
The food industry is witnessing a significant shift as lab-grown meat begins to occupy retail shelves, surprisingly at half the cost of conventional beef. This revolutionary development derives from the science of cellular agriculture and has far-reaching implications for the meat industry, the environment, and consumer perception.
The Science of Lab-grown Meat

Lab-grown meat, often referred to as cultivated meat, is produced using advanced scientific methods that involve the culturing of animal cells in a lab setting. The process begins with obtaining a small sample of animal cells, which are then nurtured in a nutrient-dense medium that encourages their growth and proliferation. Over time, these cells develop into muscle tissue, which is essentially meat. This technique, known as cellular agriculture, allows the production of meat without the need for traditional animal farming.
From a nutritional standpoint, lab-grown meat could potentially mimic, or even surpass, the nutritional value of conventional meat. This is because the production process can be controlled to optimize the nutrient content of the meat. However, there are also concerns over potential drawbacks, such as the need for antibiotics during the production process and the challenge of replicating the complex structures and flavors of traditional meat.
Economic Implications
Despite the high initial costs of developing lab-grown meat technologies, the production process has the potential to be more cost-effective than traditional meat production. The reduced requirements for land, water, and feed, along with the shorter production cycle, contribute to the lower costs. As a result, lab-grown meat has hit the stores at approximately half the price of traditional beef, reshaping the meat market’s pricing dynamics.
However, the rise of lab-grown meat also poses economic challenges for traditional meat industries. Job losses in livestock farming are a major concern, but at the same time, new job opportunities may arise in the cellular agriculture sector. The economic implications of this shift are vast and complex, requiring careful analysis and policy-making.
Environmental Impact
The environmental footprint of lab-grown meat is significantly smaller than that of traditional livestock farming. Livestock farming is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. In contrast, lab-grown meat production requires less land, water, and energy, and produces fewer greenhouse gases, making it a more sustainable option.
Furthermore, lab-grown meat could help resolve some of the pressing issues related to environmental degradation, climate change, and animal welfare. For instance, switching to lab-grown meat could reduce the need for deforestation for pasture, thereby preserving biodiversity. Additionally, it could address animal welfare concerns by eliminating the need for factory farming.
Consumer Reception and Market Expansion
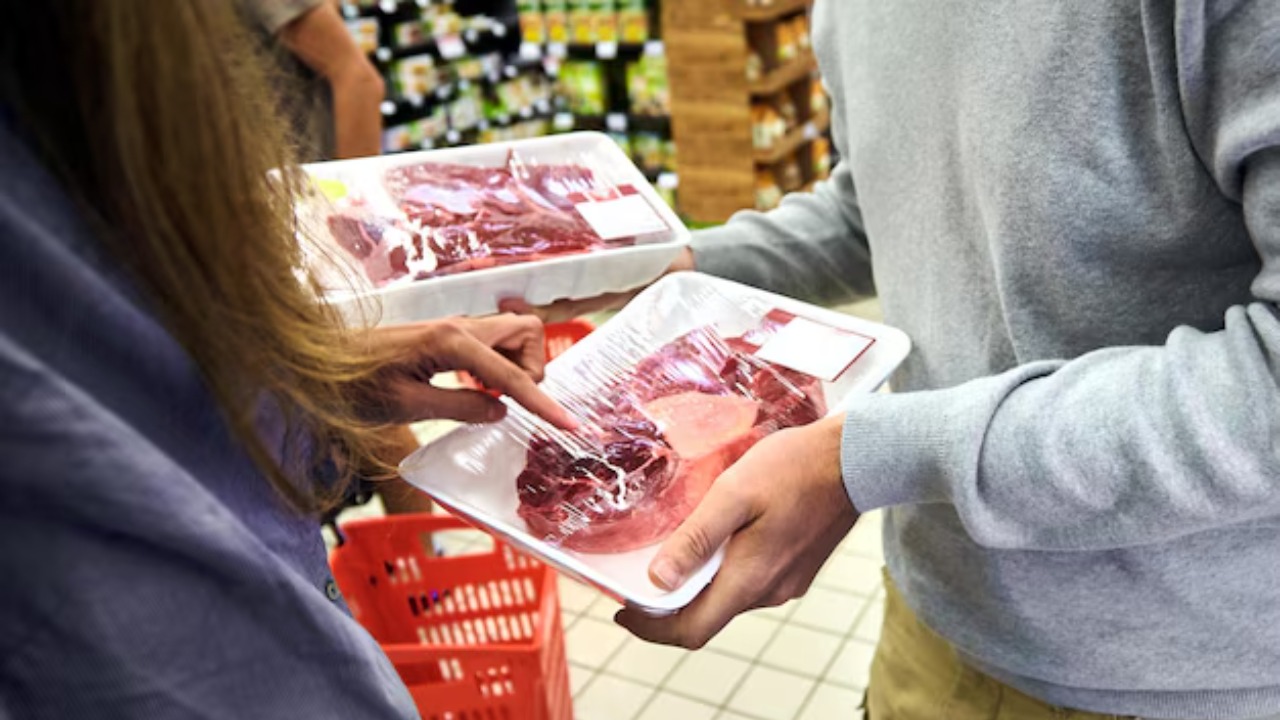

The consumer response to lab-grown meat has been mixed. While some consumers appreciate the ethical and environmental benefits, others are wary about the unnatural production process and potential health implications. However, early market analysis suggests that a significant proportion of consumers are willing to try lab-grown meat and may even be willing to pay a premium for it, indicating a promising future for the industry.
Currently, the market for lab-grown meat is still in its infancy, but there is potential for rapid expansion. For example, companies like Aleph Farms have recently received significant funding for their lab-grown meat technologies, indicating a growing interest from investors. Additionally, the market is also expanding into new areas, such as lab-grown pet food.
Legal and Ethical Considerations

The legality of lab-grown meat is a complex issue, with regulations varying from one region to another. While some countries have begun to draft regulations for lab-grown meat, others are yet to recognize it as a legitimate food product. Legal challenges related to labeling, safety testing, and intellectual property are also expected.
From an ethical perspective, lab-grown meat raises several considerations. On one hand, it could significantly reduce animal suffering and contribute to food security. On the other hand, it could disrupt traditional farming communities and raise questions about cultural and religious acceptability. As the lab-grown meat industry continues to evolve, these legal and ethical issues will require careful consideration and thoughtful dialogue.