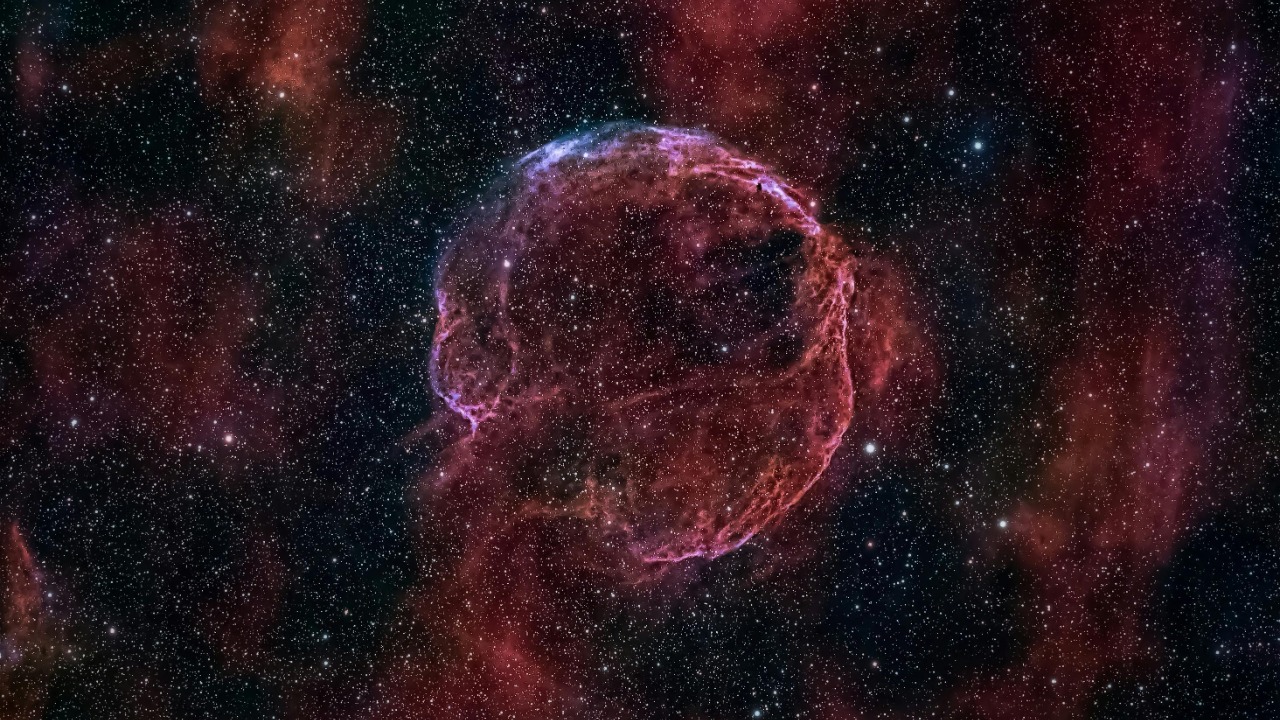

In a significant breakthrough, astronomers have recently discovered a “ghost star” nestled within the remnants of a supernova. This mesmerizing discovery provides fresh perspectives on the life cycle of stars and the enigmatic phenomena of supernovas.
