When it comes to automotive engineering, not all engines are created equal. Kia, a brand known for its affordability and innovation, has had its share of engine missteps over the years. This article explores some of the most problematic engines that have left Kia owners frustrated and mechanics busy.
The 1.6L GDI Engine in Early 2010s Models

The 1.6L GDI engine found in Kia’s early 2010s models has been a source of concern for many drivers. Known for its general reliability issues, this engine has been frequently mentioned in lists of worst cars ever made. Owners have reported problems such as engine knocking and excessive oil consumption, which can lead to costly repairs and decreased vehicle lifespan.
These issues have not only affected the driving experience but have also impacted Kia’s reputation for reliability. For potential buyers, understanding these pitfalls is crucial, especially when considering used models from this era. The 1.6L GDI engine serves as a reminder of the importance of thorough research before purchasing a vehicle.
The Theta II 2.0L Engine in 2011-2014 Optima and Sorento

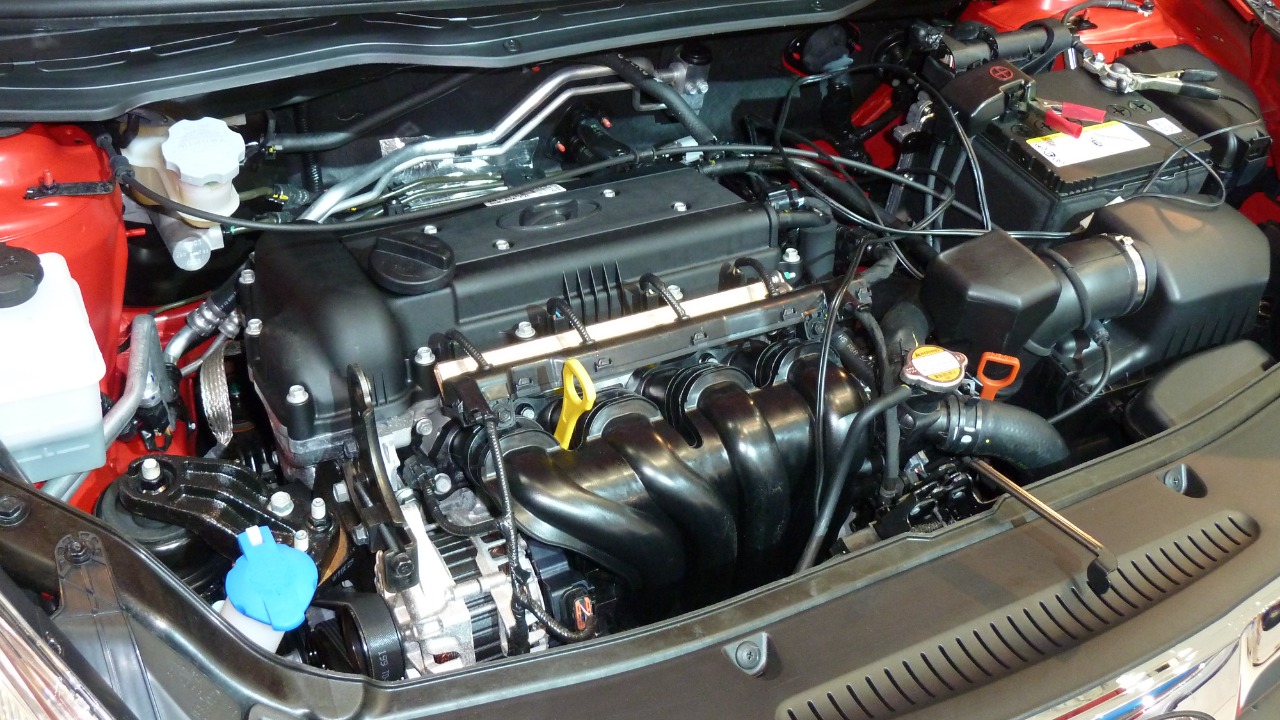
The Theta II 2.0L engine, used in the 2011-2014 Kia Optima and Sorento, has been notorious for its engine failures. According to reader reports on Jalopnik, this engine has been plagued by issues such as engine seizing and stalling, often attributed to manufacturing defects.
These problems have led to numerous recalls and legal actions, highlighting the significant impact on both consumers and the manufacturer. For Kia, addressing these issues has been essential to maintaining customer trust and brand integrity. For owners, the Theta II engine’s problems underscore the importance of staying informed about potential recalls and warranty extensions.
