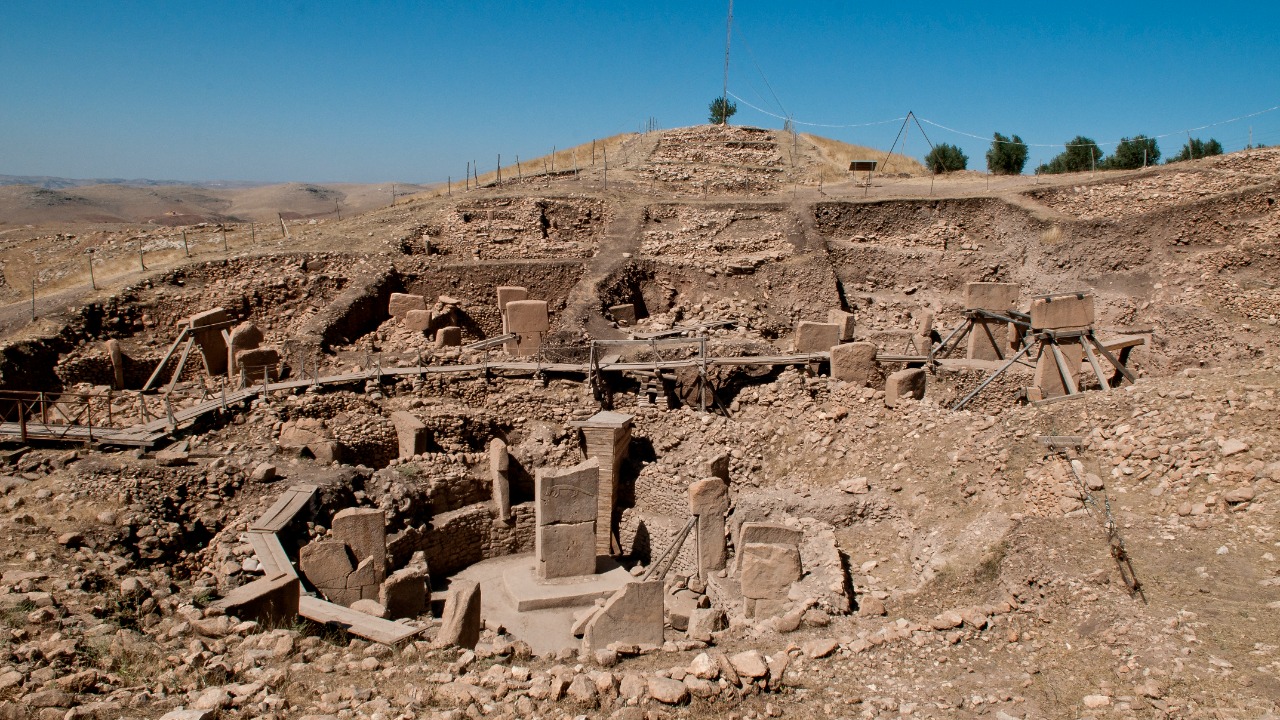

Recent archaeological discoveries have unveiled ruins believed to be part of a civilization dating back 20,000 years, challenging our understanding of human history. These findings compel researchers to re-evaluate the timeline of human development and the capabilities of ancient societies. Could this be the missing link that alters our perception of early human achievements?
The Discovery of the Ruins
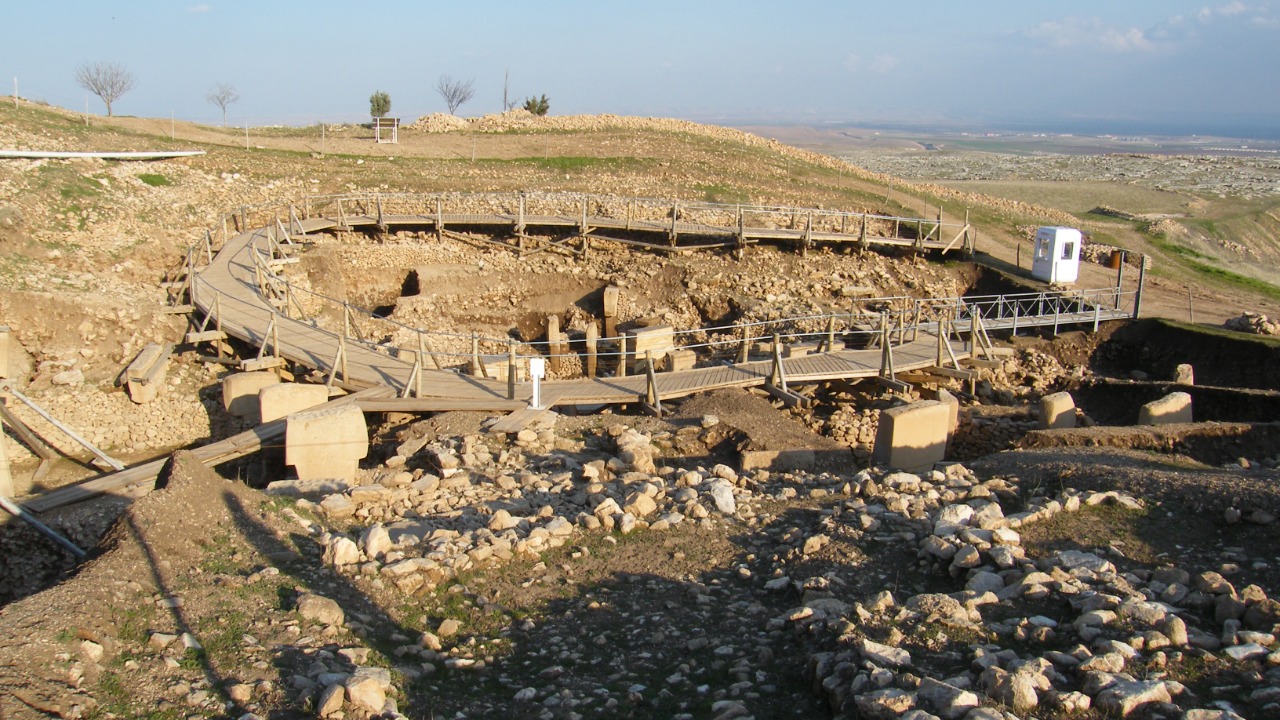

The ruins were discovered in a remote area, nestled within a landscape that has long been shrouded in mystery. The site’s exact location remains confidential, largely to protect it from looting and unauthorized exploration. However, early reports suggest that the ruins span several square miles, containing remnants of what appear to be sophisticated structures. Initial findings include stone tools, pottery shards, and what might be remnants of complex architectural designs. The sheer scale and intricacy of the site hint at a highly organized society that once thrived in what we now consider a desolate region.
Dating the ruins has been a critical aspect of this discovery. Archaeologists have employed a combination of carbon dating, stratigraphy, and advanced technologies such as ground-penetrating radar. These methods have provided consistent results, placing the age of the ruins at approximately 20,000 years. Such findings have generated a wave of excitement and skepticism within the scientific community. While some experts eagerly embrace the potential rewrite of history, others urge caution, reminding us of the complexities involved in interpreting ancient evidence.
Re-evaluating Human History
The discovery of these ancient ruins challenges long-held beliefs about the timeline of human civilization. Traditionally, historians have pointed to Mesopotamia and Egypt as the cradles of human development, dating back around 5,000 years. However, these newly discovered ruins suggest that organized societies may have existed much earlier, potentially reshaping our understanding of early human migration and development. This revelation has sparked debates among historians and archaeologists about the emergence and spread of human civilization across the globe.
