
Recent studies reveal that Earth is getting darker, a concerning trend linked to reduced reflectivity, or albedo, which may have contributed to the record heat experienced in 2023. Simultaneously, 21% of the ocean is losing sunlight, posing significant threats to marine ecosystems. As Earth becomes greener, questions arise about the implications of these changes on our climate.
The Phenomenon of Earth’s Darkening
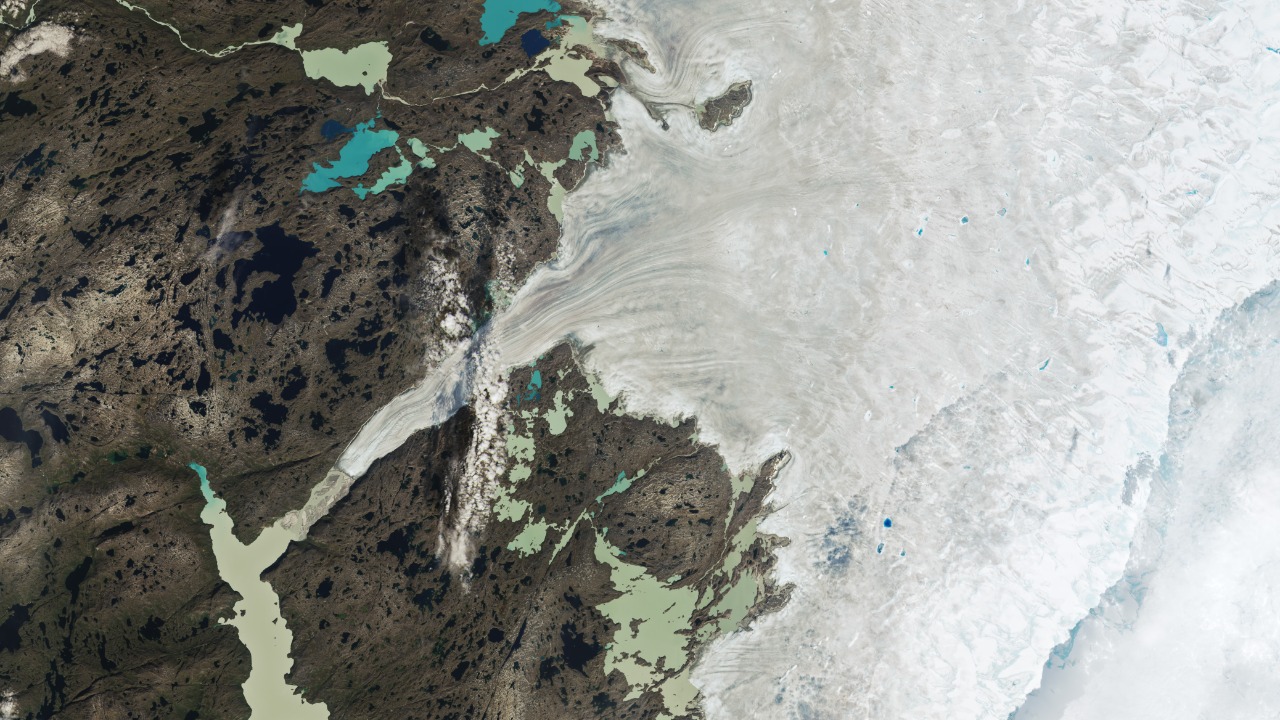
Earth’s decreasing albedo is a critical factor in the planet’s darkening. Albedo refers to the measure of how much sunlight Earth’s surface reflects back into space. A lower albedo means that more sunlight is absorbed, leading to warmer global temperatures. This phenomenon has been linked to the darker planetary conditions observed recently. According to MSN, the reduction in Earth’s reflectivity is a significant contributor to this trend.
Several factors may be causing the reduction in Earth’s reflectivity. Changes in cloud cover, ice melt, and land use can all impact albedo. For instance, as ice caps melt, darker ocean water is exposed, absorbing more sunlight. Similarly, deforestation and urbanization replace reflective surfaces with darker ones, further decreasing albedo. These changes are contributing to the warming of the planet, as highlighted by CBC.
Impacts on Global Climate

