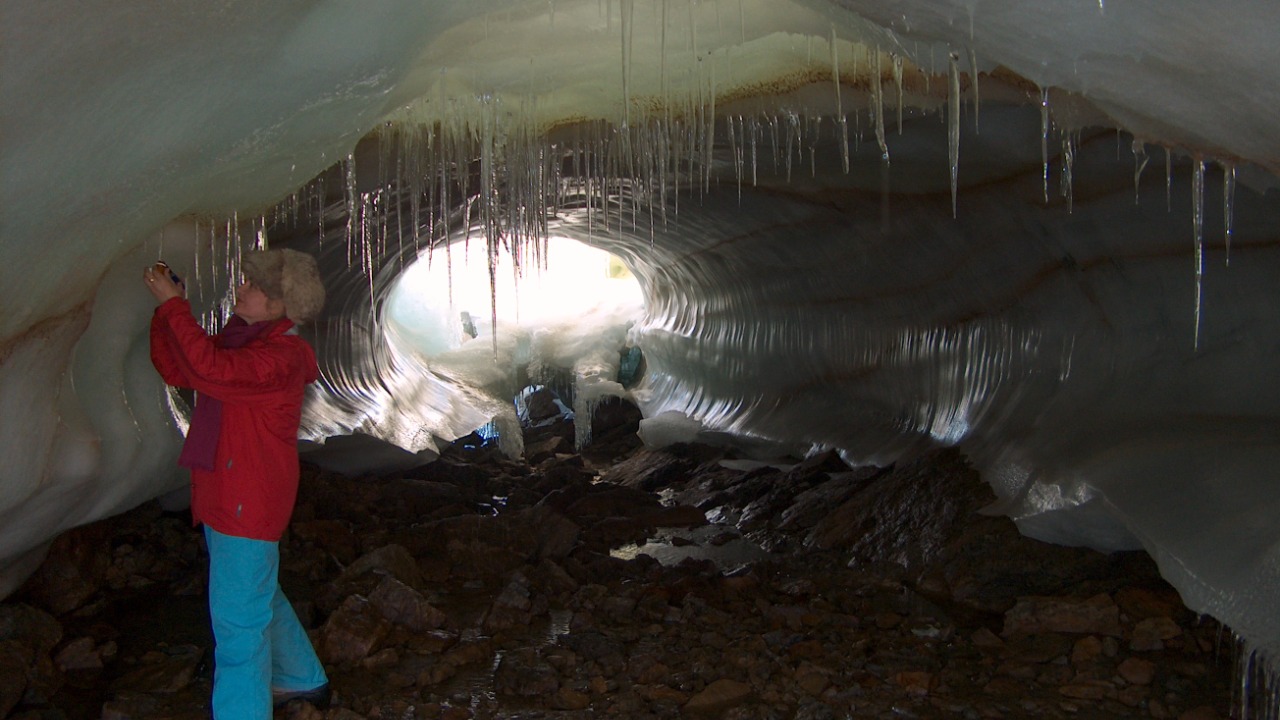

The discovery of megafauna in Antarctica’s ice caves could significantly enhance our understanding of prehistoric climate and ecology. Such findings would offer clues about the environmental conditions that supported large animals and how these conditions changed over time. This knowledge could inform models of past climate patterns and their impact on global biodiversity.
Technological advancements have revolutionized cave exploration and data collection. Robotics, remote sensing, and advanced imaging techniques allow researchers to navigate and study these challenging environments with increased precision. However, the harsh Antarctic conditions pose significant challenges. Researchers must contend with extreme cold, unpredictable weather, and logistical hurdles in transporting equipment and personnel to remote sites. Despite these difficulties, the scientific community remains committed to unearthing the secrets hidden beneath the ice.
The Possibility of Extinct Species Revival