The 2.4L GDI Engine in Mid-2010s Sportage

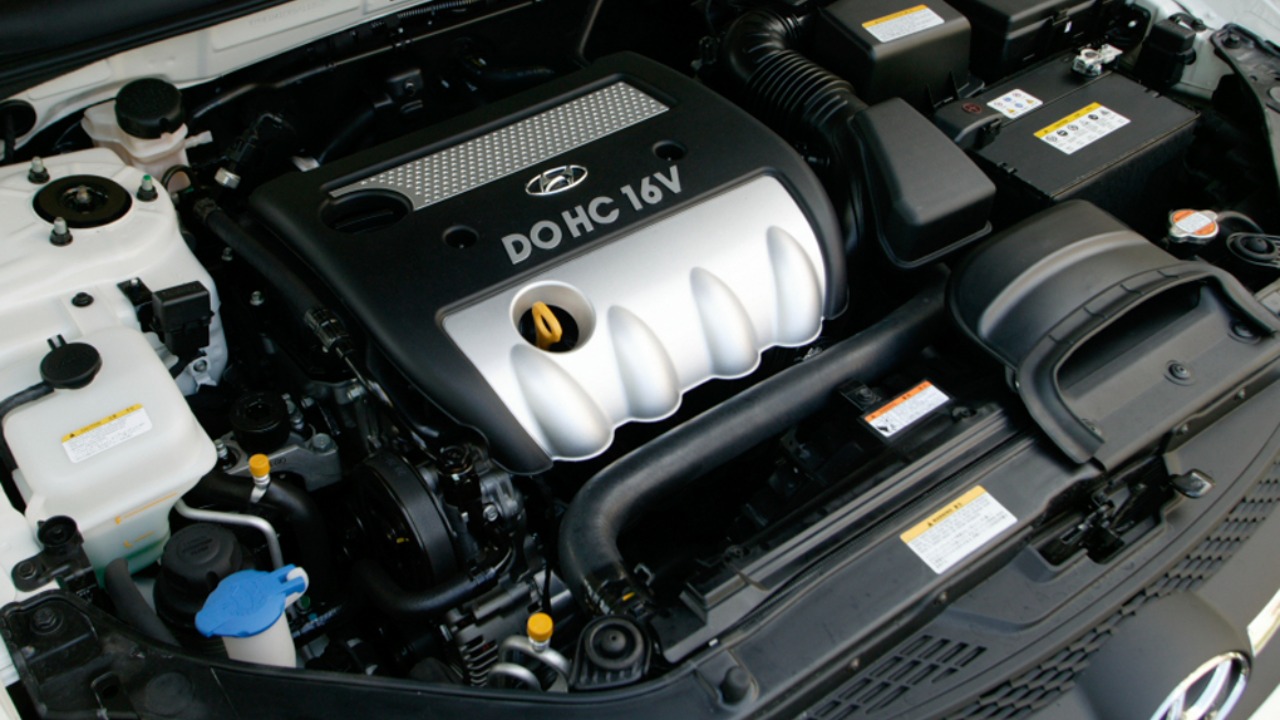
The 2.4L GDI engine in the mid-2010s Kia Sportage presents a paradox of performance and reliability. While this engine is part of some of Kia’s fastest models, it has also been associated with years to avoid due to engine problems, as noted by 24/7 Wall St.
Issues such as engine knocking and premature wear have been reported, leading to dissatisfaction among owners. These problems highlight the challenges manufacturers face in balancing performance with durability. For consumers, being aware of these issues can guide better purchasing decisions, especially when considering the long-term costs of ownership.
