
Scientists have long speculated about the possibility of our Sun having a twin star, a theory that has gained traction with recent data. The evidence and implications of a potential solar sibling shed light on the possible origins and impacts of such a discovery, challenging our understanding of the cosmos.
The Birth of Binary Stars
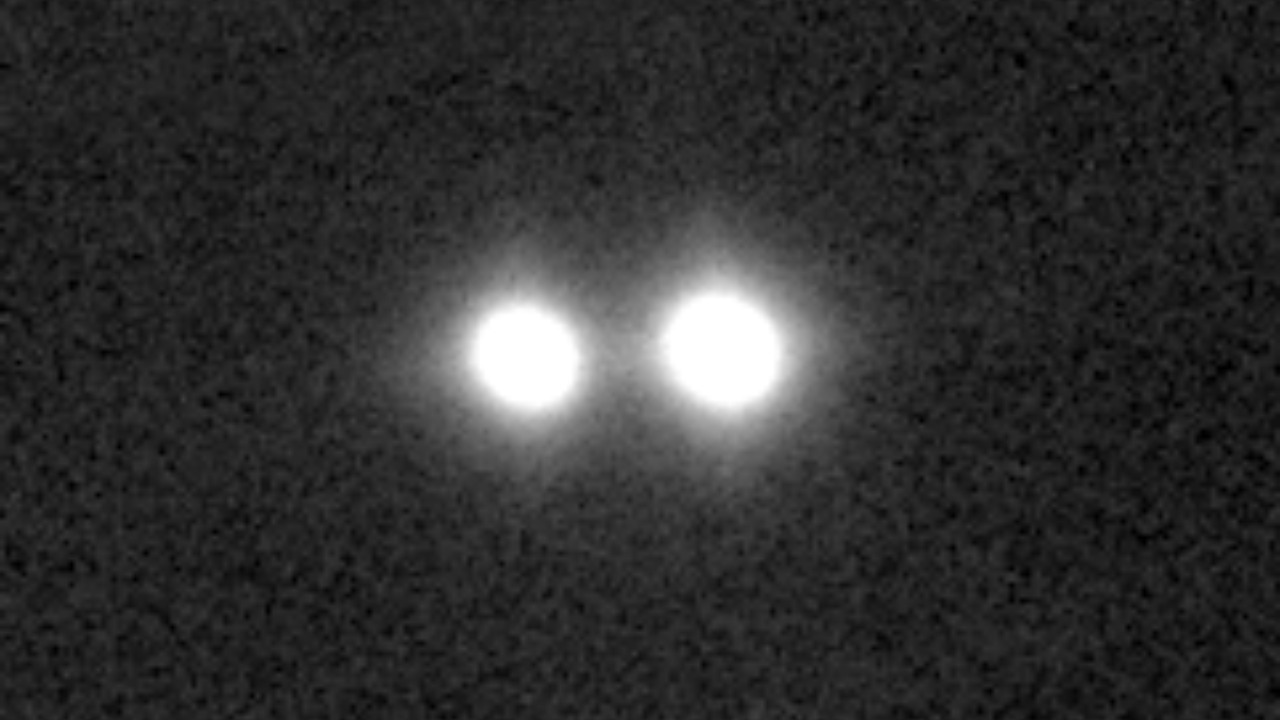

The formation of binary star systems is a fascinating aspect of astrophysics, rooted in the complex dance of collapsing molecular clouds. These clouds, dense regions in space rich with gas and dust, undergo gravitational collapse, leading to the birth of stars. However, the intricacies of this process often yield not just single stars but pairs or even multiple stars. In a binary system, two stars are gravitationally bound, orbiting a common center of mass. Theories suggest that turbulence within the molecular cloud can fragment it, giving rise to multiple cores that form stars, thus explaining the prevalence of binaries in the universe.
Historically, astronomers have been intrigued by the notion of binary systems. Observations of stars in close proximity sparked early debates about their nature. With advancements in technology and observational techniques, it became evident that binary systems were not just a curiosity but a common occurrence. The idea of our Sun having a twin has been a topic of speculation, with some early astronomers proposing that our solar system could have once been part of a binary configuration. This historical context sets the stage for the modern pursuit of our Sun’s potential twin.
Evidence of a Solar Twin

Recent astronomical studies have provided intriguing evidence that suggests the presence of a twin star to our Sun. Astrophysical data, including spectral analysis and stellar movement patterns, have been pivotal in this pursuit. By examining the light spectra emitted by stars, astronomers can infer their compositions, temperatures, and velocities. These insights have led to the identification of stars that share similar properties with our Sun, hinting at a shared origin. Moreover, the study of stellar movement patterns through advanced telescopes has revealed anomalies that could be explained by the gravitational influence of a hidden stellar companion.
A significant contributor to this field of research is the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, where recent studies have highlighted potential candidates for the Sun’s twin. These studies propose that the Sun’s twin, if it exists, may have drifted far from its original location due to dynamic interactions in the galaxy. Such findings are not only exciting for the field of astronomy but also for our understanding of how stars and their systems evolve over time.
Impact on Solar System Formation
The presence of a twin star could have profound implications for the formation and current configuration of our solar system. One of the key areas of interest is the stability of planetary orbits. In a binary system, the gravitational forces exerted by both stars can significantly influence the trajectories of surrounding planets. If the Sun had a twin, it might have played a role in shaping the orbits of planets, potentially contributing to the unique stability observed in our solar system today. Such a relationship could explain the relatively circular orbits of the planets and the spacing between them.
Beyond planetary orbits, a solar twin could have impacted the Oort Cloud and Kuiper Belt, regions filled with comets and asteroids. A twin star might have perturbed the orbits of these objects, sending some of them towards the inner solar system. This interaction could have influenced the frequency and timing of cometary visits to Earth, potentially affecting the planet’s geological and biological history. The implications of such a dynamic relationship extend to the study of mass extinctions and the role that celestial bodies play in Earth’s evolutionary timeline.
The Search for Nemesis

One of the more intriguing hypotheses related to the Sun’s potential twin is the Nemesis hypothesis. This theory suggests that a distant solar companion, dubbed Nemesis, could be responsible for periodic mass extinctions on Earth. By disturbing the Oort Cloud, Nemesis might have triggered a cascade of comets towards the inner solar system, leading to catastrophic impacts on Earth. Although the Nemesis hypothesis remains speculative, it underscores the potential significance of a solar twin in Earth’s history.
Technological advances have played a crucial role in the search for such elusive companions. Modern telescopes, equipped with cutting-edge sensors and capabilities, have enhanced our ability to detect faint stellar objects. The James Webb Space Telescope, for instance, is poised to revolutionize our understanding of distant stars and potential companions. Its advanced instrumentation allows astronomers to peer deeper into the cosmos, offering the possibility of identifying the Sun’s long-lost twin or similar stellar configurations in other systems.
Implications for Astronomy and Beyond

The discovery of a solar twin would have significant implications for the field of astronomy. It would prompt a reevaluation of existing stellar models and theories, challenging our understanding of star formation and evolution. Current models are based on the assumption that single stars like our Sun are the norm. However, if a twin is confirmed, it could reshape our perspective on stellar dynamics, binary interactions, and the life cycle of stars.
Beyond the scientific realm, the existence of a solar twin holds broader cosmic implications. Understanding the dynamics of binary systems could provide insights into the formation of planets and the conditions necessary for life. It might also lead to the identification of similar twin-star systems elsewhere in the universe, expanding our knowledge of the cosmos. As we continue to explore the depths of space, the potential discovery of our Sun’s twin serves as a reminder of the mysteries that still await us.