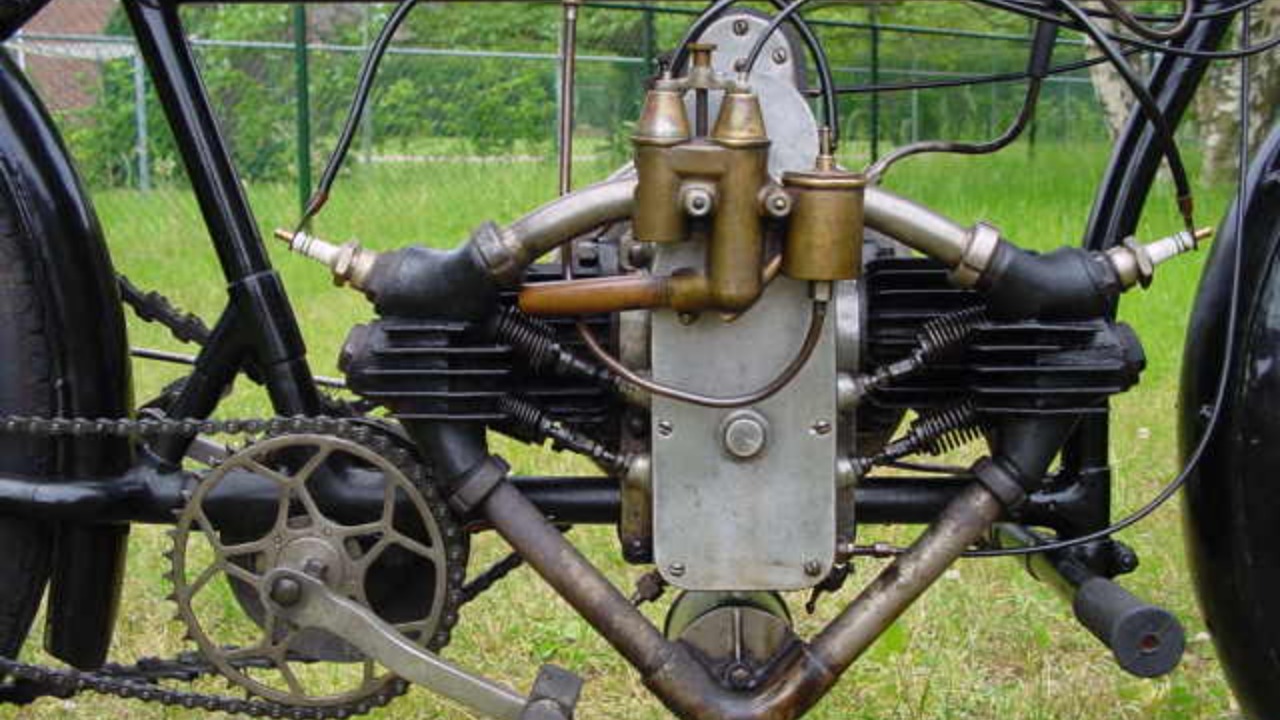
The flat-twin engine, a distinctive configuration known for its compact design and balance, has played a pivotal role in the history of engine development. Renowned for its application in both motorcycles and compact cars, this engine type has a storied past and unique characteristics that set it apart from other configurations.
Origins and Early Development
The early 20th century was a period of remarkable innovation, with the introduction of the flat-twin engine marking a significant milestone. This engine configuration made its debut in the early 1900s, quickly finding applications in both the motorcycle and automobile industries. The flat-twin’s compact design was particularly appealing to manufacturers looking to maximize efficiency and performance in smaller vehicles. Key pioneers in this field, such as Karl Benz, recognized the potential of this design early on. Benz’s contributions set the stage for other innovators to explore and refine the flat-twin configuration, leading to its widespread adoption.