The Nu 2.0L MPI Engine in 2010s Forte
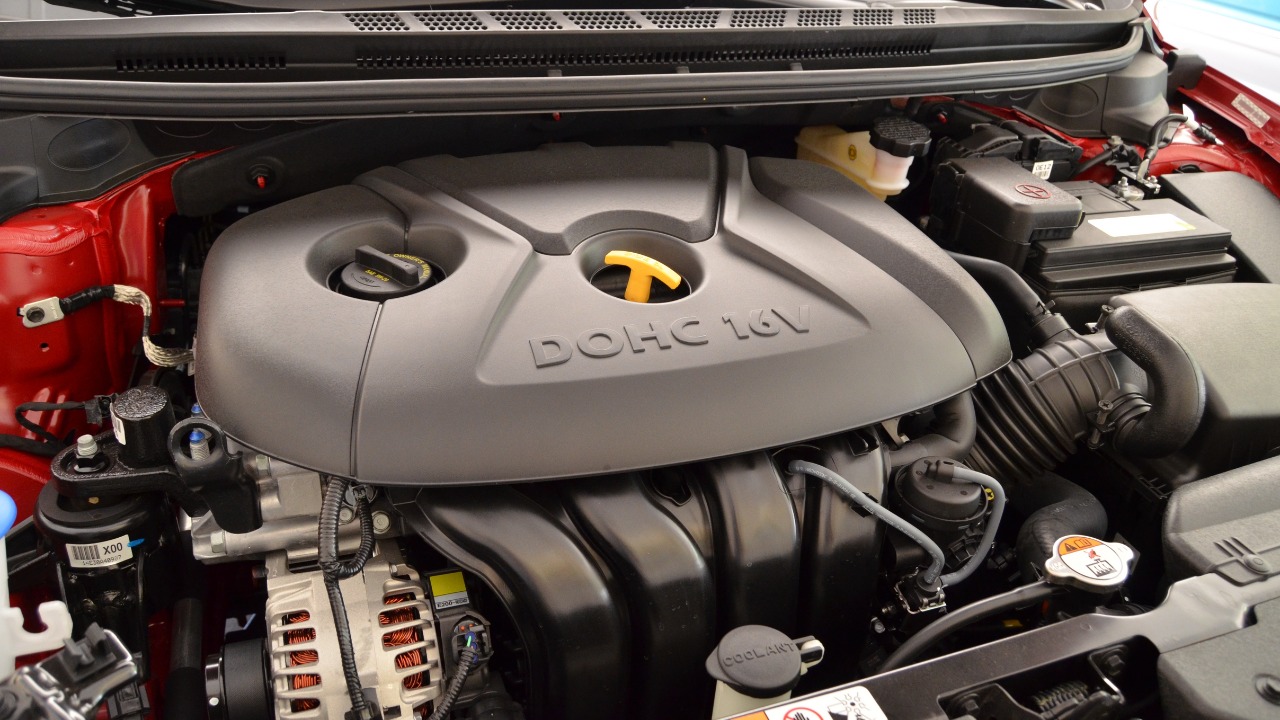

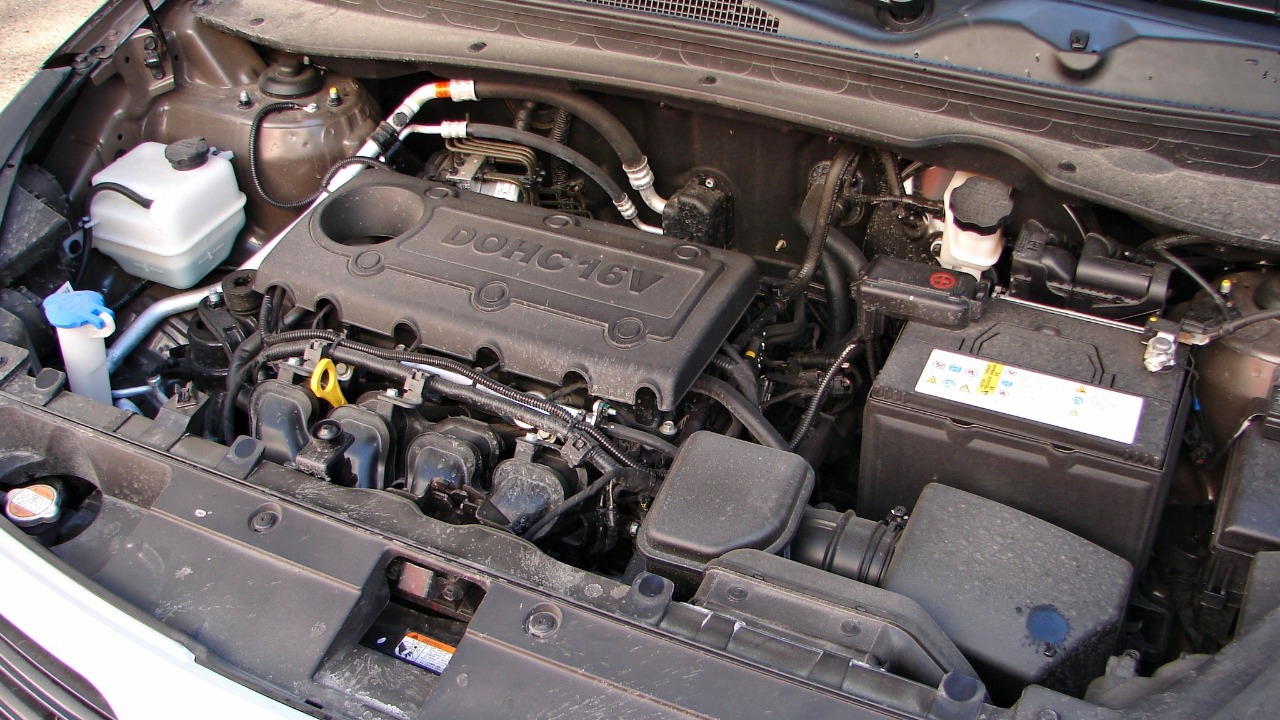
The Nu 2.0L MPI engine, used in the 2010s Kia Forte, has been criticized for its lack of durability. As highlighted in broader manufacturer critiques on Carwow, this engine has faced issues such as excessive oil consumption and engine failure.
