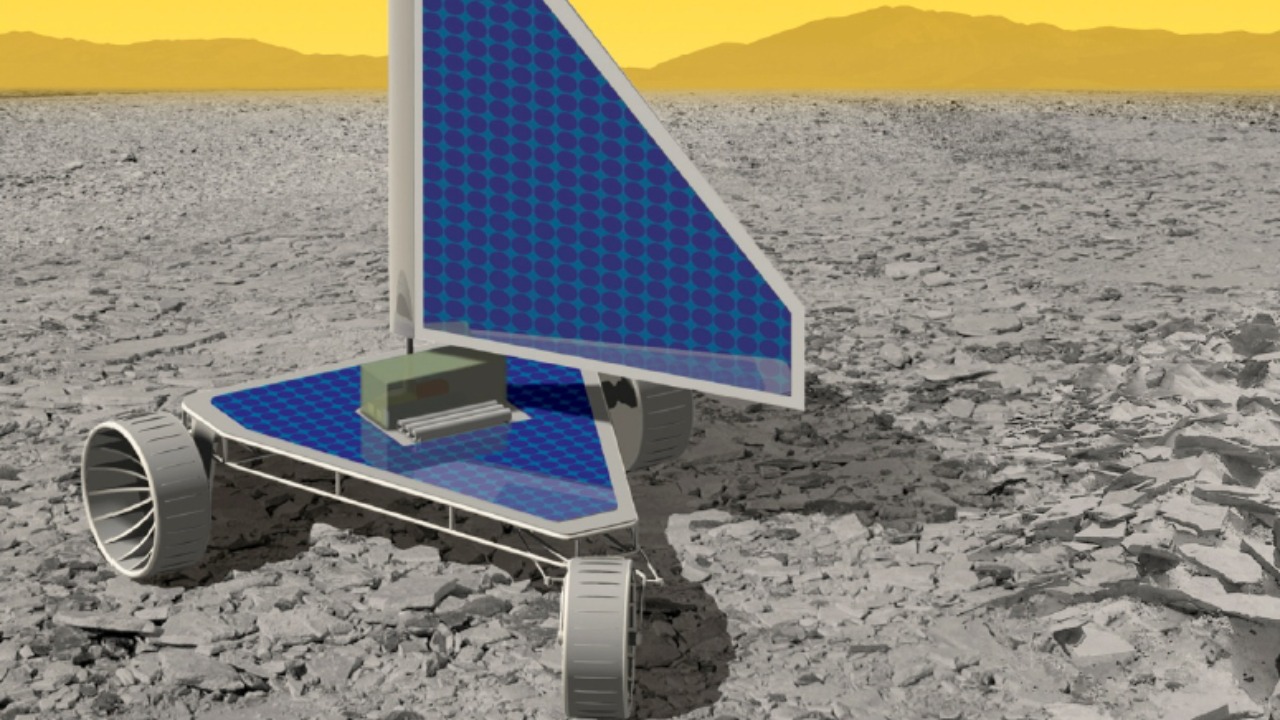
Recent discoveries by Venus rovers have unveiled metallic structures on the planet’s surface, sparking curiosity and various hypotheses among scientists. These metallic ruins raise questions about their origins, composition, and what they reveal about Venus’s history and environment. The enigmatic nature of these structures has opened up discussions in the scientific community, ranging from natural geological phenomena to more speculative theories involving ancient civilizations.
Historical Exploration of Venus

The exploration of Venus has long been a challenging yet intriguing endeavor for space agencies around the world. Early missions, such as the Soviet Union’s Venera program, were groundbreaking, providing the first images and data from the surface of Venus despite the harsh conditions. These missions revealed a planet with a thick, toxic atmosphere and temperatures high enough to melt lead. The Venera landers’ brief transmissions painted a picture of a rocky, volcanic landscape shrouded in mystery.
Following these early missions, NASA’s Magellan mission in the 1990s used radar mapping to provide detailed images of Venus’s surface, uncovering vast volcanic plains and evidence of tectonic activity. However, the exploration of Venus has always been fraught with challenges due to its hostile environment. The planet’s surface pressure is over 90 times that of Earth’s, and temperatures soar above 450 degrees Celsius, which has necessitated significant advancements in rover technology. Engineers have had to develop innovative solutions to create machines capable of withstanding these extreme conditions, pushing the boundaries of materials science and robotics.
Theories Behind Metallic Ruins

The discovery of metallic structures on Venus has led scientists to propose several theories regarding their origins. One prevailing hypothesis is that these formations are the result of natural geological processes. Venus is known for its active volcanic landscape, and it’s possible that these metallic structures could be mineral deposits formed through volcanic activity. The planet’s volcanic history might lead to unique formations composed of metals such as lead or bismuth, which could explain the presence of metallic ruins.
On the more speculative side, some theorists suggest that the metallic structures could be remnants of ancient alien civilizations or advanced technology. While there is no concrete evidence to support this idea, the possibility has captured the imagination of many. The lack of definitive answers about these structures makes it a fertile ground for speculation, albeit with a healthy dose of skepticism from the scientific community. Regardless of their origins, the metallic ruins on Venus provide an intriguing puzzle for researchers to unravel.
Metallic Frost and Surface Composition