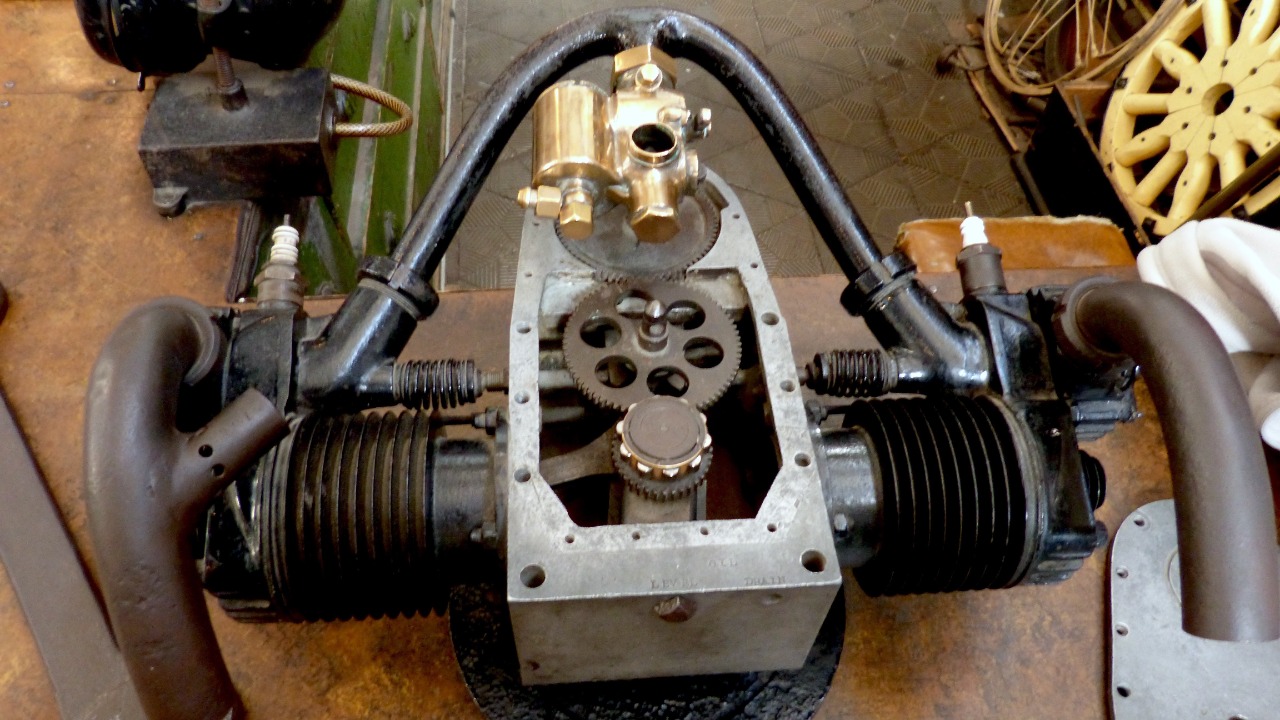
As the decades progressed, technological advancements continued to enhance the flat-twin engine’s design and performance. One of the most notable improvements was the development of more efficient cooling systems, which allowed for better thermal management and increased reliability. This evolution was driven by the need to address the limitations of early designs and to meet the growing demands of consumers for more robust and efficient engines. By continuously refining the flat-twin engine, manufacturers were able to maintain its relevance in a rapidly changing automotive landscape.
Unique Characteristics of the Flat-Twin Engine
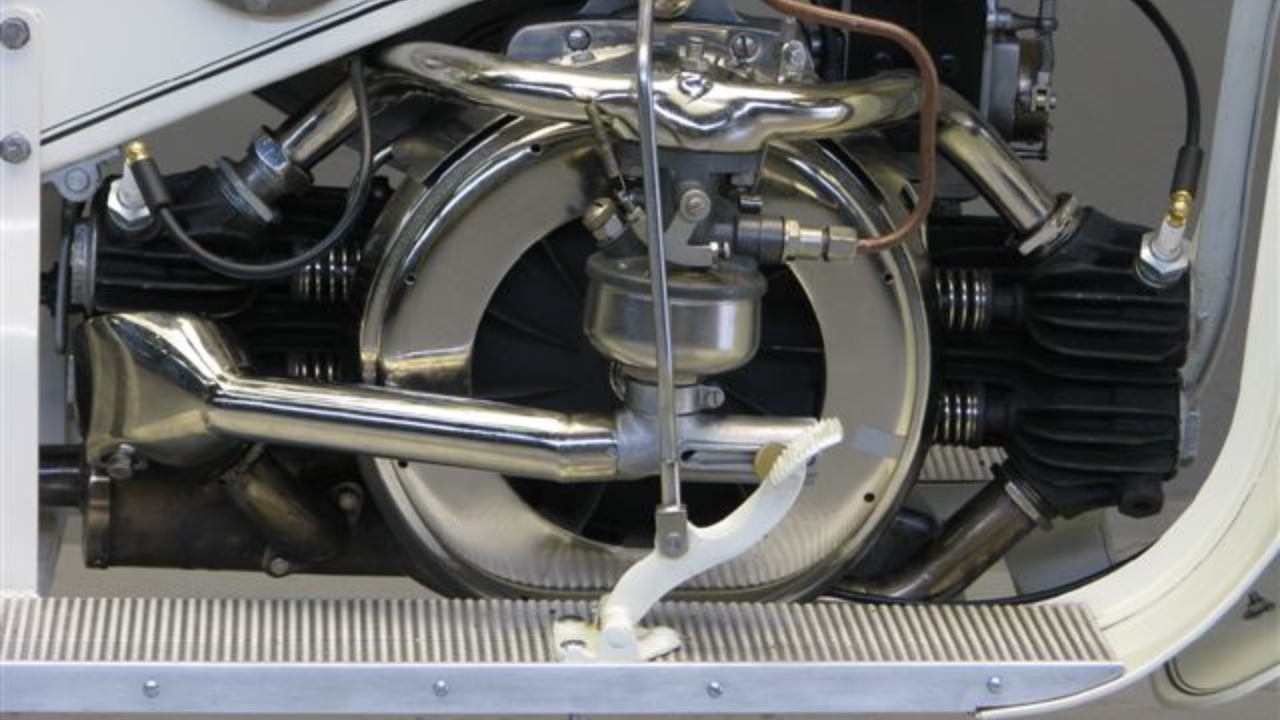
The flat-twin engine’s unique design and configuration set it apart from other engine types. Its horizontal layout, where the two cylinders lie flat on opposite sides, contributes to a lower center of gravity. This design not only enhances the balance of the vehicle but also improves handling and stability, particularly in motorcycles. When compared to other configurations, such as the inline or V engines, the flat-twin offers a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. For instance, while it provides better balance and cooling efficiency, it may not always match the power output of larger, more complex engine designs.