Comparisons with known ancient civilizations highlight the potential significance of these findings. While Mesopotamia and Egypt are renowned for their advancements in writing, agriculture, and governance, the newly discovered site may offer insights into an even older societal framework. The implications of this discovery extend beyond historical timelines, prompting researchers to reconsider the evolution of human ingenuity and adaptability. If these ruins indeed belong to a civilization that predates known ancient societies, it could lead to a profound re-evaluation of how we perceive the origins of human culture and innovation.
Technological and Cultural Insights

An examination of the site has revealed evidence of advanced technology that challenges our understanding of prehistoric capabilities. Archaeologists have uncovered tools and construction methods that suggest a level of sophistication previously thought impossible for a society of this age. Intricately carved stone implements and evidence of large-scale construction projects indicate that these ancient people possessed a highly developed understanding of engineering and craftsmanship.
Culturally, the site offers a fascinating glimpse into the social organization and beliefs of this ancient civilization. Artifacts such as pottery, sculptures, and possible religious structures hint at a society rich in cultural expression. These findings raise questions about the daily life and survival strategies of the people who once inhabited this region. How did they interact with their environment? What were their social hierarchies and belief systems? The potential to uncover insights into these aspects of ancient life is a tantalizing prospect for researchers and historians alike.
Controversies and Skepticism

