Researchers at Rice University have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of quantum physics, unveiling a powerful quantum interference effect. This significant advancement involves manipulating quantum states in superconducting materials, holding promise for the future of quantum computing and sensing technologies.
The Discovery of Quantum Interference at Rice
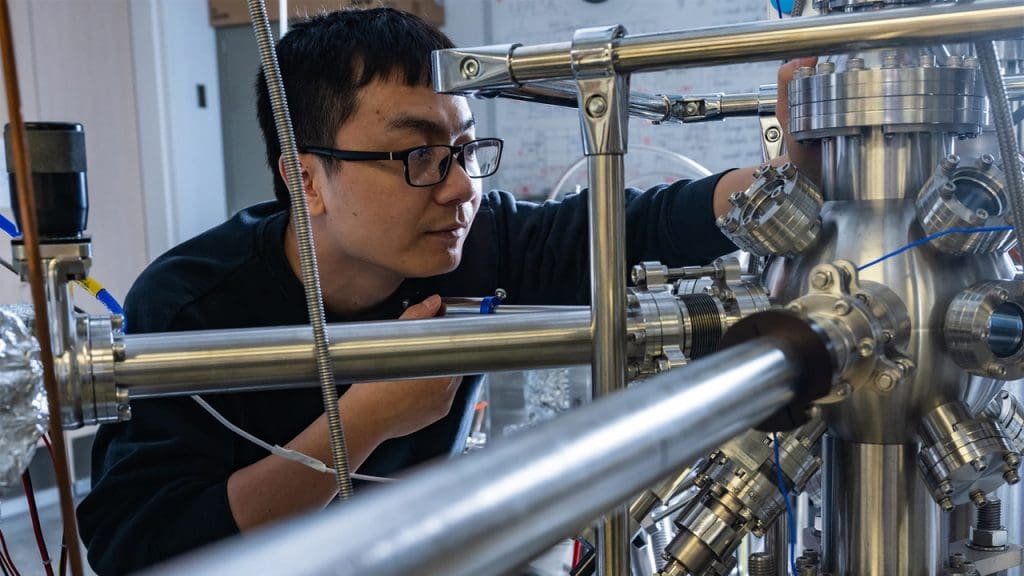

At the heart of this discovery is the research team’s innovative approach to exploring quantum interference. By utilizing an intricate experimental setup, they employed superconducting materials known for their zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields. These materials, when cooled to ultra-low temperatures, exhibit quantum properties that are typically unobservable in ordinary conditions. The team meticulously observed quantum interference patterns by directing particles through superconducting circuits, effectively creating a scenario where particles could simultaneously exist in multiple states.
The team’s findings have profound implications. By analyzing the behavior of quantum particles within these materials, they have not only expanded our understanding of quantum mechanics but also challenged existing theories. The observed quantum interference provides new insights into the behavior of quantum particles, specifically how they interact and influence each other in superconducting states. This could potentially lead to new models that better describe the quantum world, pushing the boundaries of what we know about the fundamental laws of physics.
Implications for Quantum Computing
The enhancement of quantum bits, or qubits, through interference is a particularly exciting aspect of this discovery. Qubits are the fundamental units of information in quantum computing, analogous to the bits used in classical computing. However, qubits are notoriously unstable, often losing coherence due to environmental interference. This new understanding of quantum interference could significantly improve qubit stability and coherence, paving the way for more reliable quantum computers that can perform complex calculations far beyond the reach of current technology.
Moreover, the discovery opens avenues for advancements in quantum algorithms and error correction techniques. By leveraging the principles of quantum interference, researchers can develop new algorithms that capitalize on the unique properties of quantum mechanics. These could lead to more efficient problem-solving methods and strategies to reduce computational errors, a critical challenge in the development of practical quantum computers.
Applications in Quantum Sensing
Beyond computing, the implications of enhanced quantum interference extend into the realm of quantum sensing. Quantum sensors, which exploit quantum states to measure physical quantities with extreme precision, stand to benefit significantly from this research. The improved understanding and control of phonon interference—the quantum vibrations within materials—can lead to the development of more sensitive sensors. Such advancements could revolutionize fields like medical imaging, where early detection and accurate diagnostics are crucial, as well as environmental monitoring, where precise measurements are vital for assessing ecological changes.
The role of quantum interference in advancing quantum communication technologies is another promising area. By exploring the potential for creating more secure communication channels through quantum entanglement and information transfer, researchers can enhance the security of data transmission. This could lead to breakthroughs in protecting sensitive information, an ever-growing concern in our increasingly digital world.
Future Research Directions

Despite these promising developments, several challenges and open questions remain in the field. Technical hurdles, such as maintaining quantum coherence over extended periods and scaling up quantum systems, continue to pose significant obstacles. Additionally, there are theoretical challenges that need addressing to fully harness the potential of quantum interference. This underscores the need for further research and exploration to unlock the full capabilities of quantum technologies.
Collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary research are essential in overcoming these challenges. The integration of expertise from physicists, engineers, computer scientists, and other disciplines will be crucial in pushing the boundaries of quantum technology. By fostering an environment of collaboration, these diverse fields can come together to tackle the complex problems that lie ahead, ultimately driving the innovation needed to realize the full potential of quantum interference.