
The recent unveiling of a novel self-recycling polymer, capable of maintaining its integral strength even after numerous recycling operations, holds immense promise for environmental sustainability and waste reduction. This cutting-edge advancement might herald a transformative era for the plastics sector, markedly minimizing the detrimental effects of plastic refuse.
Understanding the Concept of Self-Recycling Polymers

Self-recycling polymers, as the name implies, are advanced materials capable of recycling themselves. The concept of self-recycling polymers was introduced in the late 20th century, but recent research has led to significant advancements in this field. These polymers undergo a process known as self-recycling, wherein the polymer chains break down and reform, effectively allowing the material to “recycle” itself.
Self-recycling polymers play a crucial role in sustainability and waste reduction. With the ever-increasing global plastic waste crisis, these polymers offer a viable solution for reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and oceans. They also lessen the demand for virgin plastic production, thereby reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
Key Features of the New Polymer
The new polymer is a remarkable material that retains its full strength after undergoing multiple recycling cycles. At a molecular level, the polymer chains are designed to disassemble under specific conditions and then reassemble, maintaining the original material properties. This design allows the polymer to retain its strength, unlike traditional polymers that weaken with each recycling cycle.
Compared to conventional polymers, this new material exhibits unique characteristics. For instance, it can self-recycle without the need for external chemical agents or catalysts. Moreover, the recycling process does not produce any harmful by-products, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional polymer recycling methods.
Scientific Breakthrough in Polymer Research
The discovery of this self-recycling polymer is attributable to the tireless efforts of scientists at Bournemouth University. Using a combination of organic chemistry and material science principles, the research team developed a polymer with strategically placed weak bonds that allow for controlled disassembly and reassembly.
The research findings, published in the RSC Advances journal, highlight the polymer’s ability to maintain its mechanical properties even after multiple recycling cycles. This breakthrough opens new avenues for the development of sustainable materials, with potential applications spanning various industries.
Implications for the Plastics Industry and the Environment
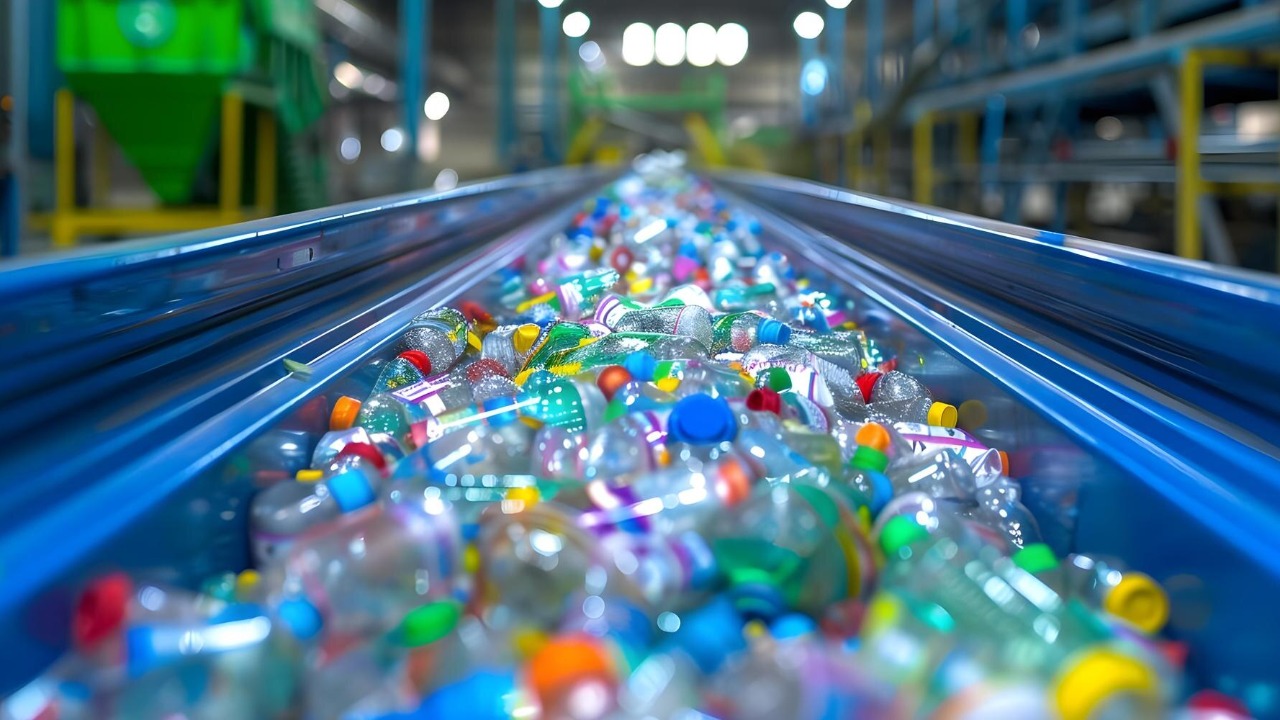