One fascinating phenomenon observed on Venus is the occurrence of metallic frost in its mountainous regions. This frost is believed to form from metallic compounds that precipitate out of the planet’s dense atmosphere at high altitudes, coating the mountain tops with a metallic sheen. The presence of this frost could be linked to the metallic structures found on the surface, suggesting a complex interplay between Venus’s atmosphere and geological activity.
Studies of Venus’s surface composition have revealed a wealth of information about its geochemical processes. The planet’s surface is primarily composed of basalt, a volcanic rock, but also contains a variety of metallic elements. Understanding the distribution and formation of these metals is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of the metallic ruins. By analyzing the chemical makeup of these structures, scientists hope to gain insights into the planet’s volcanic history and the atmospheric conditions that may have influenced their formation.
Implications for Future Missions
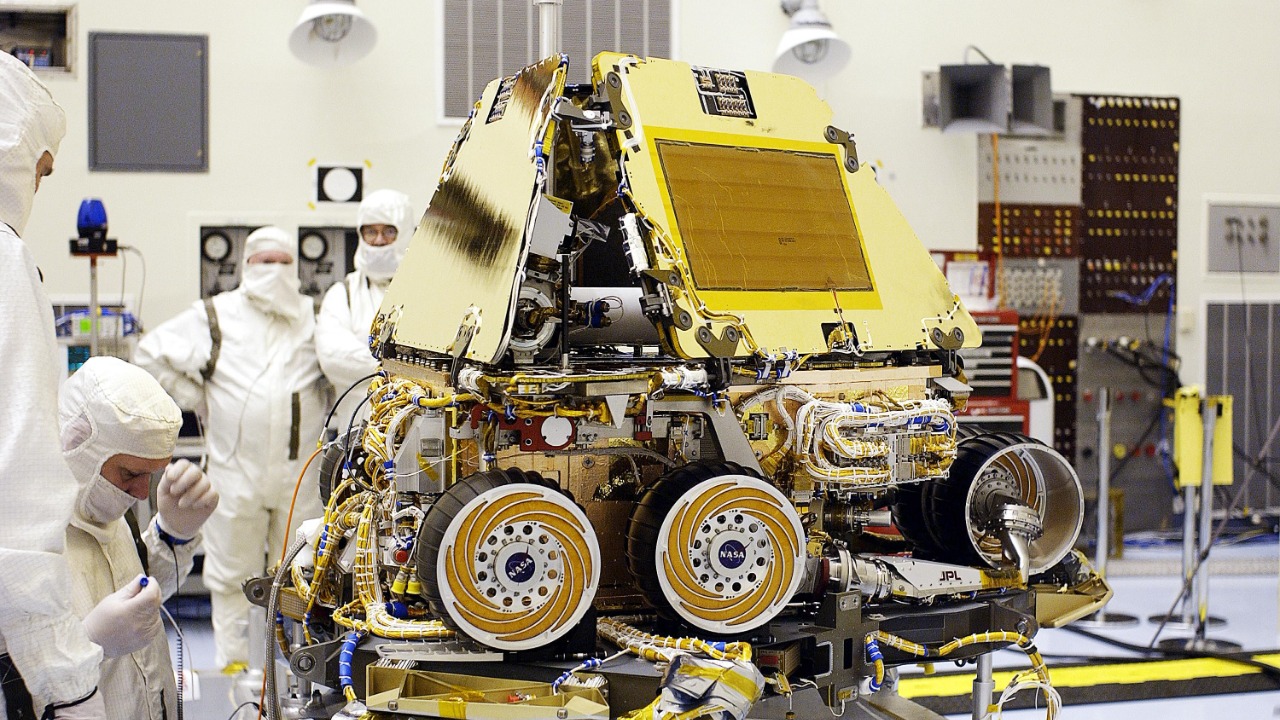
Exploring Venus further requires significant technological innovations. Future missions will need to develop new materials and power sources that can endure the planet’s extreme conditions. Concepts such as advanced cooling systems, durable alloys, and innovative energy solutions are being explored to extend the operational life of rovers on Venus. These technological advancements will not only aid in the exploration of Venus but could also have applications in other extreme environments, including deep-sea exploration on Earth.
Scientific goals for upcoming missions to Venus include a detailed analysis of the metallic ruins and a deeper understanding of the planet’s geological and atmospheric processes. These missions aim to determine the origins of the metallic structures and assess the potential for life on Venus. By studying the planet’s surface and atmosphere, scientists hope to uncover clues about Venus’s past and its potential to harbor life, drawing parallels with Mars exploration.
Comparative Analysis with Mars
Exploration of Mars and Venus presents both similarities and stark differences. While both planets pose environmental challenges, Mars’s surface conditions are somewhat more manageable, allowing for longer rover missions. Mars has been the focus of numerous missions seeking evidence of past water and potential signs of life, providing valuable insights that can inform Venus exploration strategies. The discoveries on Mars, such as ancient riverbeds and signs of water ice, have invigorated the search for similar features on Venus that might suggest a more habitable past.
Lessons learned from Martian discoveries are crucial for developing effective strategies for Venus exploration. The technological advancements made in Mars missions, such as autonomous navigation and advanced imaging systems, can be adapted for use on Venus. Additionally, the experience gained in analyzing Martian geology and atmosphere will be invaluable in understanding the complex environment of Venus. By leveraging these lessons, scientists hope to unlock the secrets of Venus and its mysterious metallic ruins, shedding light on the planet’s enigmatic history.