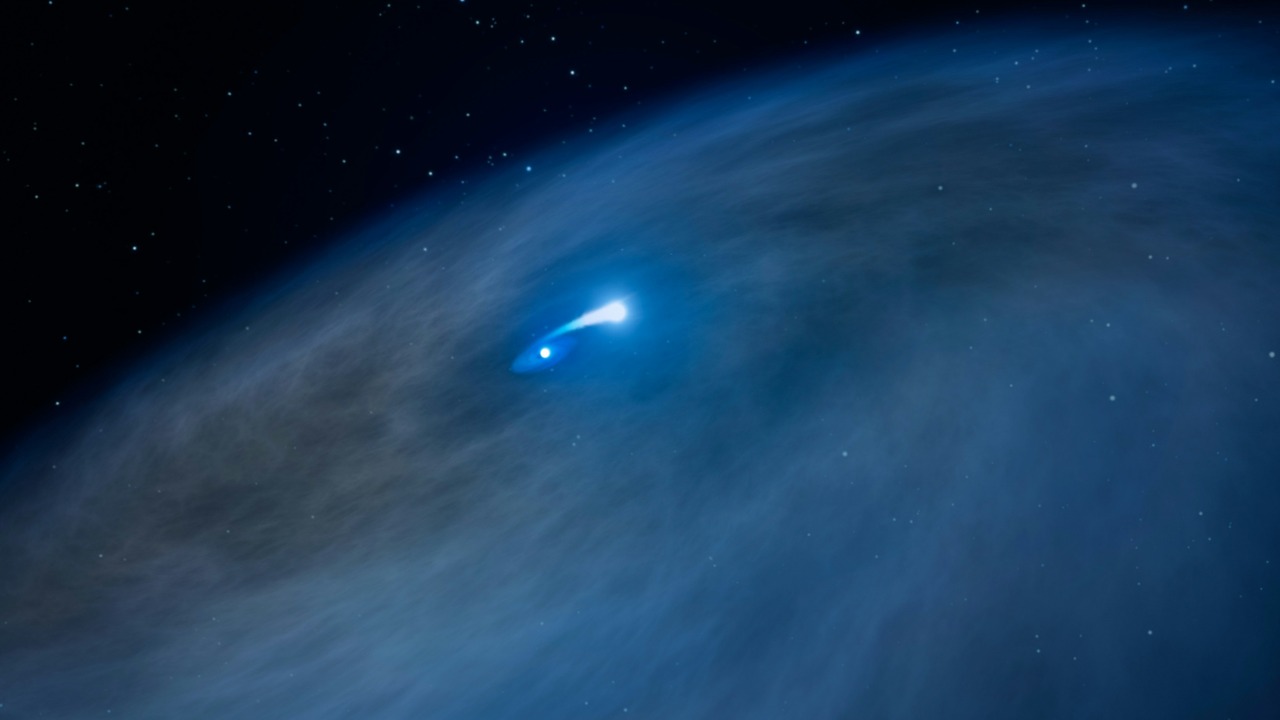

In an unprecedented astronomical event, scientists are left astounded by the mysterious disappearance of a star without the expected explosive finale. Typically, stars end their life cycle in a brilliant supernova, but recent observations defy this norm, prompting a reevaluation of stellar death processes. This unexpected phenomenon has intrigued astronomers and challenged existing theories about the fate of massive stars.
