
Breaking away from conventional methods, NASA has recently unveiled an ambitious and unique plan to “harpoon” an asteroid. This innovative approach marks a significant stride in the realm of space exploration, promising a deeper understanding of asteroids and showcasing the advancements in space technology.
The Concept of Harpooning an Asteroid

The concept of harpooning an asteroid is a departure from the traditional touch-and-go technique used in previous asteroid missions. Instead of landing on the asteroid, the spacecraft deploys a harpoon to capture a sample. This method eliminates the risks associated with landing on an unpredictable and unstable asteroid surface. A similar idea was explored in a study conducted back in 2011.
Previous missions such as the Hayabusa and the Osiris-Rex have attempted to interact with asteroids in different ways. For instance, the Hayabusa mission used a small projectile to kick up particles from the asteroid’s surface, while the Osiris-Rex extended a sampling arm to collect the regolith. However, the harpooning concept offers a more controlled and safer way to retrieve samples.
Details of NASA’s Harpoon Asteroid Mission

The primary goal of NASA’s mission is to obtain and return samples from an asteroid. These samples are invaluable as they hold the keys to understanding the formation and evolution of our solar system. The choice of the asteroid is based on several factors, including its size, spin rate, and composition. The asteroid must also follow an orbit that allows the spacecraft to return to Earth within a reasonable timeframe.
The exact timeline of the mission is yet to be finalized. Various stages of the mission such as the design and development of the spacecraft, its launch, the harpooning process, and the journey back to Earth will span over several years. The completion of the mission is expected to provide a wealth of data for scientists to analyze and interpret.
Technology Behind the Harpoon

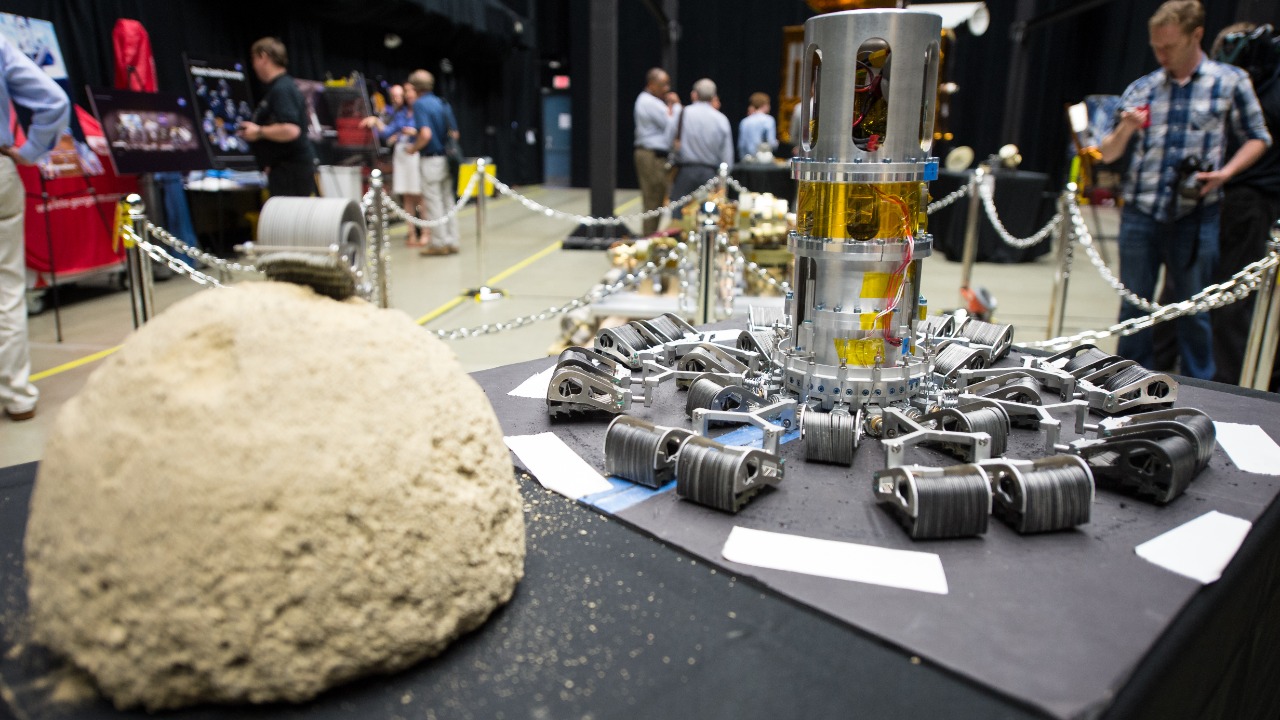
The asteroid harpoon is a marvel of engineering and technology. It is designed to penetrate the surface of the asteroid and collect a substantial amount of material. The design is influenced by the successful Comet Harpoon mission by NASA. The harpoon is equipped with a chamber that closes after the sample collection, ensuring the material does not escape during the return flight.
Developing the harpoon technology presented a unique set of challenges. The harpoon had to be lightweight yet robust enough to withstand the impact with the asteroid. Additionally, it needed to function in the harsh and unpredictable conditions of space. Despite these hurdles, NASA’s engineers have managed to create a tool that is expected to revolutionize asteroid exploration.
Implications of the Harpoon Mission
The successful execution of the mission will significantly enhance our understanding of asteroids and the early solar system. The collected samples will provide insights into the materials that contributed to the formation of planets and possibly life on Earth. They could even offer clues about the potential for life on other planets.
The mission also has profound implications for future space exploration. The harpoon technology could be used to divert potentially hazardous asteroids away from Earth, playing a crucial role in planetary defense. However, it is not without controversies. Some experts express concerns over the ethical and legal implications of asteroid missions, particularly regarding the commercial exploitation of asteroid resources.
The Future of Asteroid Missions

NASA has an array of plans for future asteroid missions. The success of this mission may pave the way for more ambitious ventures, such as sending human missions to asteroids. The harpoon technology is expected to play a vital role in these future missions, potentially becoming a standard tool for asteroid interaction.
Apart from harpooning, NASA is also considering other innovative approaches for asteroid exploration. For instance, the Asteroid Redirect Mission planned to capture an asteroid and bring it into the lunar orbit for study. Although the mission was eventually cancelled, it represented a bold new approach towards asteroid exploration. As we venture deeper into space, we can expect even more innovative and daring missions in the future.