Recent observations of the Kuiper Belt have revealed anomalies that suggest the presence of an undiscovered Neptune-sized planet. This potential celestial body, often referred to as “Planet Y,” could provide new insights into our understanding of the outer solar system. Such a discovery could reshape our knowledge of solar system dynamics and planetary formation.
Kuiper Belt Anomalies
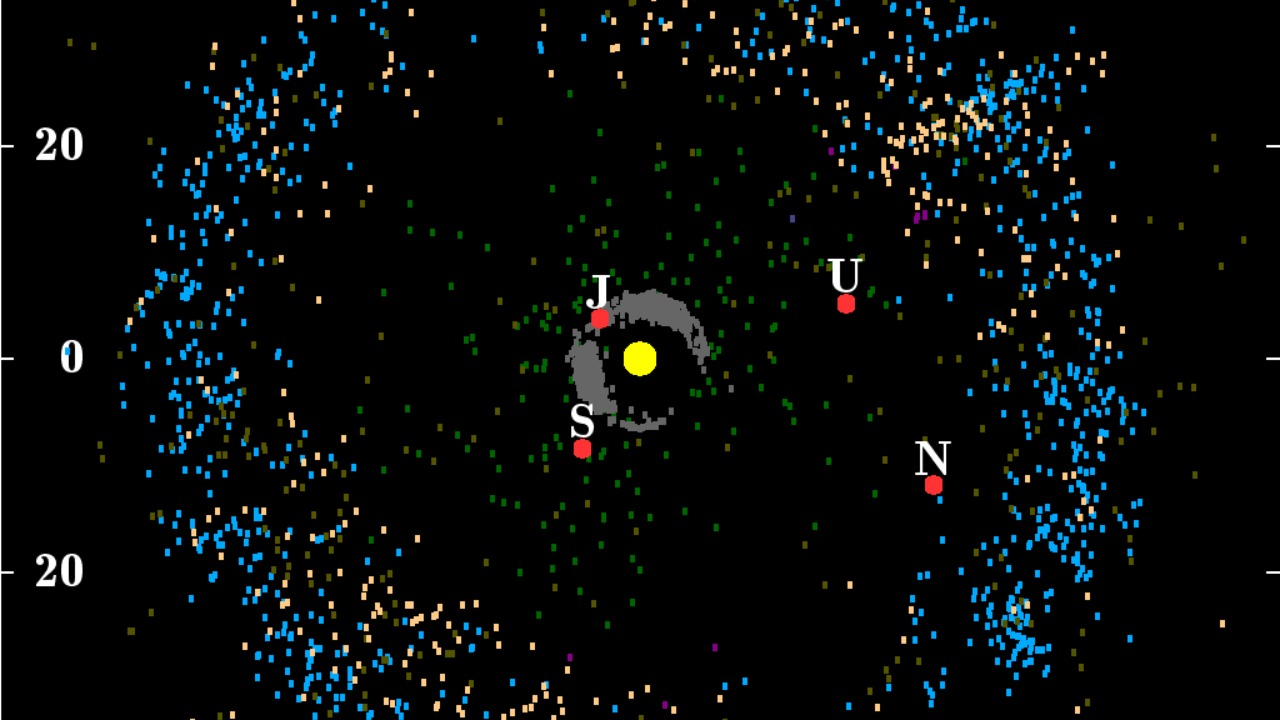
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Kuiper Belt anomalies is the unexpected orbital patterns observed in Kuiper Belt Objects (KBOs). These objects exhibit unusual elliptical orbits that deviate significantly from what current models predict. Such deviations suggest gravitational influences from an unknown source, possibly a massive planet lying beyond Neptune. The peculiarities in the orbits of these KBOs have led scientists to hypothesize the existence of a Neptune-sized planet, which is influencing their paths.
Historical data review plays a crucial role in understanding these anomalies. Past observations have occasionally hinted at similar irregularities, but they were often dismissed due to insufficient evidence. However, with the advent of more advanced observational tools and techniques, researchers are now able to compare these anomalies with predicted models of solar system formation. These comparisons reveal inconsistencies that further support the hypothesis of an additional massive body exerting gravitational forces on the Kuiper Belt.
Hypotheses of a Neptune-Sized Planet

The theoretical characteristics of “Planet Y,” a Neptune-sized celestial body beyond Neptune, offer fascinating possibilities. If it exists, it could be similar in size and mass to Neptune, yet situated much farther from the Sun. The gravitational influence of such a planet could explain the current configuration of the Kuiper Belt, affecting the orbits of numerous KBOs. This potential discovery could lead to revisions in our understanding of the solar system’s architecture and the processes that govern planetary formation.
