Type 5 diabetes, a previously overlooked form of the disease, has gained formal recognition as of April 2025. This marks a pivotal moment in addressing its impact on malnourished children, particularly in regions like India where malnutrition is prevalent. The recognition underscores the years of oversight in global health efforts to classify this variant separately from other types, highlighting the need for increased awareness and targeted interventions.
Understanding Type 5 Diabetes
Type 5 diabetes is now recognized as a distinct subtype of diabetes, primarily linked to malnutrition rather than the typical metabolic factors associated with types 1 through 4. This form of diabetes has been classified as a “neglected form” due to its evasion of standard diabetes frameworks until its recent formal naming. The classification aims to improve understanding and management of the disease, which has unique characteristics compared to other types of diabetes. International health bodies have played a crucial role in advocating for this recognition, which is expected to enhance tracking and research efforts globally [source].
The formal naming of type 5 diabetes is a significant step forward in addressing a gap in diabetes classification. This new category acknowledges the unique challenges faced by children in malnourished populations, where traditional diabetes management strategies may not be effective. By recognizing type 5 diabetes, health professionals can better tailor their approaches to diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving outcomes for affected children [source].
Causes and Risk Factors
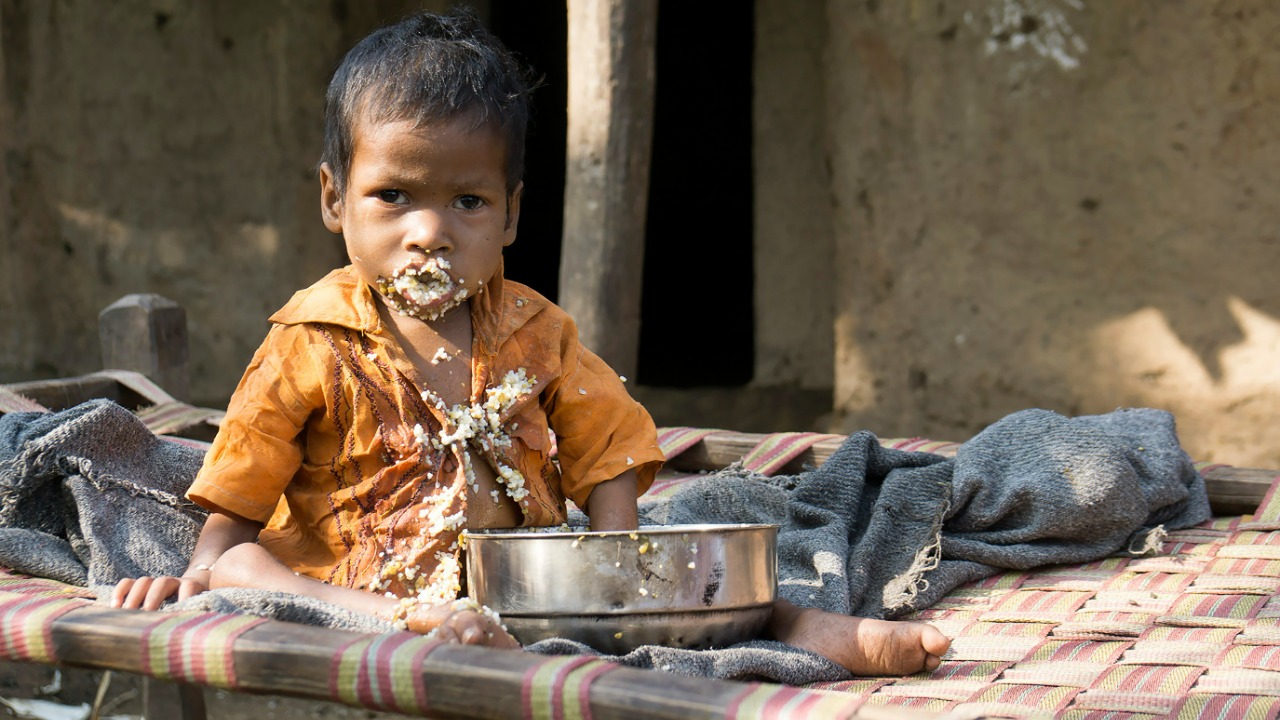

Chronic malnutrition in children is the primary cause of type 5 diabetes, disrupting normal glucose regulation in ways that are unique to undernourished populations. This form of diabetes is particularly prevalent in low-income areas of India and other regions with significant food insecurity. The condition is exacerbated by factors such as stunted growth and micronutrient deficiencies, which contribute to its onset in early childhood. These geographic and nutritional risks highlight the urgent need for targeted interventions in affected regions [source].
Understanding the specific causes and risk factors of type 5 diabetes is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. The condition’s link to malnutrition means that addressing food insecurity and improving nutritional standards are essential components of any comprehensive approach. By focusing on these underlying issues, health organizations can work towards reducing the incidence of type 5 diabetes and improving the overall health of vulnerable populations [source].
Symptoms and Identification

Type 5 diabetes presents with unusual symptoms, including severe fatigue, growth delays, and atypical blood sugar fluctuations not seen in other types of diabetes. These symptoms often mimic other pediatric conditions, leading to frequent misdiagnosis in malnourished children. Parents and healthcare providers need to be vigilant in monitoring for signs such as recurrent infections, which are often tied to poor nutrition. Early identification of these symptoms is key to providing timely and effective treatment [source].
The challenge of identifying type 5 diabetes lies in its symptom overlap with other conditions common in malnourished populations. This overlap can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment, exacerbating the health challenges faced by affected children. By increasing awareness of the specific symptoms associated with type 5 diabetes, healthcare providers can improve diagnostic accuracy and ensure that children receive the care they need [source].
Diagnosis and Management

Diagnosing type 5 diabetes presents unique challenges, as it requires nutritional assessments alongside standard glucose tests to confirm the condition. This dual approach is necessary to accurately identify the disease in children who may not fit the typical profile of diabetes patients. Management strategies for type 5 diabetes focus on nutritional rehabilitation rather than relying solely on insulin therapy. Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications and improve long-term health outcomes for affected children [source].
Ongoing research is essential to develop targeted therapies for type 5 diabetes, particularly in light of its recent recognition. Understanding the specific needs of children with this condition will enable healthcare providers to offer more effective treatment options. As research progresses, it is hoped that new therapies will emerge that can address the unique challenges posed by type 5 diabetes, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected [source].