
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has unveiled breathtaking images of Saturn’s North Pole, capturing the iconic hexagonal cloud patterns in unprecedented detail. These observations shed new light on the atmospheric dynamics of the gas giant, sparking fresh curiosity and scientific inquiry into the enigmatic meteorological phenomena that characterize Saturn.
The Phenomenon of Saturn’s Hexagon
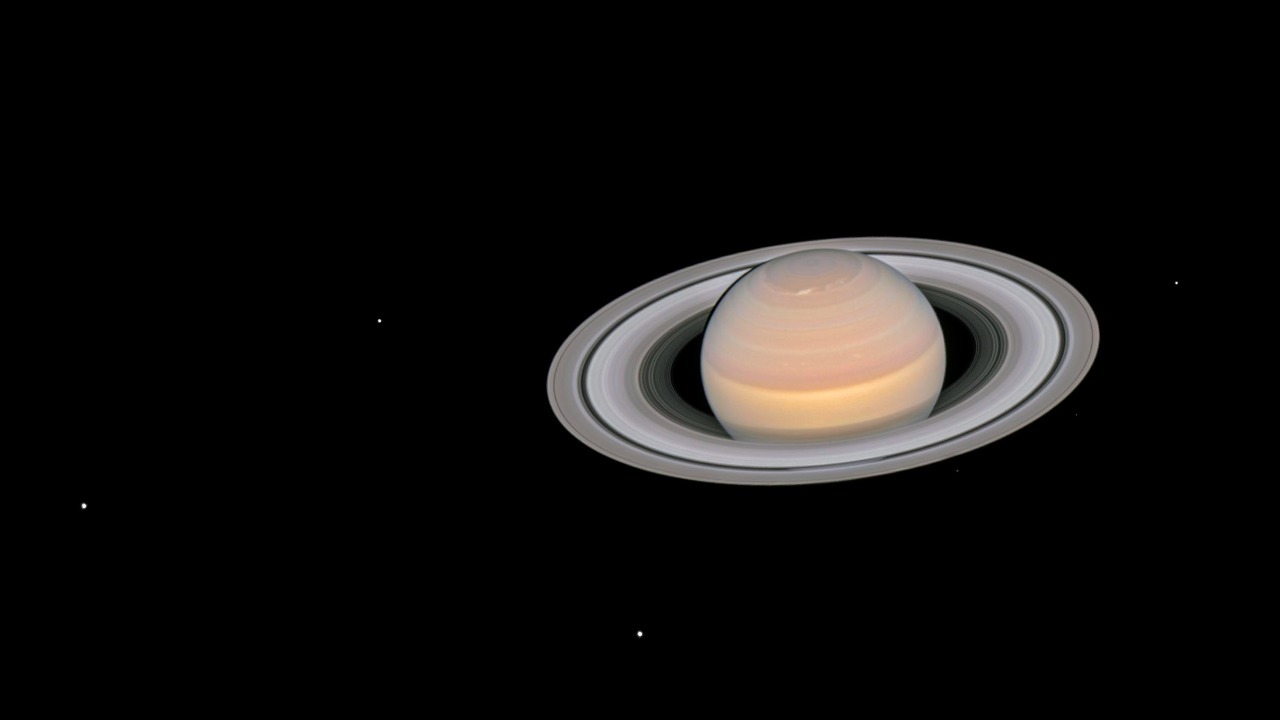
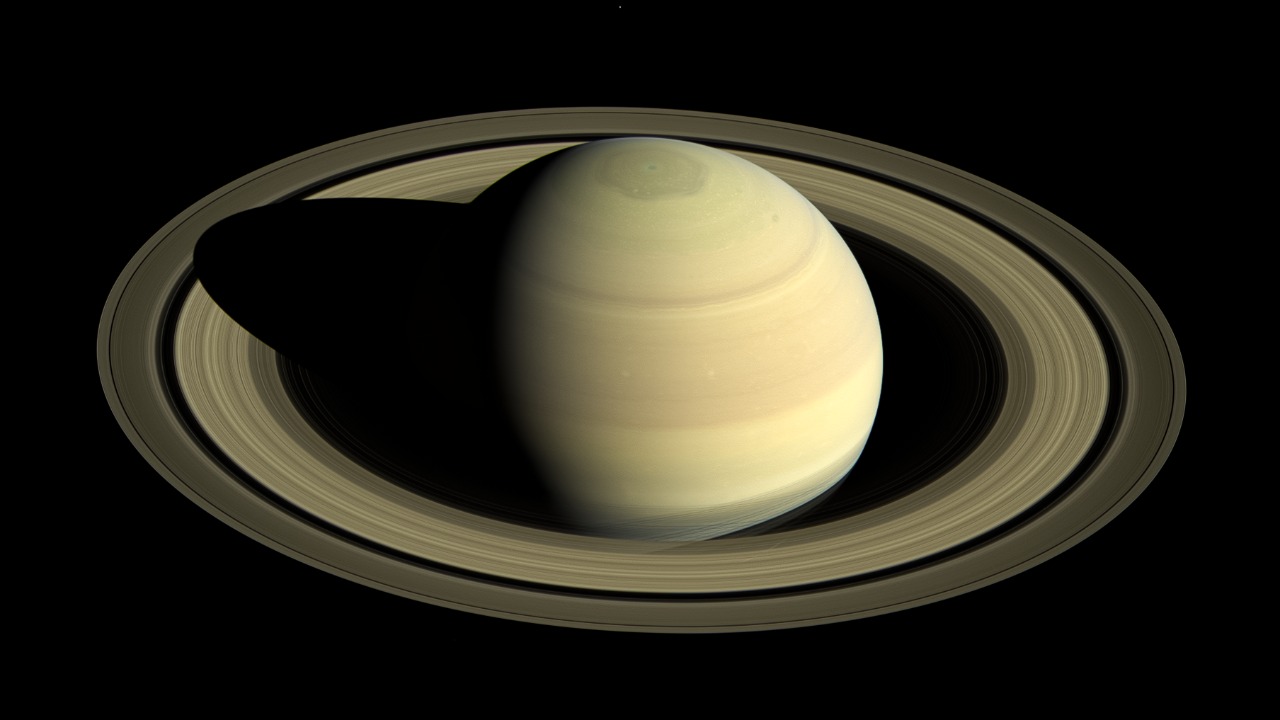
The discovery of Saturn’s hexagon dates back to the early 1980s when the Voyager spacecraft first captured images of this extraordinary feature. This hexagonal cloud pattern, swirling around the planet’s North Pole, has since captivated scientists and fueled continued study by subsequent missions, notably the Cassini mission. These missions have not only confirmed the hexagon’s presence but also highlighted its complexity, keeping it a hot topic in planetary science.
