
NASA’s recent confirmation of unusual heat signatures beneath the Martian soil has sparked a wave of excitement in the scientific community. This discovery could potentially revolutionize our understanding of Mars’ geology and the planet’s potential for life.
Discovery of Heat Signatures

The detection of these unusual heat signatures was made possible by NASA’s advanced technology and persistent exploration of Mars. Heat signatures, or thermal anomalies, are patterns of heat radiation that can reveal significant information about the geological and biological activities of a planet. They are typically detected using thermal imaging technology, which captures the infrared radiation emitted by objects.
The heat signatures detected on Mars are particularly unusual due to their patterns. Unlike the relatively uniform heat distribution expected on a seemingly inactive planet like Mars, these signatures suggest localized sources of heat beneath the surface. This could indicate geological activity or other phenomena that are yet to be understood.
Implications for Martian Geology
The detection of these heat signatures could significantly alter our understanding of Mars’ geological makeup. On Earth, similar heat signatures are often associated with geological activities such as volcanic activity or tectonic movement. If such activities are occurring on Mars, it would suggest a far more geologically active planet than previously thought.
Comparisons between Earth and Mars based on these findings could also yield fascinating insights. For instance, the presence of heat signatures could suggest that Mars, like Earth, has a heat-generating core. This could potentially explain the planet’s magnetic field, which has puzzled scientists for years.
Significance for Astrobiology

The discovery of heat signatures on Mars also has significant implications for astrobiology, the study of potential life beyond Earth. Heat is a fundamental requirement for life as we know it, providing the energy necessary for biological processes. The presence of heat beneath the Martian surface could therefore suggest conditions conducive to life.
This discovery fits into a larger picture of ongoing research into the potential for life on Mars. Past discoveries, such as the presence of methane in the Martian atmosphere, have already suggested the possibility of biological activity. The detection of heat signatures adds another piece to this intriguing puzzle.
Potential Water Presence on Mars

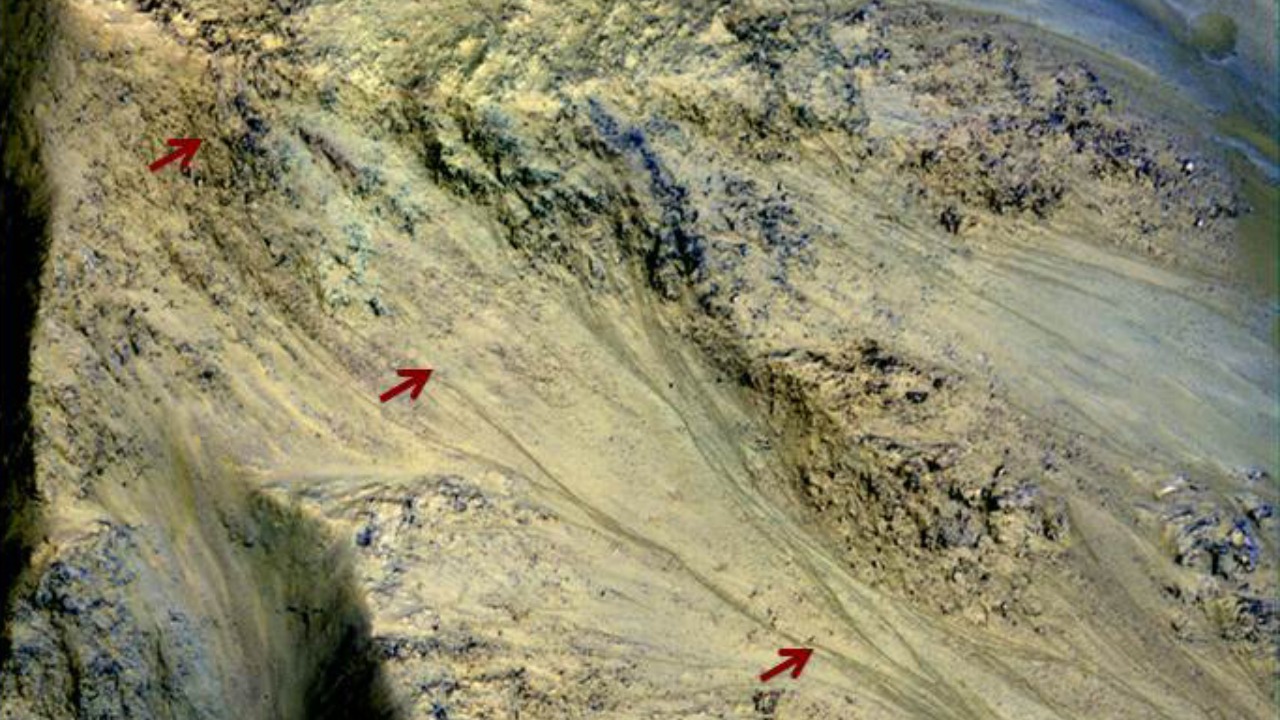
The heat signatures detected on Mars could also be linked to the presence of water beneath the planet’s surface. On Earth, heat signatures are often associated with underground water systems, as water’s high heat capacity allows it to absorb and retain heat. If similar processes are occurring on Mars, it could suggest the presence of subsurface water reservoirs.
This possibility aligns with past evidence of water on Mars. For instance, in 2015, NASA confirmed that the bizarre ‘dark finger’ marks on the Martian surface were signs of liquid water. The presence of water is crucial in the search for life on other planets, as it is a fundamental requirement for all known forms of life.
Future Explorations and Studies

This discovery is likely to influence future Mars missions and studies. NASA and other space agencies may develop new technologies or methodologies to further study these heat signatures and what they reveal about Mars’ geology and potential for life.
The detection of heat signatures beneath the Martian surface opens exciting possibilities for our understanding of Mars and the solar system. It adds a new dimension to our exploration of the Red Planet and brings us one step closer to answering the age-old question: Are we alone in the universe?