Understanding Supernovas
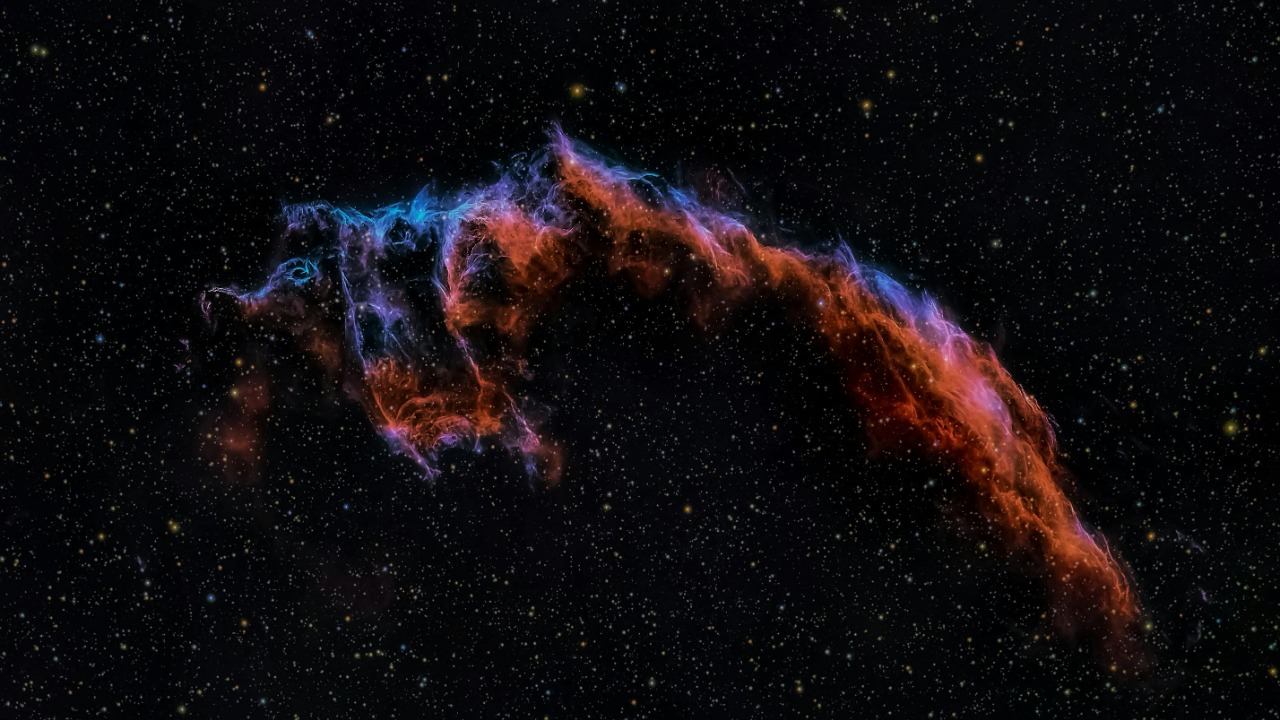

A supernova is a powerful explosion of a star that occurs towards the end of its life cycle. This catastrophic event releases immense amounts of energy, outshining all the stars in its galaxy combined. The explosion is so powerful that it disperses heavy elements throughout the universe, serving as a key mechanism for cosmic chemical enrichment.
Stars, like our Sun, go through a life cycle that ultimately leads to a supernova explosion. During their lifetime, stars undergo nuclear fusion, converting hydrogen into helium. As they exhaust their hydrogen fuel, they begin burning heavier elements, leading to instability and eventually causing a massive explosion known as a supernova.
The Discovery of the “Ghost Star”
The recent detection of the “ghost star” was made possible by the diligent work of astronomers and the use of sophisticated instruments, notably the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope. This observatory, located in Chile, houses some of the world’s most advanced telescopes, enabling astronomers to explore the cosmos in unprecedented detail. Using these tools, they were able to peer into the remnants of a supernova and discover the hidden “ghost star”.