The hexagon itself is a massive structure, approximately 30,000 kilometers across, and it has exhibited a remarkable degree of stability over the decades. This regular, six-sided pattern is unlike anything seen on other planets, and its origins remain a subject of intense study. Scientists believe that the hexagon results from a combination of atmospheric jet streams and fluid dynamics, though the exact mechanisms are still not fully understood. The challenge lies in deciphering how these atmospheric processes can maintain such a stable and distinct geometric shape over time.
James Webb Space Telescope’s Contribution
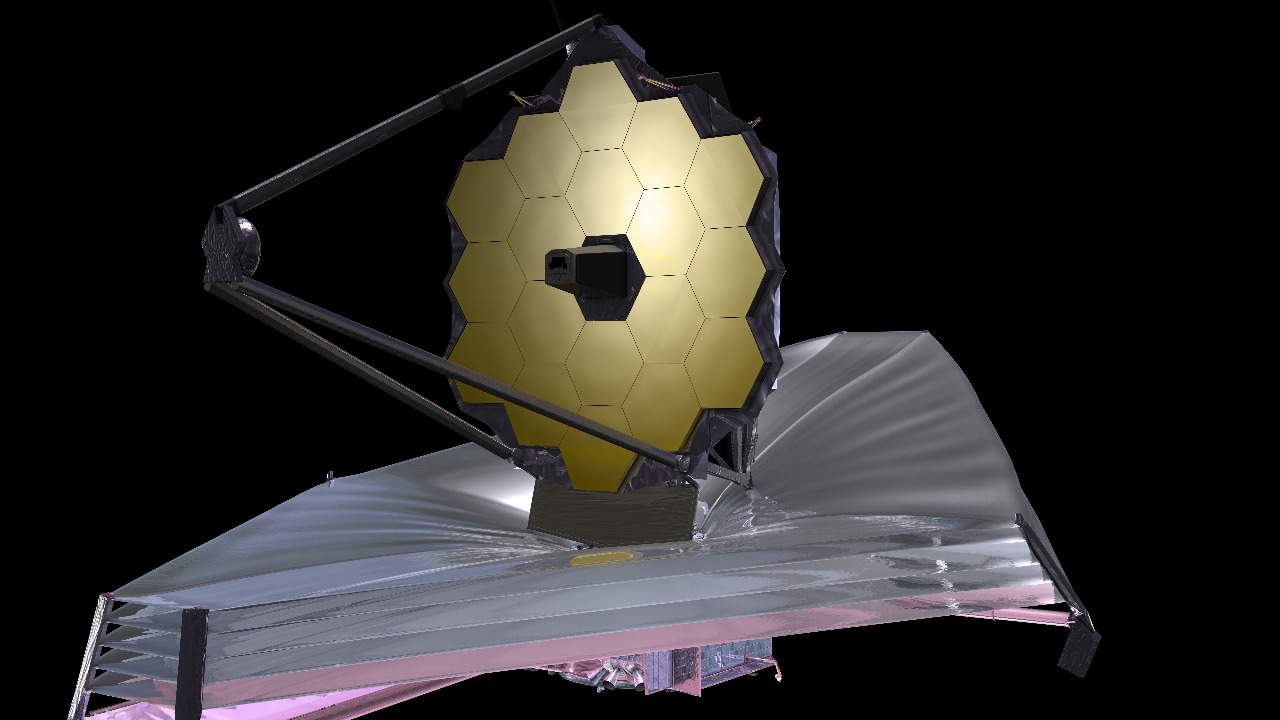
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) represents a significant leap forward in our ability to observe distant celestial phenomena. Equipped with advanced imaging capabilities, it can capture high-resolution images across a range of wavelengths, offering a level of detail previously unattainable. This technological prowess allows the JWST to provide unprecedented insights into Saturn’s atmospheric conditions, surpassing the capabilities of older telescopes.