While the existence of Planet Y is a compelling explanation for the observed anomalies, alternative theories have also been proposed. Some scientists suggest that other phenomena, such as primordial black holes or the presence of dark matter, could be responsible for the gravitational effects observed in the Kuiper Belt. These alternatives present significant challenges in terms of confirmation and detection, as they require different approaches and technologies to verify their presence. The debate over these competing hypotheses highlights the complexities and uncertainties involved in unraveling the mysteries of the outer solar system.
Technological Advances and Observational Efforts
The search for Planet Y and the study of the Kuiper Belt anomalies have been greatly aided by advancements in telescope technology. Modern telescopes and space observatories are equipped with cutting-edge instruments capable of detecting faint and distant objects that were previously beyond reach. Upcoming missions and projects, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, are expected to provide even more precise data, potentially confirming the existence of a new planet.
Data analysis techniques have also evolved, with machine learning and artificial intelligence playing crucial roles in sifting through vast amounts of astronomical data. These technologies enable researchers to identify patterns and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. International collaboration further enhances discovery efforts, with teams from around the world pooling resources and expertise to explore the outer reaches of our solar system. Such cooperation is essential in tackling the challenges posed by the search for distant celestial bodies.
Implications for Astronomy and Cosmology
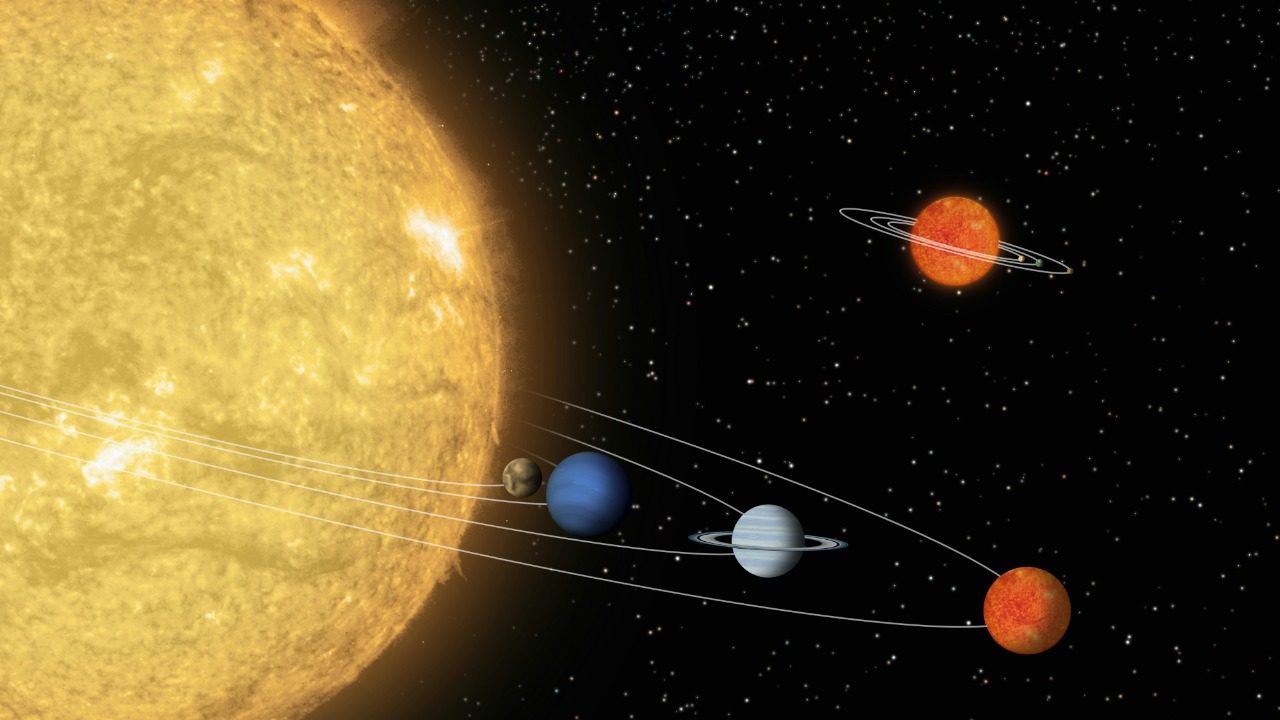
The potential discovery of a new planet in the outer solar system could have profound implications for our understanding of solar system formation. It may require scientists to reevaluate existing theories of planetary formation and migration, as well as the processes that govern the evolution of planetary systems. The presence of a massive, distant planet could offer insights into the dynamics of other stellar systems, providing a valuable point of comparison for astronomers studying exoplanets.
Future research directions will likely focus on further exploration and study of the outer solar system regions. Continued investment in space research and technology development is crucial for advancing our knowledge and uncovering the secrets of our cosmic neighborhood. As observational capabilities improve and new missions are launched, the possibility of discovering additional celestial bodies or confirming the existence of Planet Y becomes increasingly likely. These efforts not only expand our understanding of the solar system but also inspire curiosity and wonder about the universe beyond.