Despite the excitement surrounding this discovery, it has also sparked a fair share of controversy and skepticism. Some historians and archaeologists question the validity of the findings, citing the challenges of interpreting incomplete or fragmented evidence. The nature of archaeological research is inherently complex, and new discoveries often prompt debates about their significance and authenticity. Critics argue that without more conclusive evidence, it is premature to declare these ruins as proof of a 20,000-year-old civilization.
The role of media in shaping public perception cannot be overlooked in this context. As news of the discovery spreads, it is crucial to approach the information with a critical eye and resist the temptation to sensationalize or draw definitive conclusions. The spread of misinformation can be detrimental to the scientific process, leading to misunderstandings and misconceptions about the true nature of the findings. It is essential to balance the excitement of discovery with a healthy dose of skepticism and rigorous scientific inquiry.
Future Research and Exploration
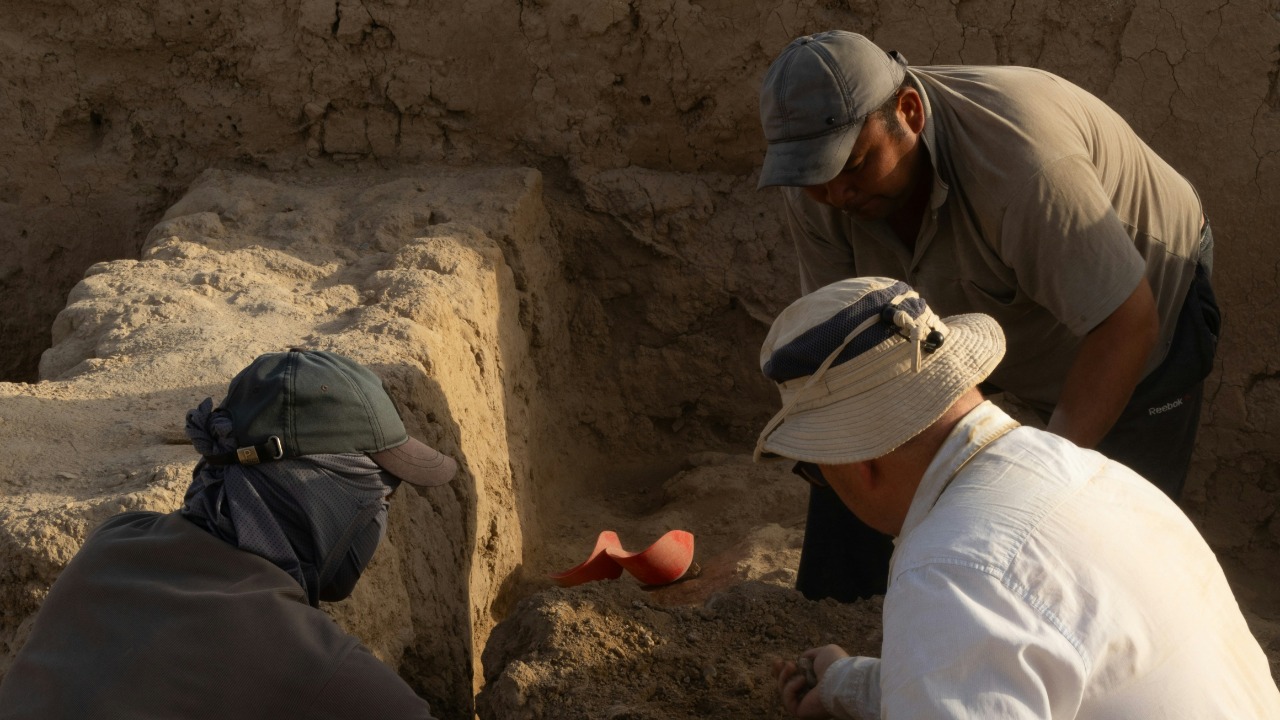

Looking ahead, numerous expeditions and research projects are planned to uncover more about this ancient civilization. Archaeologists and historians are eager to delve deeper into the site, employing an interdisciplinary approach that combines archaeology, anthropology, and other sciences to unravel the mysteries of this ancient society. The potential for groundbreaking discoveries is immense, with each new piece of evidence offering a deeper understanding of our shared human history.
These findings also have the potential to influence future archaeological methods and theories. As new technologies and techniques are developed, they may provide fresh insights into ancient civilizations, challenging existing paradigms and opening new avenues for exploration. The discovery of these ruins serves as a reminder of the vastness of human history and the ongoing quest to uncover the secrets of our past. With each step forward, we move closer to a more comprehensive understanding of the origins and evolution of human civilization.