The Phenomenon of Disappearing Stars
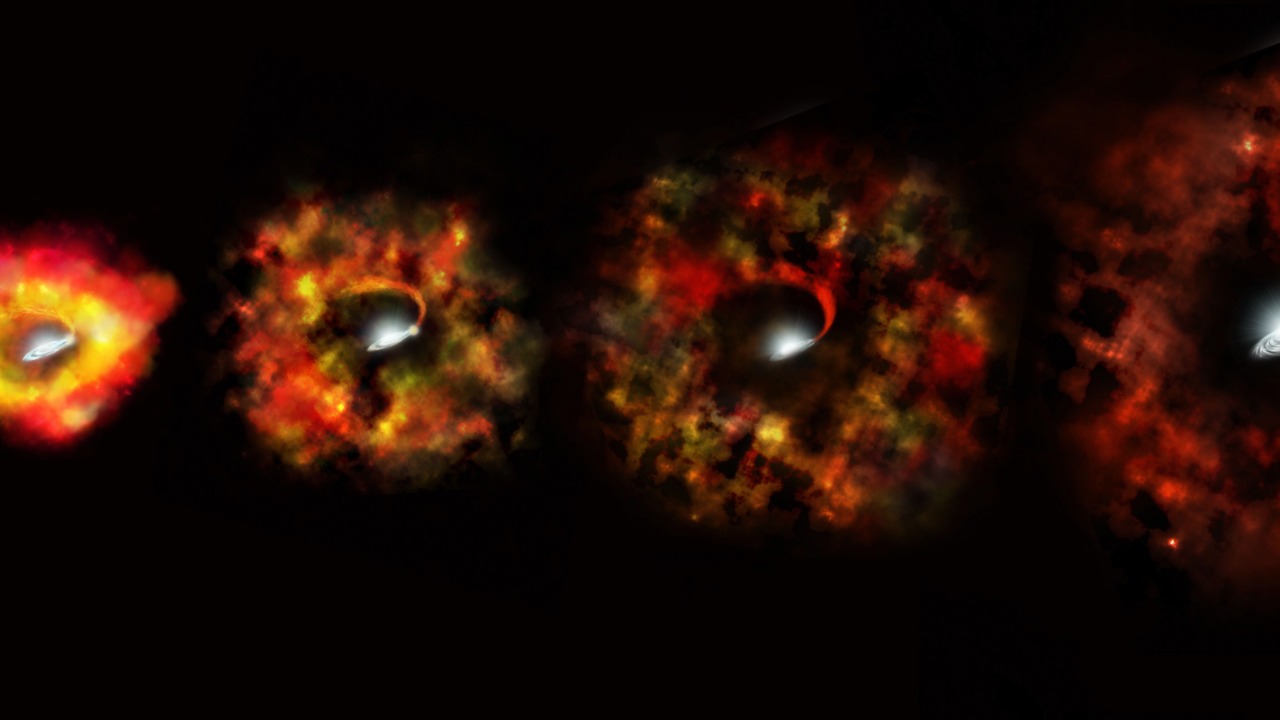
Stars, the celestial bodies that illuminate our night sky, generally follow a predictable life cycle. They are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, evolve over millions to billions of years, and ultimately meet their demise in a spectacular supernova explosion if they are massive enough. This explosive event disperses elements into space and leaves behind a neutron star or a black hole. However, the sudden disappearance of a star without such a cosmic fireworks display suggests that our understanding of stellar endpoints might be incomplete.
Historically, there have been instances where stars have vanished without a trace, leaving astronomers puzzled. For instance, the star N6946-BH1, observed by the Large Binocular Telescope, faded away without an explosive end, leading scientists to speculate that it might have collapsed directly into a black hole. These cases, although rare, raise significant questions about the processes governing the death of massive stars. The recent disappearance adds to this list of mysteries, prompting a fresh examination of our theories on stellar evolution and death.
Investigating the Mysterious Disappearance
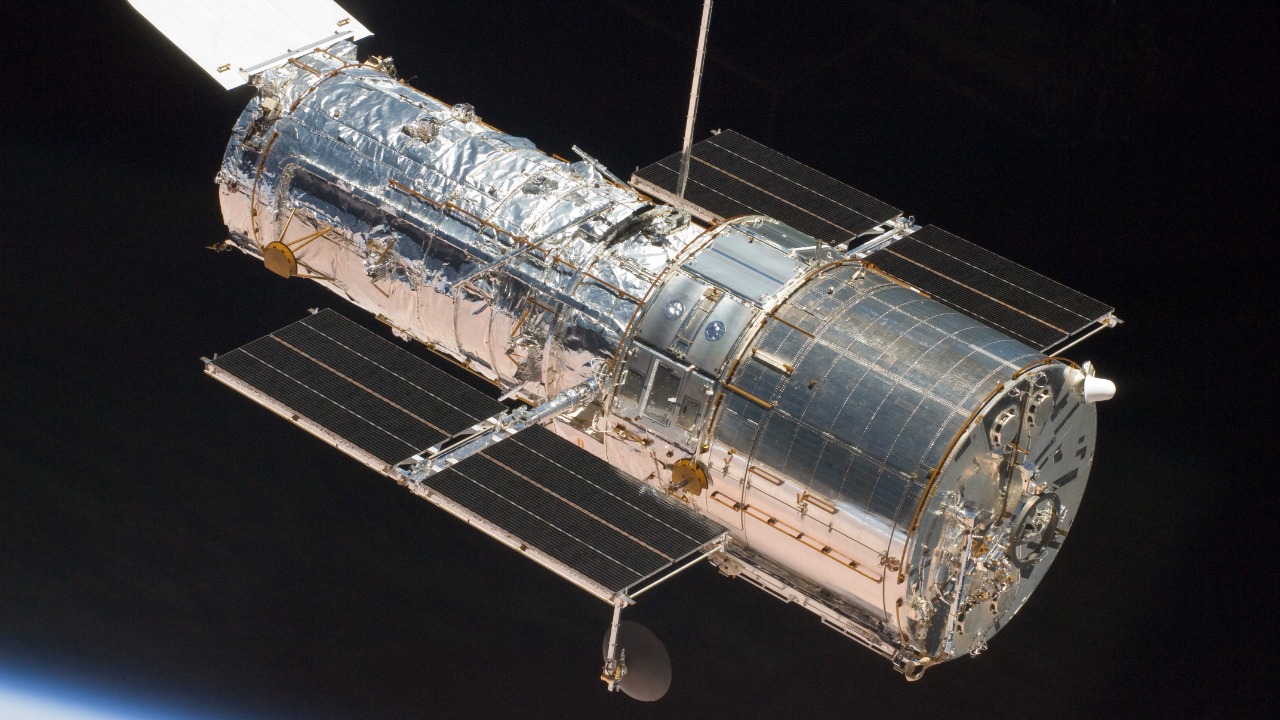
The ability to detect and monitor stars has significantly advanced with technology. Telescopes equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and imaging capabilities allow astronomers to observe stars in unprecedented detail. In the case of the missing star, instruments such as the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories played a crucial role in tracking its final moments. The data collected revealed the star’s gradual dimming until it vanished, without the signature explosion that typically accompanies the death of a massive star.