The notion of de-extinction, or bringing extinct species back to life, presents both ethical and scientific considerations. Advances in genetic engineering and cloning have made it conceivable to consider reviving species from preserved DNA samples. However, such efforts raise questions about the potential consequences for existing ecosystems and biodiversity. Introducing species that have been absent for millennia could disrupt current ecological balances.
Case studies of successful DNA extraction from extinct species, such as the woolly mammoth, illustrate the potential for de-extinction. While such projects are still in their infancy, they offer a glimpse into a future where extinct species might walk the Earth once more. The ethical debate continues as scientists weigh the benefits of restoring lost species against the potential risks to modern ecosystems.
The Future of Antarctic Exploration
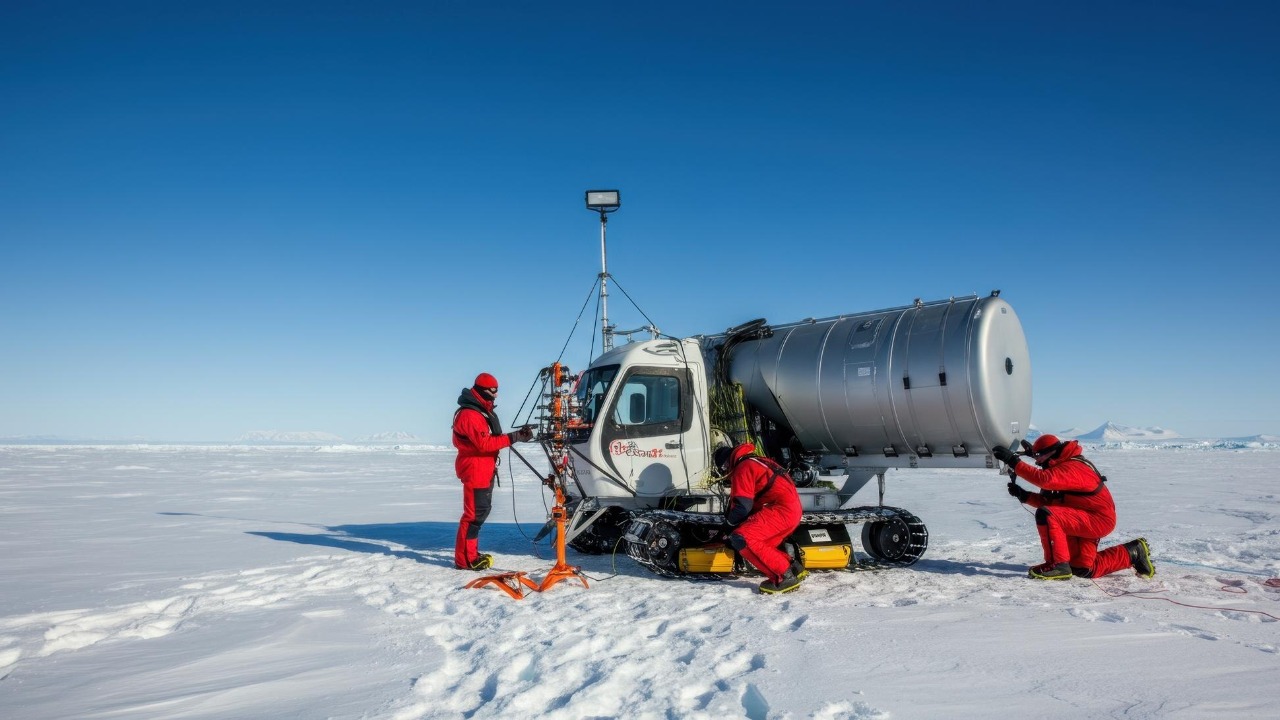

Future expeditions and research initiatives focusing on Antarctic caves are poised to push the boundaries of scientific discovery. International collaboration plays a crucial role in these endeavors, with countries pooling resources and expertise to advance polar research. Funding remains a persistent challenge, but the growing public interest in Antarctica’s mysteries helps garner support for these initiatives.
The role of public interest and awareness cannot be underestimated in supporting scientific endeavors. Documentaries, educational programs, and news articles help to raise awareness about the importance and potential of Antarctic exploration. As more people become informed about the scientific significance of these explorations, they are more likely to support funding and policies that facilitate research. This growing interest could lead to an era of unprecedented discovery and understanding of our planet’s past and its hidden wonders.