Performance and efficiency are key aspects that define the flat-twin engine. Its design inherently supports efficient cooling, as the horizontally opposed cylinders allow for more effective air circulation. This cooling efficiency, combined with the engine’s mechanical simplicity, contributes to its overall fuel efficiency and reliability. The flat-twin’s power output, while modest compared to larger engines, is often sufficient for the types of vehicles it powers. The engine’s simplicity also means fewer moving parts, which reduces the likelihood of mechanical failures and simplifies maintenance.
Notable Applications and Their Impact
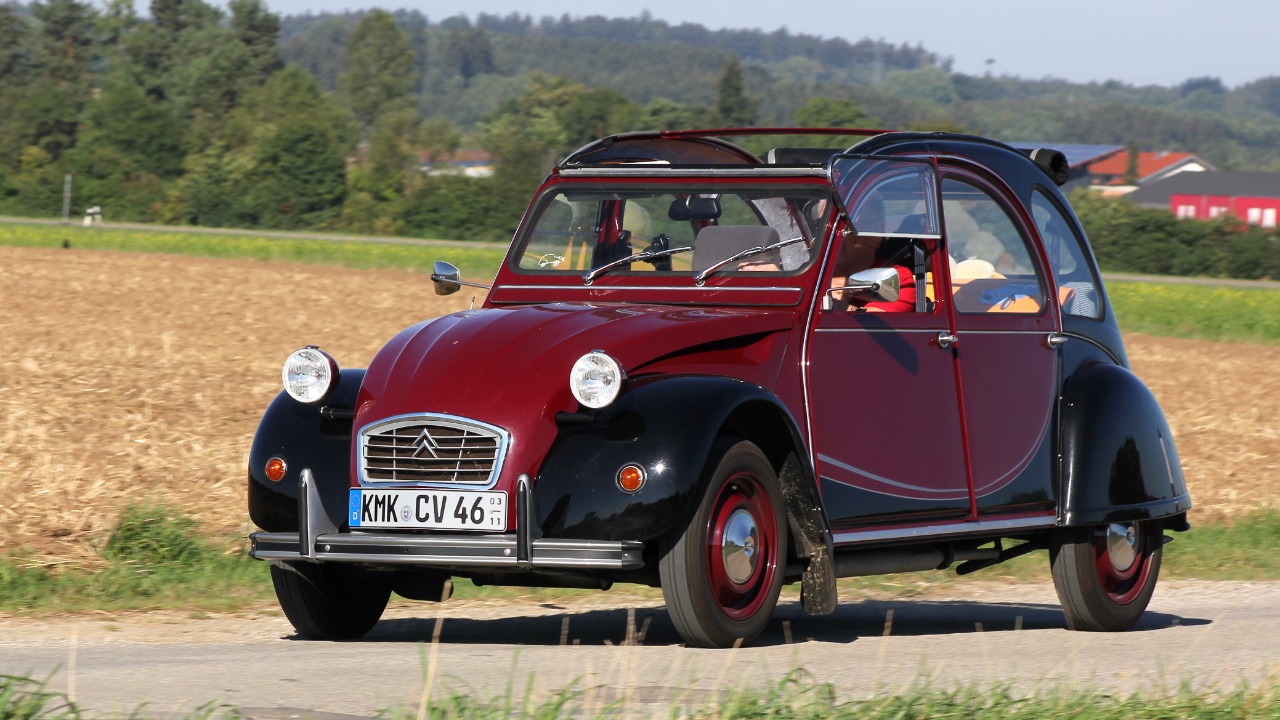

The flat-twin engine has found its place in a variety of applications, most notably in motorcycles and small vehicles. Iconic models such as the BMW motorcycles have long utilized flat-twin engines, taking advantage of their balance and performance characteristics. Similarly, the Citroën 2CV, a compact car that became a symbol of post-war France, relied on a flat-twin engine to deliver practicality and efficiency. These vehicles not only achieved commercial success but also left a lasting impact on consumer markets and automotive history.