Several theories have been proposed to explain this phenomenon. One possibility is observational error, where the star might have been obscured by interstellar dust or was too faint to be detected. Alternatively, it could be an entirely new type of stellar event not yet fully understood. Scientists are also considering whether the star might have quietly collapsed into a black hole, bypassing the supernova stage. These hypotheses, while intriguing, require further investigation and more data to confirm.
Scientific Theories and Hypotheses
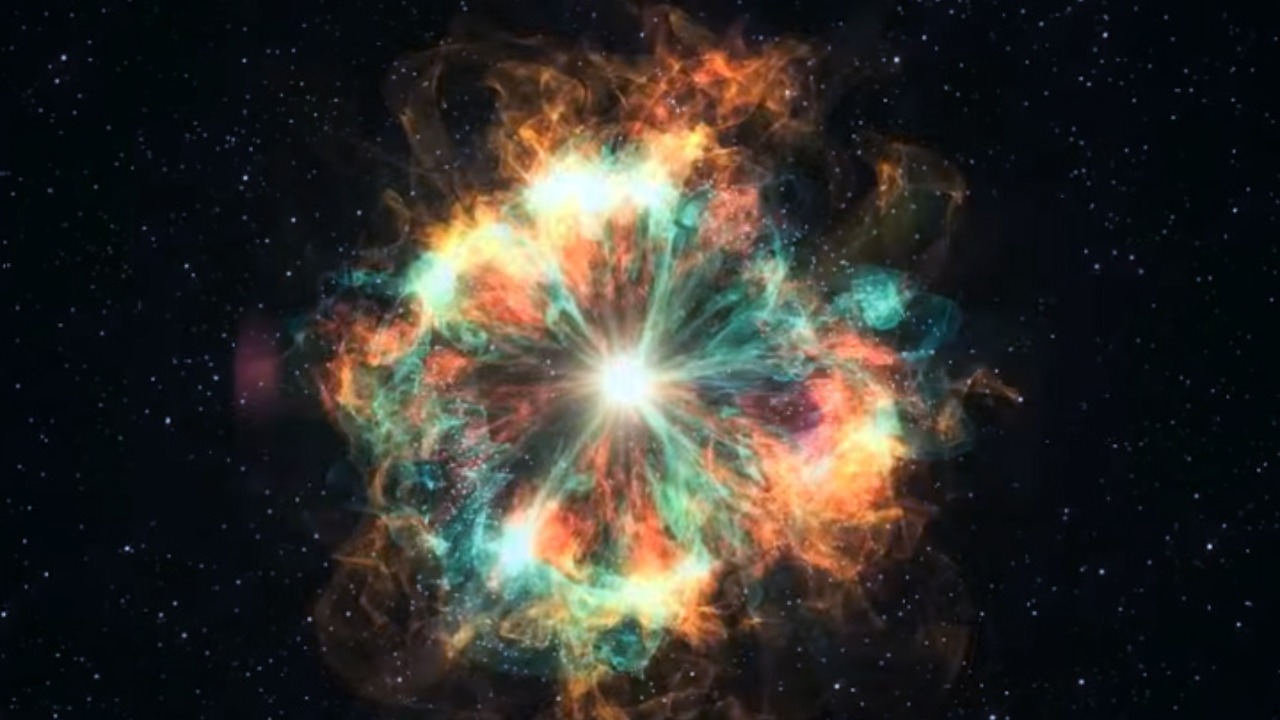

One of the leading theories to explain this star’s disappearance is the “Failed Supernova” hypothesis. According to this concept, if a star loses its outer layers before collapsing, it may directly form a black hole without an explosion. This theory, discussed in recent scientific literature, suggests that certain conditions could lead to such an outcome, challenging the conventional understanding of supernova mechanics.