These problems have not only affected the vehicle’s performance but have also led to increased maintenance costs for owners. For Kia, addressing these durability concerns is crucial to improving customer satisfaction and vehicle reliability. For potential buyers, understanding these issues can help in making informed decisions when considering a used Kia Forte.
The Gamma 1.6L Turbo Engine in Later 2010s Models
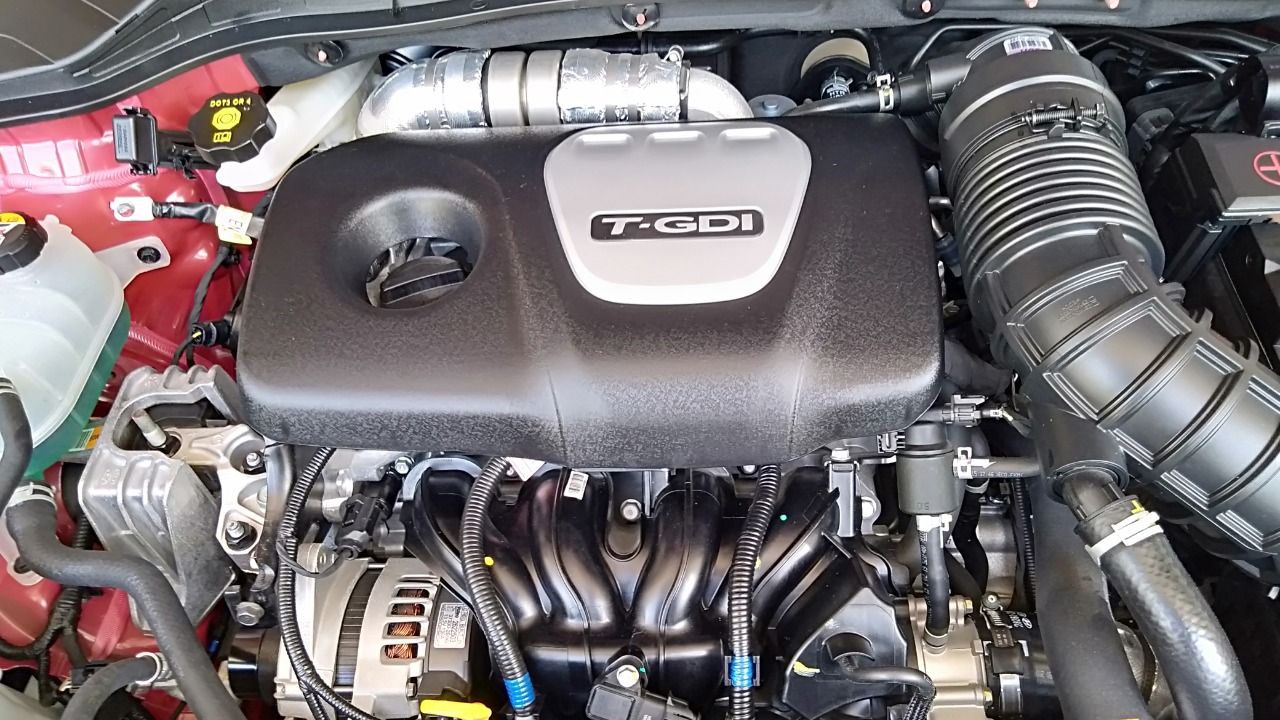

The Gamma 1.6L Turbo engine, found in later 2010s Kia models, has been noted for its potential drawbacks in high-performance applications. Despite being part of some of Kia’s fastest models, this engine has faced criticism for reliability issues.
Problems such as turbocharger failures and engine overheating have been reported, impacting the vehicle’s performance and owner satisfaction. These issues highlight the challenges of integrating turbo technology into mass-market vehicles. For consumers, being aware of these potential pitfalls can aid in making more informed decisions, particularly when considering performance-oriented models.