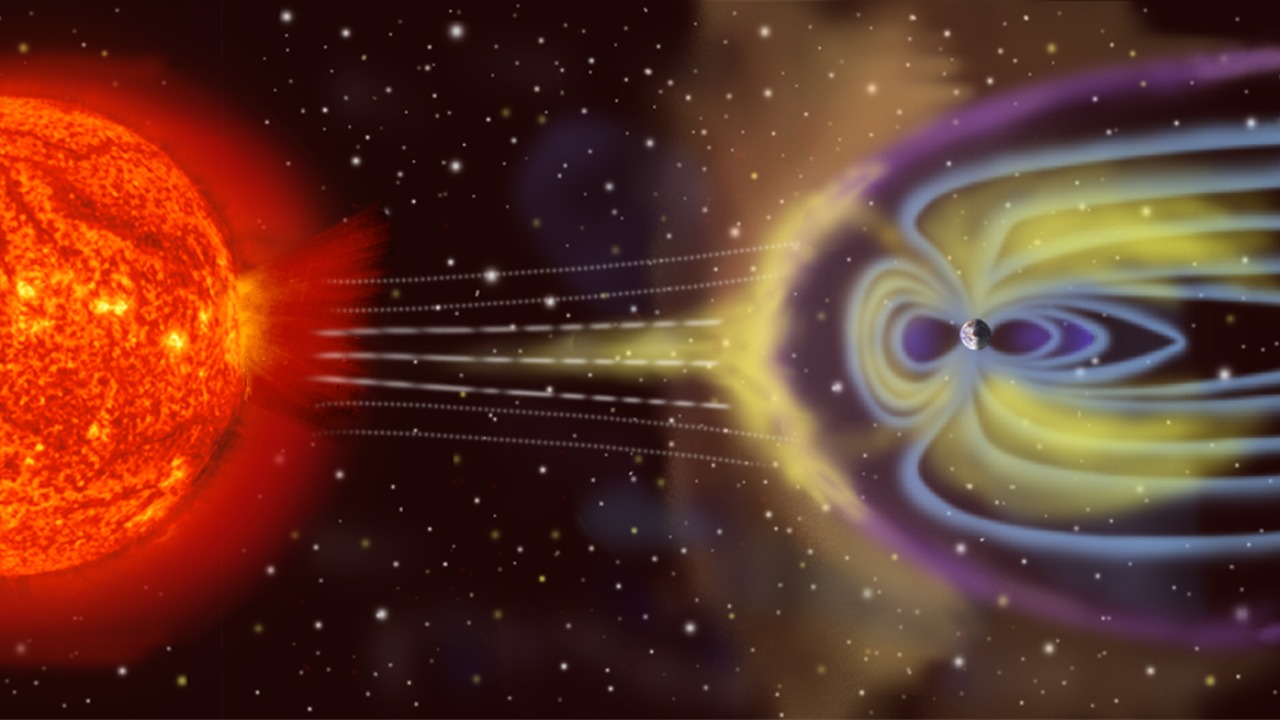
Recent research has revealed a surprising discovery about Earth’s magnetosphere that challenges long-standing theories, potentially reshaping our understanding of how this protective shield functions against solar radiation. This finding builds on earlier revelations, including a discovery about Earth’s core that could affect the length of a day, and another shocking discovery 1,700 miles beneath Earth’s surface that probes deep geophysical processes. Together, these insights underscore rapid advances in exploring Earth’s hidden dynamics.
Understanding the Magnetosphere Discovery
The recent discovery about Earth’s magnetosphere has unveiled unexpected deviations from established models of magnetic field interactions with solar wind. This revelation, reported on October 20, 2025, challenges decades of theory in magnetospheric physics. Scientists utilized advanced satellite observations and simulations to uncover these anomalies, which suggest that the magnetosphere’s behavior is more complex than previously thought. This breakthrough could significantly impact our understanding of space weather forecasting, as experts are now reevaluating how solar wind and magnetic fields interact.
Initial reactions from the scientific community highlight the potential implications for space weather forecasting. With the magnetosphere playing a crucial role in shielding Earth from harmful solar radiation, any changes in its behavior could affect auroral activity and radiation exposure for satellites and astronauts. This discovery emphasizes the need for updated models to predict space weather more accurately, ensuring the safety and reliability of technological infrastructure in space.
Links to Earth’s Inner Core Dynamics
The surprising discovery about Earth’s core, reported on February 18, 2025, suggests that changes in the core’s rotation could influence the length of a day. This finding highlights the interconnectedness of Earth’s internal processes and their impact on the planet’s outer layers. The core’s fluctuations are believed to play a role in generating and stabilizing the magnetosphere, further emphasizing the importance of understanding these deep Earth dynamics.
Additionally, a shocking discovery 1,700 miles beneath Earth’s surface, reported on June 17, 2025, revealed structural anomalies that could provide insights into the planet’s geophysical processes. These findings suggest that the inner workings of Earth are more dynamic than previously understood, with potential implications for the stability and strength of the magnetosphere. By connecting these discoveries, scientists are gaining a more comprehensive view of how Earth’s internal processes influence its protective magnetic shield.
Broader Impacts on Planetary Protection
The discovery about the magnetosphere has significant implications for planetary protection, particularly in terms of auroral activity and radiation exposure. Revised theories on magnetic field behavior could alter predictions for these phenomena, impacting both satellites and astronauts. As space exploration continues to expand, understanding the magnetosphere’s behavior is crucial for ensuring the safety of missions beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
Moreover, the potential long-term effects on Earth’s climate and technological infrastructure cannot be overlooked. Changes in the magnetosphere could influence weather patterns and climate systems, highlighting the need for interdisciplinary research to explore these connections. As scientists continue to investigate the links between Earth’s core and magnetosphere, they may uncover new insights into how these processes interact over time.
Related Surprising Finds in Earth’s Environment
In addition to discoveries about Earth’s magnetosphere and core, scientists have made a surprising discovery in waters below offshore wind farms. Reported on June 8, 2025, researchers are trying to understand the environmental monitoring challenges posed by this oceanic revelation. This finding is relevant to broader Earth system studies, as it highlights the complexity of interactions between natural and human-made environments.
These unexpected discoveries, while distinct, share parallels with space-based surprises, such as the Chandrayaan-2 mission’s findings about the Moon’s ionosphere. Each revelation refines models of protective layers around Earth, emphasizing the importance of continuous exploration and monitoring. By integrating these insights, scientists can develop more accurate models to predict and mitigate potential impacts on Earth’s environment and technological systems.