The introduction of this self-recycling polymer could have a profound impact on the plastics industry. By offering a material that retains its full strength after recycling, manufacturers could reduce their reliance on virgin materials, leading to significant cost and energy savings. Furthermore, the potential to recycle products at the end of their life cycle could drastically reduce the amount of plastic waste entering the environment.
From an environmental perspective, the benefits are equally substantial. By reducing the need for new plastic production, the technology could significantly lower carbon emissions and energy consumption. However, implementing this new technology is not without challenges. For example, scaling up production to meet industrial demand and managing the lifecycle of these products in existing waste infrastructure are potential hurdles to overcome.
The Future of Self-Recycling Polymers
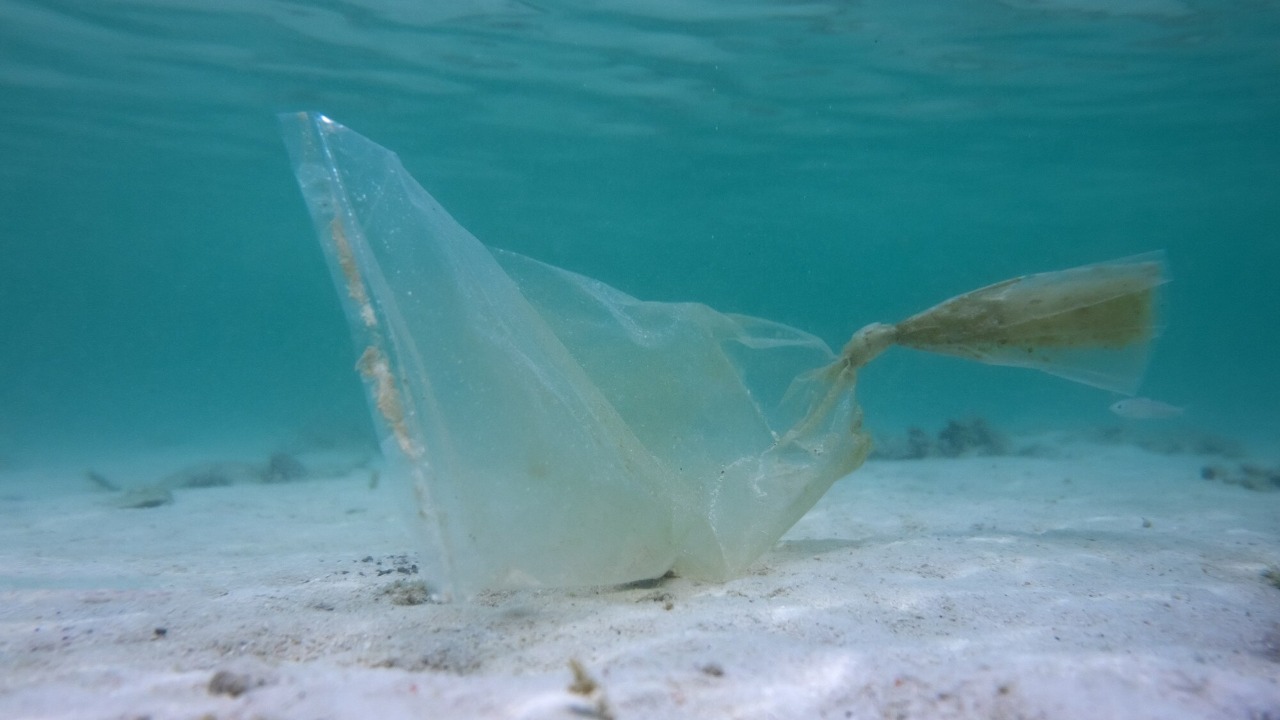

The future holds immense promise for self-recycling polymer technology. With ongoing research and development, we might see further innovations that improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these materials. These advancements could open up new applications and markets for self-recycling polymers such as in packaging, automotive, and construction industries.
Furthermore, self-recycling polymers could play a vital role in achieving global sustainability goals. By promoting a circular economy model, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible, these polymers could help us move towards a more sustainable future. However, for this to happen, continued research, collaboration among stakeholders, and supportive policies are essential.