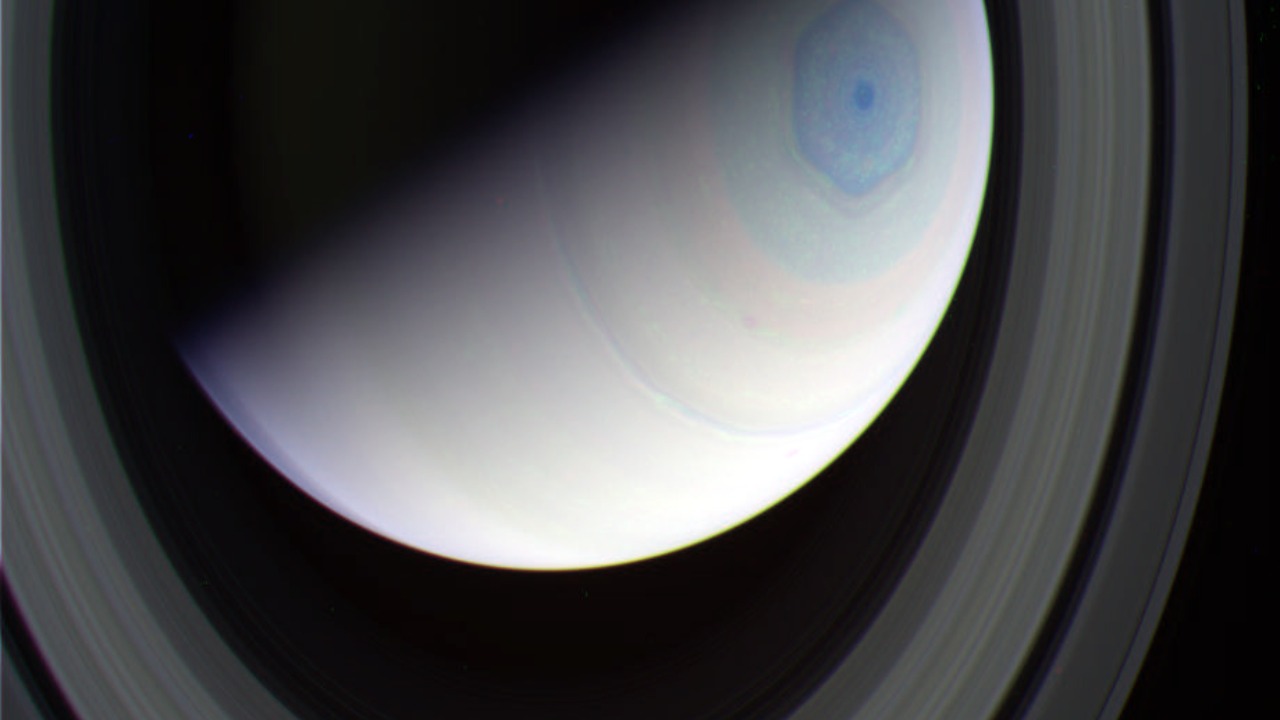
In its recent observations, the James Webb Space Telescope has revealed new intricacies within the hexagonal cloud patterns at Saturn’s North Pole. These images offer a clearer view of the atmospheric dynamics at play, illuminating the complex interactions between Saturn’s jet streams and its overall climate system. The data from JWST not only enhances our understanding of Saturn but also opens the door to revisiting existing theories and possibly developing new ones regarding the gas giant’s atmospheric dynamics.
