
The intersection of gemology and quantum physics may seem unlikely, but lab-grown diamonds are carving out a unique and promising niche in the realm of quantum computing. This journey takes us from the intricacies of diamond engineering to the future of quantum technology, exploring both the potential and the challenges of this fascinating development.
The Science Behind Lab-Grown Diamonds and Quantum Computing

Lab-grown diamonds, also known as synthetic or cultured diamonds, are not mere simulacra of their natural counterparts. They possess the same physical and chemical properties as mined diamonds, making them ideal for certain technological applications. What makes these diamonds particularly suitable for quantum computing are their unique quantum properties. These properties, in turn, create the opportunity for diamond-based quantum bits or ‘qubits’ – the fundamental units of quantum information.
A specific type of impurity in these diamonds, called a nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center, can be manipulated and measured at room temperature, which is a significant advantage over other quantum systems. This process forms the basis for creating qubits, allowing lab-grown diamonds to overcome some of the challenges inherent in traditional quantum computing methods. For a deep dive into the science behind it, refer to this research article.
Advancements in Diamond-Based Quantum Computers

The recent breakthroughs in diamond-laced computer chips are reshaping the landscape of quantum computing. These advancements have the potential to increase both the speed and power of quantum computers, as detailed in this Live Science article. One of the pioneers in this field is Quantum Brilliance, a company striving to build the world’s first mobile quantum computer using lab-grown diamonds.
Further potential advancements lie in the domain of diamond-based power electronics, which could significantly impact the aerospace industry by enabling more efficient systems with reduced size and weight. For more information on the potential impact in the aerospace industry, check out this article.
Challenges and Limitations in Diamond-Based Quantum Computing
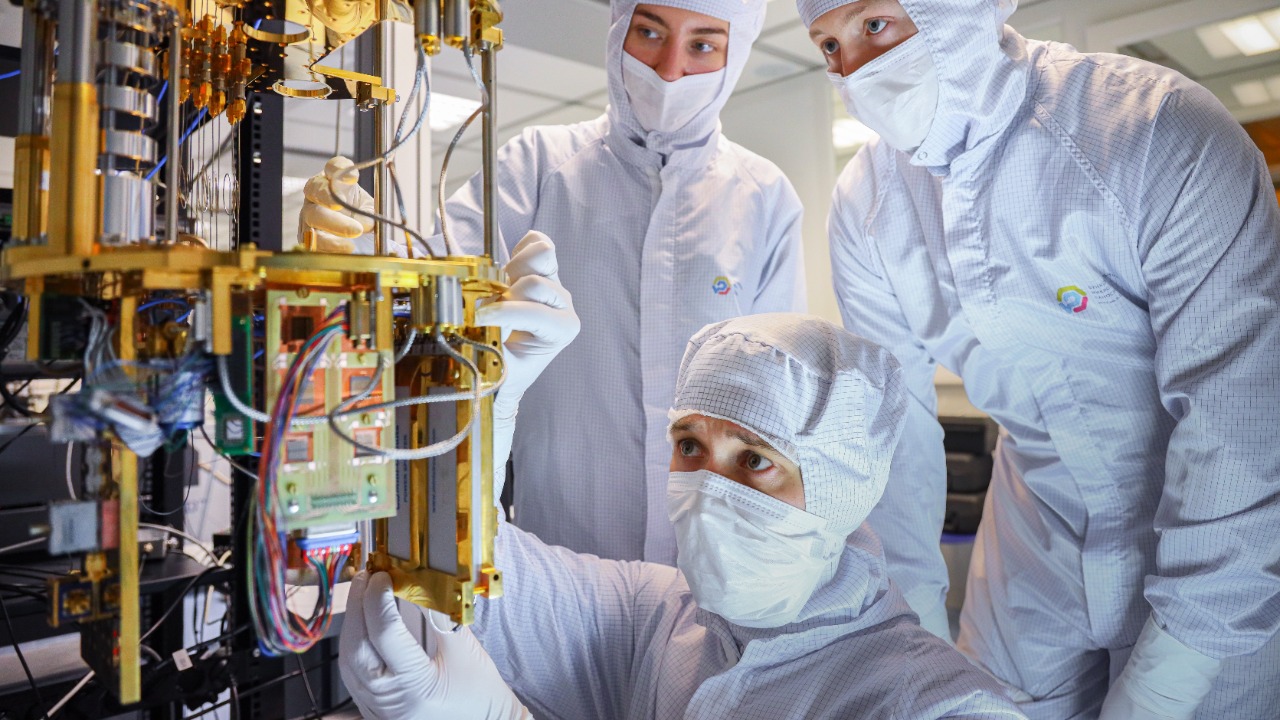