The term “ghost star” refers to a neutron star hidden inside a supernova remnant. After the explosion of a supernova, the core of the star often remains, collapsing under its gravity to form a neutron star. If this neutron star is encased within the remnants of the supernova, it is termed as a “ghost star”. The recent discovery of such a star is an extraordinary achievement in the field of astronomy.
The Significance of the “Ghost Star”
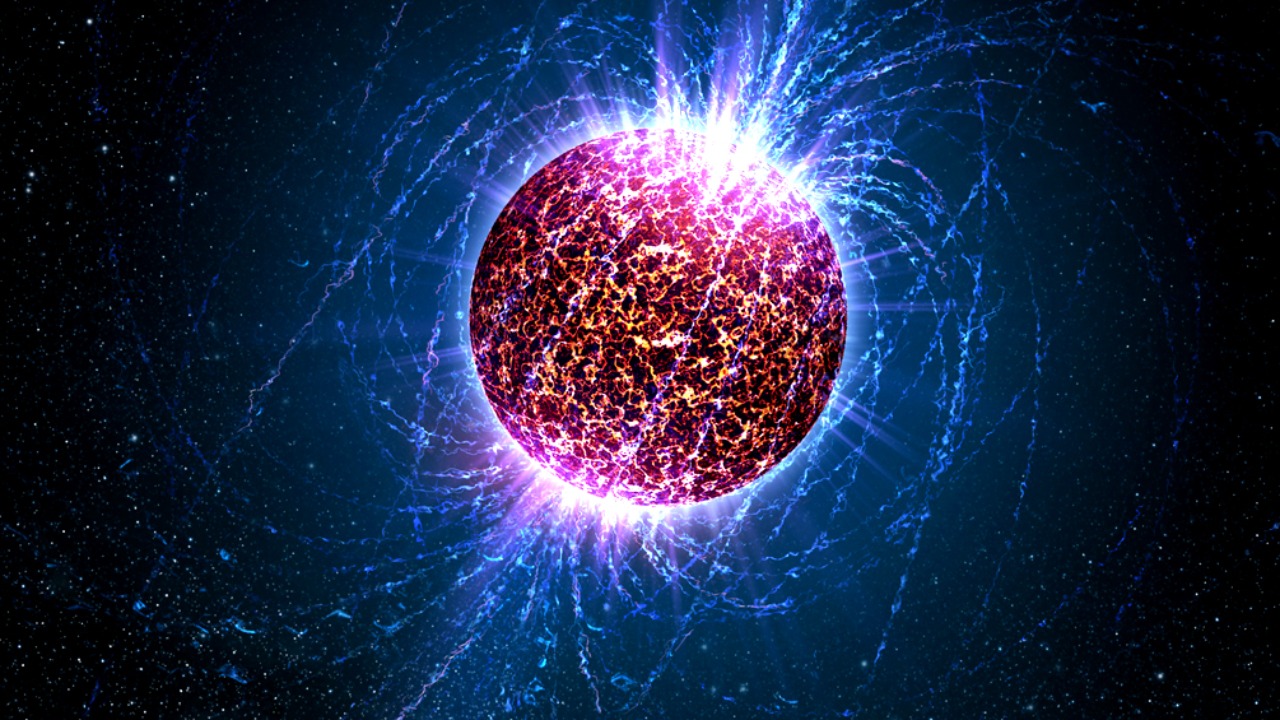

The discovery of the “ghost star” is an important milestone in astronomical research. Neutron stars, despite their tiny size, are incredibly dense and have extreme physical conditions. Studying them can provide valuable insights into the nature of matter and the universe. Moreover, the detection of a “ghost star” is a testament to the advancements in astronomical technology and techniques.
However, detecting neutron stars is not an easy task. They are incredibly small and faint, making them difficult to spot, especially when hidden inside a supernova remnant. Despite these challenges, the recent detection has unlocked new scientific potential, paving the way for more discoveries in the future.
Neutron Stars and Their Characteristics
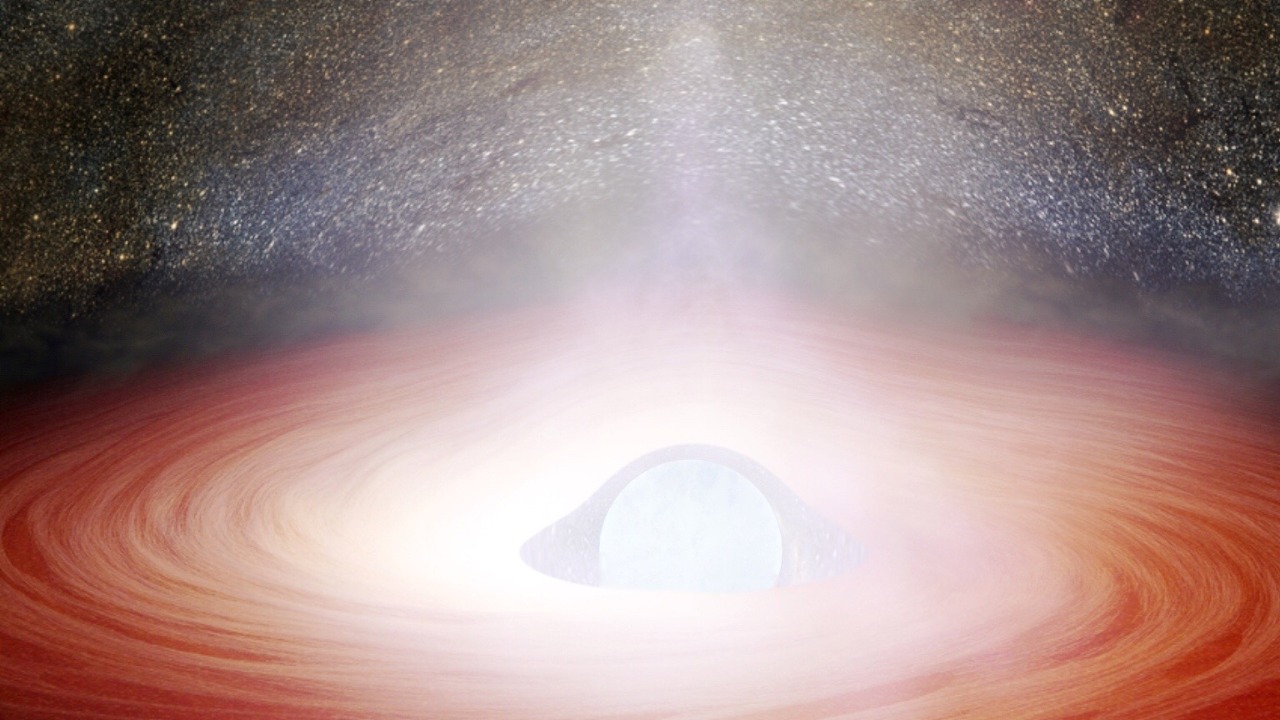

A neutron star is a celestial object that forms from the remnants of a massive star after it explodes as a supernova. Despite being only about 20 kilometers in diameter, a neutron star is extremely dense, with a mass greater than that of our Sun. They possess unique features such as rapid rotation and intense magnetic fields.