Scientific Theories and Debates
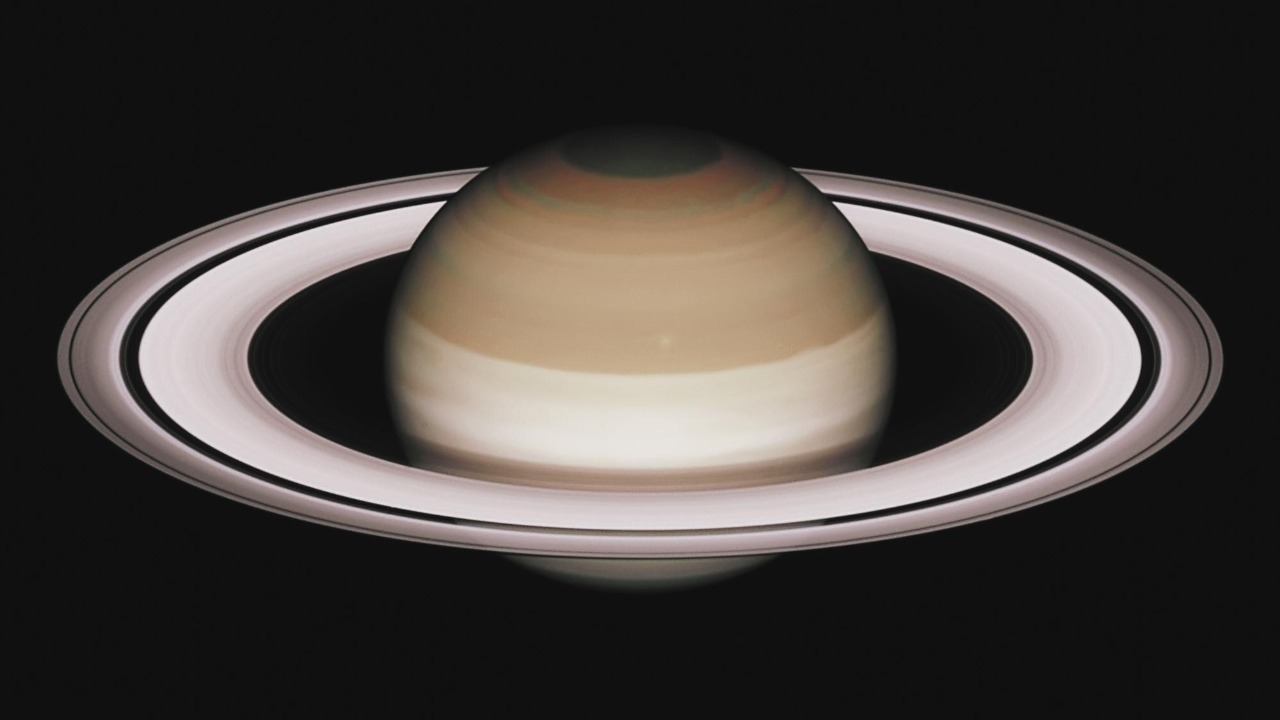

Several theories have been proposed to explain Saturn’s hexagon, with fluid dynamics and atmospheric jet streams being the most prominent. These theories suggest that the hexagon forms due to the interaction of different jet streams flowing at varying speeds, creating standing wave patterns that result in the hexagonal shape. However, the new findings from JWST may prompt a reevaluation of these theories, potentially offering new insights into the hexagon’s origin and persistence.
The scientific community remains divided on some aspects of the hexagon’s formation and stability. While the leading theories provide a framework for understanding the phenomenon, they do not fully account for its long-term stability and precise geometric shape. The latest data from the James Webb Space Telescope introduces new variables into the equation, challenging existing models and inspiring fresh debates among scientists. This ongoing discourse underscores the complexity of planetary atmospheres and the need for continued exploration and study.
Implications for Planetary Science
The insights gained from studying Saturn’s hexagon have broader implications for our understanding of gas giants, both within our solar system and beyond. By unraveling the mysteries of Saturn’s atmospheric dynamics, scientists can apply these findings to other gas giants like Jupiter, potentially identifying similar patterns or phenomena. This knowledge is invaluable as it enhances our comprehension of planetary atmospheres and the forces that shape them.
The potential for discovering hexagonal patterns on exoplanets is an exciting prospect for planetary scientists. As we continue to search for planets beyond our solar system, the lessons learned from Saturn may guide us in identifying and interpreting atmospheric features that could resemble those of the gas giants we are more familiar with. Such discoveries could revolutionize our understanding of exoplanetary atmospheres and the diversity of planetary systems in the universe.
Looking ahead, the observations made by the James Webb Space Telescope pave the way for future research and exploration. Scientists are eager to build on these findings, utilizing upcoming missions and telescopes to delve deeper into the mysteries of Saturn and similar planetary bodies. This continued exploration promises to enhance our knowledge of the solar system and beyond, offering new insights into the dynamic processes that govern planetary atmospheres.