Despite the promising prospects, diamond-based quantum computing is not without its challenges. On the technical side, producing and implementing diamond-based quantum computers pose a plethora of difficulties. These range from creating high-quality synthetic diamonds with the correct impurities to refining the control and measurement of the qubits.
There are also questions regarding the economic feasibility of diamond-based quantum computers. High production costs and potential limitations of diamond technology in quantum computing are significant hurdles to overcome. However, as with any nascent technology, these challenges present opportunities for innovation and refinement in the field.
Future Implications and Potential of Diamond-Based Quantum Computing
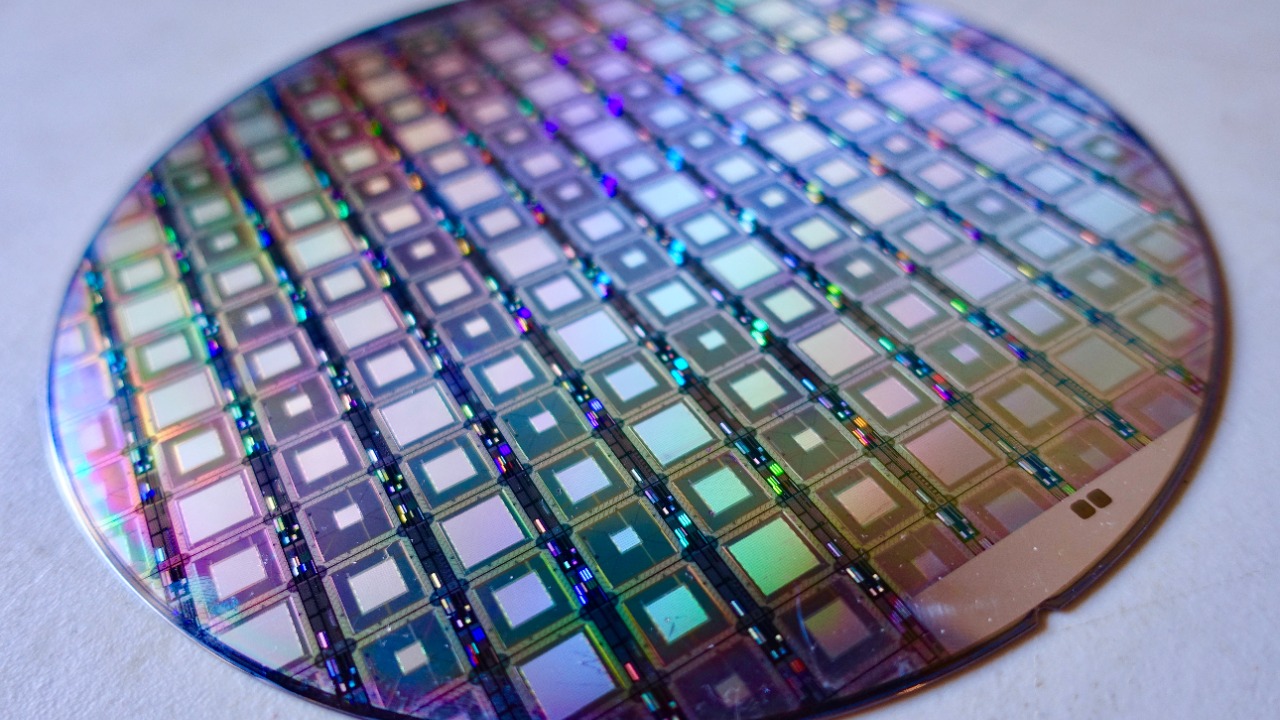
Diamond-based quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize numerous industries. In healthcare, they could enable faster and more accurate diagnostics. In finance, they could provide superior risk assessment and fraud detection. In logistics, they could optimize routes and inventory management. This technology could also play a critical role in advancing artificial intelligence and machine learning, opening up new avenues for exploration and development.
One of the standout aspects of diamond-based quantum computing is the potential for increased accessibility and portability. Companies like Quantum Brilliance are working to make quantum computers smaller, more robust, and more user-friendly, which could democratize access to this powerful technology. For more on Quantum Brilliance’s work, you can read this article.
The Ethical and Environmental Impact of Lab-Grown Diamonds

Lab-grown diamonds have a significant environmental advantage over mined diamonds. Mining diamonds is a destructive process that can devastate ecosystems, whereas growing diamonds in a lab has a much smaller environmental footprint. Consequently, the increased use of lab-grown diamonds in quantum computing could contribute to a reduction in diamond mining and its associated environmental harm.
On the ethical front, the use of diamond technology in quantum computing raises some interesting questions. For instance, how will this new demand for lab-grown diamonds affect the global diamond industry and the communities that rely on it? And how can we ensure that this technology is developed and used responsibly? These are complex issues that will require thoughtful consideration as diamond-based quantum computing continues to evolve.