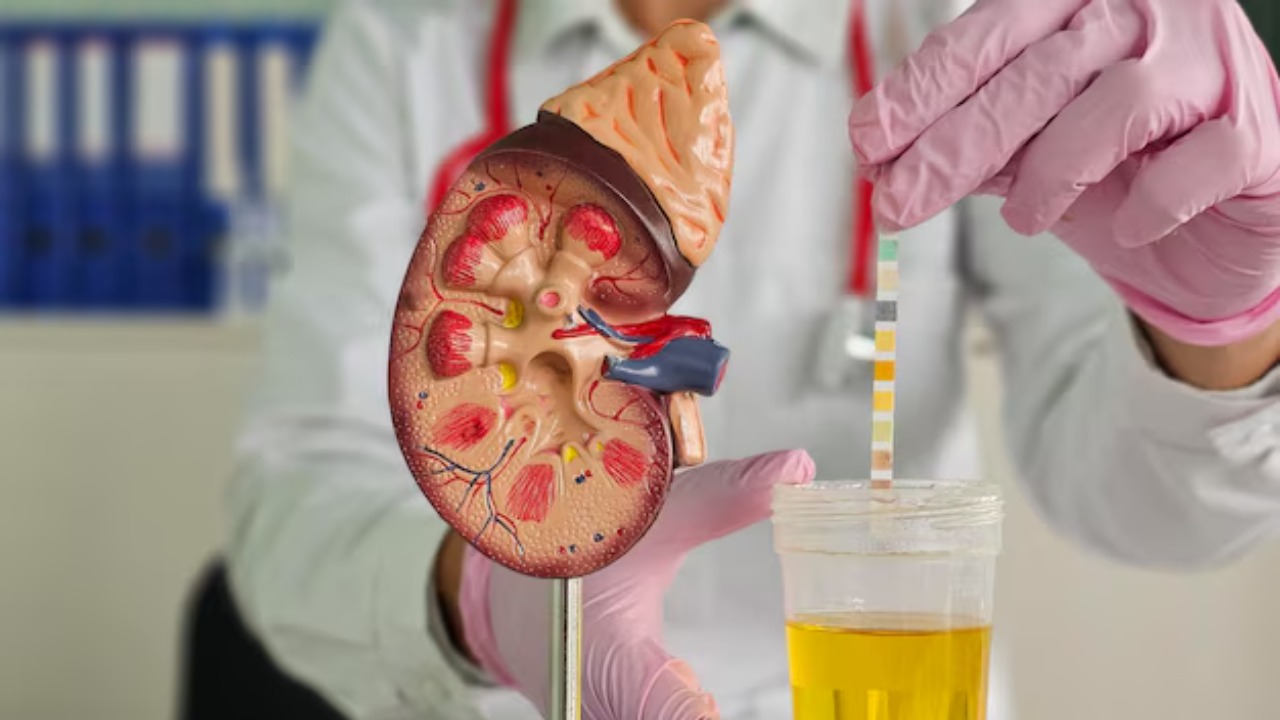
A recent scientific breakthrough has seen lab-grown kidneys successfully functioning in a human trial. This promising development has far-reaching implications for organ transplant procedures and the future of regenerative medicine.
The Science of Lab-Grown Kidneys

Developing kidneys in a lab environment is complex and challenging. It involves the use of a scaffold, typically a decellularized kidney, onto which pluripotent stem cells are seeded. These stem cells, having the ability to develop into any cell type in the body, grow and differentiate into the various cells that make up a functional kidney.
The process is not without its difficulties, however. The exact conditions required for the stem cells to grow and differentiate correctly are still being fine-tuned, and there are challenges in ensuring the lab-grown kidneys have a functional blood supply once transplanted. Despite these challenges, the advancements made in this field are truly groundbreaking.
Human Trial Success

The recent success in the human trial of the lab-grown kidney marks a significant step forward. In the trial, the lab-grown kidney was transplanted into a patient and monitored closely for signs of functionality and rejection. The kidney not only began functioning, but also showed no signs of being rejected by the patient’s body.
Following this success, plans are underway for additional human trials. Although caution is still necessary, this initial success has sparked optimism among researchers and medical professionals, paving the way for further advancements in organ transplantation.
Implications for Kidney Transplants
Kidney transplants currently face several challenges, not least of which is a critical shortage of donors. Thousands of patients are left waiting for a kidney transplant, with many sadly passing away before a suitable organ becomes available. Lab-grown kidneys could potentially solve this pressing issue, providing a reliable and readily available source of transplantable kidneys.
Moreover, lab-grown kidneys could potentially reduce the risk of transplant rejection. Since the kidneys are grown from the patient’s own stem cells, the body is less likely to recognize them as foreign and launch an immune response. This could revolutionize transplant medicine, significantly improving patient outcomes.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine

The success of lab-grown kidneys holds promise for the broader field of regenerative medicine. If kidneys can be grown in a lab, it stands to reason that other organs might also be grown in a similar way. This could potentially revolutionize the treatment of numerous diseases, offering hope to millions of patients worldwide.
However, this development also raises several ethical and practical considerations. For instance, the process of growing organs in a lab is resource-intensive and currently very expensive. There are also ethical questions around the use of stem cells, and potential concerns about the long-term safety and efficacy of lab-grown organs. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of this approach are undeniable.
Public and Medical Reception

The public reaction to this scientific breakthrough has been largely positive, with many hailing it as a major step forward in medicine. However, there is also a degree of caution, with some expressing concerns about the potential for misuse and the need for robust regulation.
The medical community has also welcomed this development, recognizing its potential to significantly improve patient outcomes. However, they emphasize the need for further research and rigorous clinical trials to ensure the safety and effectiveness of lab-grown organs. The potential societal impacts of widespread organ growth and transplantation are profound, and careful thought and planning will be needed to navigate these new waters.
Overall, the successful human trial of a lab-grown kidney represents an exciting step forward in the field of regenerative medicine. It offers hope for the future of organ transplantation and holds the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes. As research continues, we can look forward to further advancements in this exciting and rapidly evolving field.