The darkening of Earth has significant implications for global climate patterns. The record heat of 2023 has been partially attributed to this phenomenon. As Earth’s surface absorbs more sunlight, global temperatures rise, exacerbating the effects of climate change. This warming trend is not only a concern for the immediate future but also poses long-term risks to the planet’s climate stability. The CBC report emphasizes the role of decreased albedo in these temperature increases.
Looking ahead, the potential long-term effects of decreased albedo are concerning. If current trends continue, we may see more frequent and severe weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems worldwide. The MSN article discusses the potential for these changes to accelerate if mitigation strategies are not implemented.
Consequences for Marine Life

The alarming statistic that 21% of the ocean is losing sunlight highlights a critical issue for marine ecosystems. As reported by SciTechDaily, reduced sunlight penetration affects photosynthesis in marine plants, which are foundational to oceanic food webs. This reduction can lead to decreased biodiversity and disrupt the balance of marine life.
Marine ecosystems rely heavily on sunlight for energy and growth. The loss of sunlight impacts not only plant life but also the animals that depend on these plants for food. As these ecosystems are disrupted, the effects ripple through the food chain, potentially leading to declines in fish populations and other marine species. The SciTechDaily article underscores the importance of addressing these changes to protect marine biodiversity.
Furthermore, the reduction in sunlight can lead to a decrease in the productivity of phytoplankton, which are crucial for carbon sequestration in the ocean. Phytoplankton absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, and their decline could result in higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming. This change not only affects marine biodiversity but also has broader implications for global carbon cycles and climate regulation. According to SciTechDaily, the loss of these organisms can significantly alter marine food webs and reduce the ocean’s capacity to act as a carbon sink.
The Role of Earth’s Greening

Earth’s greening presents a paradoxical impact on climate change. While increased vegetation can absorb more carbon dioxide, potentially mitigating some effects of climate change, it also affects Earth’s albedo. As Vox explains, more vegetation can lead to a darker surface, reducing reflectivity and contributing to warming.
The increase in vegetation is driven by higher carbon dioxide levels, which promote plant growth. However, this greening can have unintended consequences. While it may seem beneficial, the reduction in albedo can offset the positive effects of carbon absorption, leading to higher global temperatures. The Vox article highlights the complexity of these interactions and the need for a nuanced understanding of Earth’s greening.
Additionally, the greening of Earth can influence local climates by altering patterns of evapotranspiration, which is the process by which water is transferred from land to the atmosphere by evaporation and transpiration from plants. As vegetation increases, so does evapotranspiration, potentially affecting local humidity and precipitation patterns. This can lead to changes in weather patterns, which may not always be beneficial. The Vox article notes that while greening can enhance carbon uptake, it can also complicate efforts to predict and manage climate impacts due to these complex interactions.
Future Outlook and Mitigation Strategies

Addressing Earth’s darkening and its climate impacts requires comprehensive mitigation strategies. Potential solutions include enhancing reflectivity through geoengineering techniques, such as increasing cloud cover or deploying reflective materials. These strategies aim to counteract the warming effects of decreased albedo. The MSN article discusses these potential approaches.
Policy and scientific initiatives are crucial in understanding and counteracting these changes. Collaborative efforts between governments, scientists, and environmental organizations can lead to innovative solutions and policies that address the root causes of Earth’s darkening. By prioritizing research and development in this area, we can better prepare for and mitigate the impacts of these climate trends. The MSN article emphasizes the importance of these initiatives in shaping a sustainable future.
In addition to technological solutions, natural approaches such as reforestation and wetland restoration can enhance Earth’s natural reflectivity and carbon absorption capabilities. These strategies not only help mitigate climate change but also restore vital ecosystems that support biodiversity. The MSN article highlights the importance of integrating these natural solutions with technological advancements to create a comprehensive approach to climate mitigation. By fostering resilience in natural systems, we can better adapt to the changing climate and reduce the severity of its impacts.