Understanding the relationship between neutron stars and supernovas is critical in astronomy. The explosion of a supernova leads to the formation of a neutron star, and studying these “ghost stars” can provide insights into the processes involved in their creation. The recent detection of the “ghost star” is a significant step forward in this research field.
Future Perspectives in Star Studies
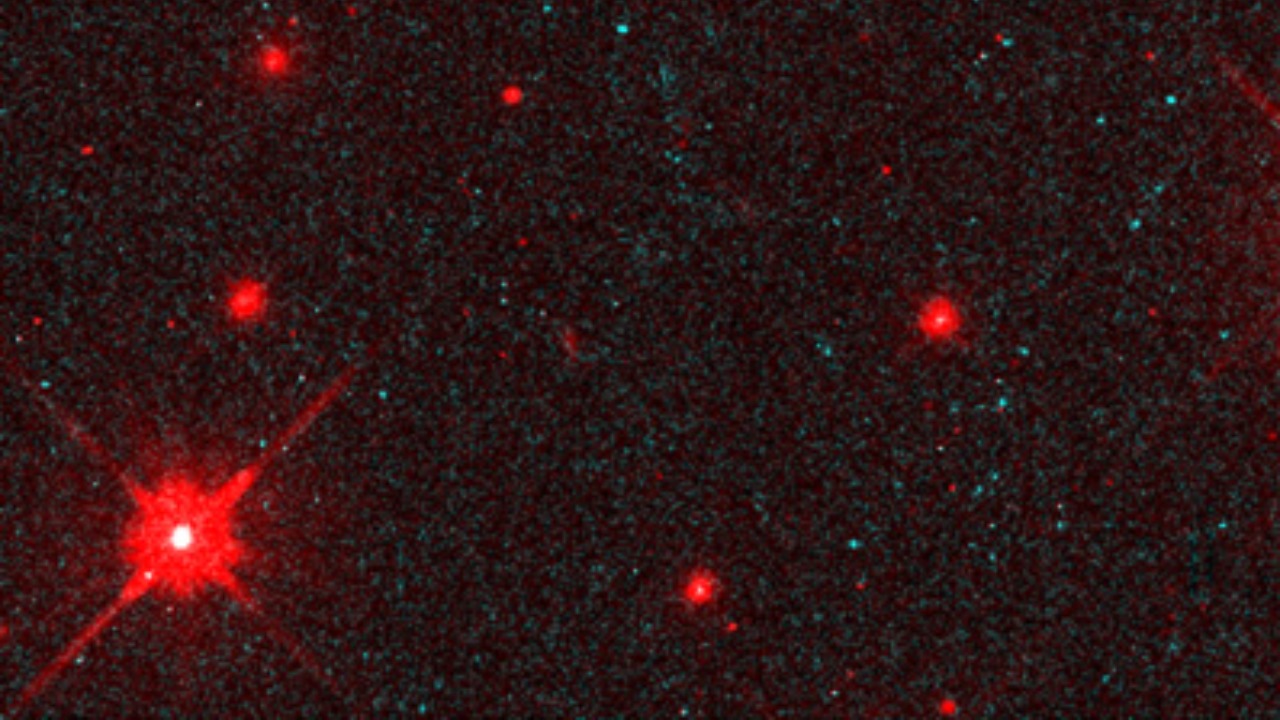

The exciting discovery of the “ghost star” has opened new avenues for further research. As our understanding of these celestial bodies increases, so does our capacity to develop novel astronomical technologies. Additionally, this discovery has sparked interest in the scientific community, encouraging more extensive research into neutron stars and supernovas.
Moreover, this breakthrough has highlighted the potential for future exploration and understanding of the universe. As technology advances and our knowledge expands, we can look forward to more discoveries that will continue to challenge our understanding of the cosmos. The discovery of the “ghost star,” for instance, has already led to the first-ever detection of a star core, further unravelling the mysteries of star death and rebirth.