Alternative explanations include the possibility that the star underwent a process known as “fallback supernova,” where the explosion occurs but is not visible due to the immediate collapse of ejected material back onto the core, forming a black hole. This idea is explored in depth in astrophysical models. These hypotheses suggest a complex interplay of factors that dictate whether a star ends its life in an observable explosion or a silent collapse, raising new questions about the limits of our current models.
Implications for Astrophysics and Future Research
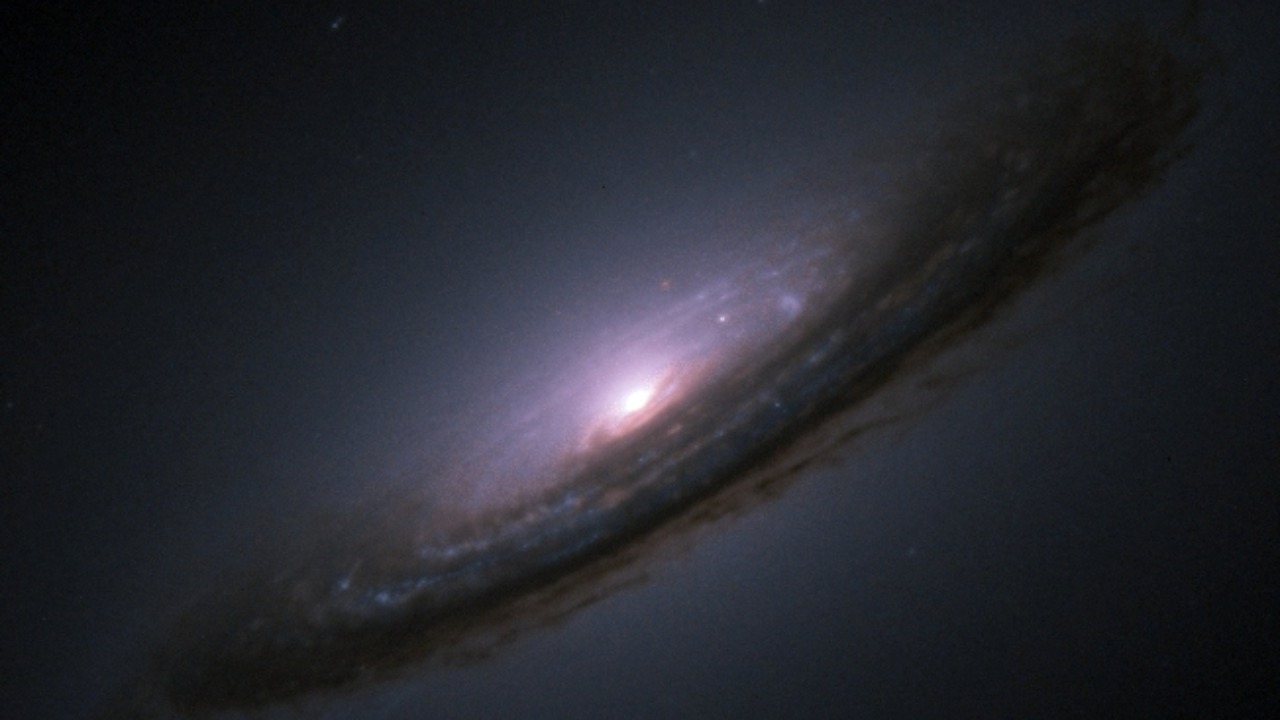

The vanishing of a star without a supernova challenges the existing models of stellar evolution and the life cycle of massive stars. If such events are more common than previously thought, it could necessitate a significant revision of our theoretical frameworks regarding how stars die. The implications extend to our understanding of black hole formation and the distribution of elements in the universe.
Future research will focus on identifying similar cases and understanding the conditions that lead to a star’s silent collapse. Enhanced observation techniques and the development of more sophisticated models will be essential in this endeavor. The potential for new discoveries is vast, as researchers aim to uncover the hidden mechanisms behind these mysterious disappearances. The ongoing study of such phenomena could reshape our comprehension of the cosmos and the processes that govern its evolution.
Community and Public Reaction

The astronomical community has reacted with a mix of excitement and curiosity to the star’s disappearance. Leading scientists and institutions have issued statements expressing the need for further study and collaboration to unravel the mystery. The event has also captured public interest, with media coverage highlighting the enigma and its implications for our understanding of the universe.
Citizen science and amateur astronomers have played a crucial role in observing and reporting unusual stellar events. Their contributions, alongside those of professional astronomers, help build a more comprehensive picture of the cosmos. As we continue to explore these celestial mysteries, the collaboration between professionals and the public will be invaluable in advancing our knowledge of the universe.