Beyond land vehicles, the flat-twin engine has also made its mark in aviation. Its role in light aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) showcases its versatility and adaptability. The engine’s lightweight and efficient design make it an ideal choice for aircraft manufacturers looking to optimize performance while minimizing weight. Emerging uses of flat-twin engines in modern engineering fields, such as UAV applications, continue to highlight the engine’s relevance and potential for innovation. For more on UAV applications, see this research paper.
The Flat-Twin Engine in Modern Context
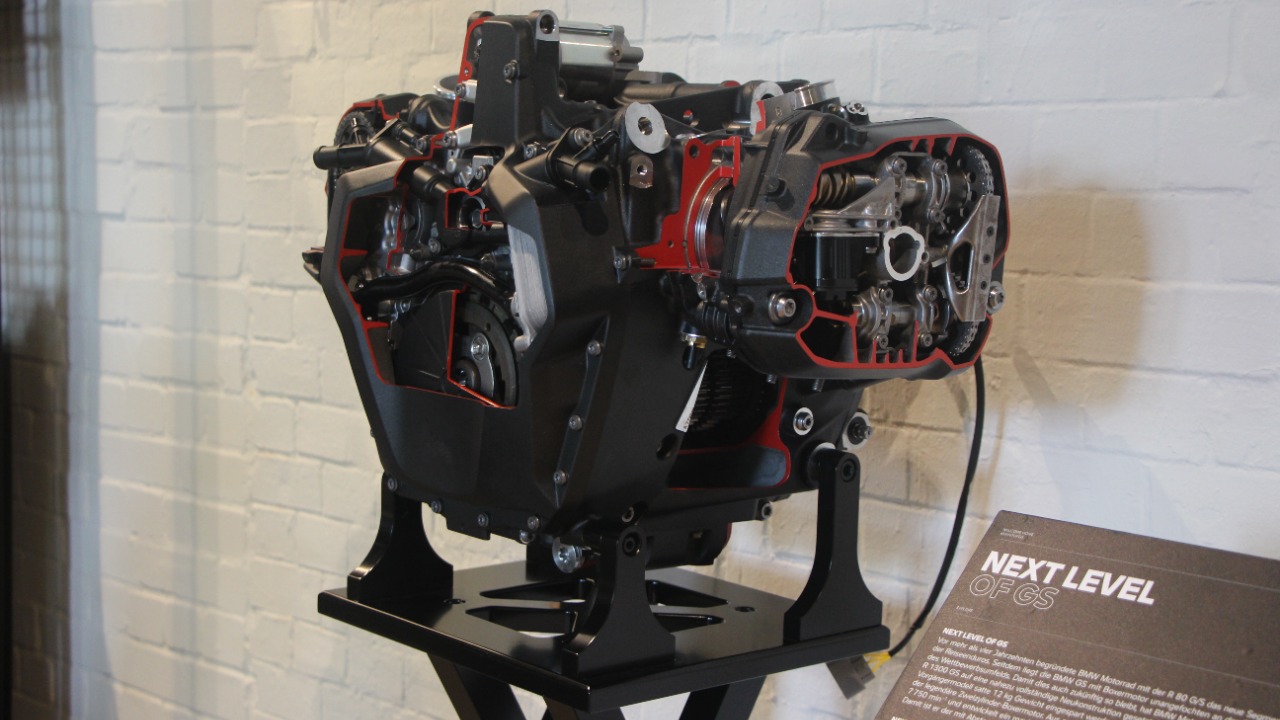
Today, the flat-twin engine continues to hold a place in the automotive and engineering world. Contemporary manufacturers are integrating flat-twin engines into modern designs with a focus on sustainability and efficiency. Recent technological advancements have further enhanced the engine’s capabilities, enabling it to meet the stringent environmental standards of today. These innovations are paving the way for future engine development, ensuring that the flat-twin remains a viable and competitive option in the market.
The cultural and historical significance of the flat-twin engine cannot be overstated. For automotive and motorcycle enthusiasts, it represents a piece of engineering history that embodies both tradition and innovation. The enduring legacy of the flat-twin engine is a testament to its unique qualities and its ability to adapt to changing demands over the years. As we look to the future, the flat-twin engine will likely continue to inspire and influence engineers and designers, maintaining its place as a symbol of ingenuity and progress.