
In recent years, nuclear fusion has moved beyond theoretical boundaries to become a commercially viable energy source. This transition is largely due to significant advancements in technology and increased investment, which have collectively transformed the fusion landscape. The potential impact on the global energy grid could be profound, offering a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable energy solution.
Technological Breakthroughs in Fusion Research
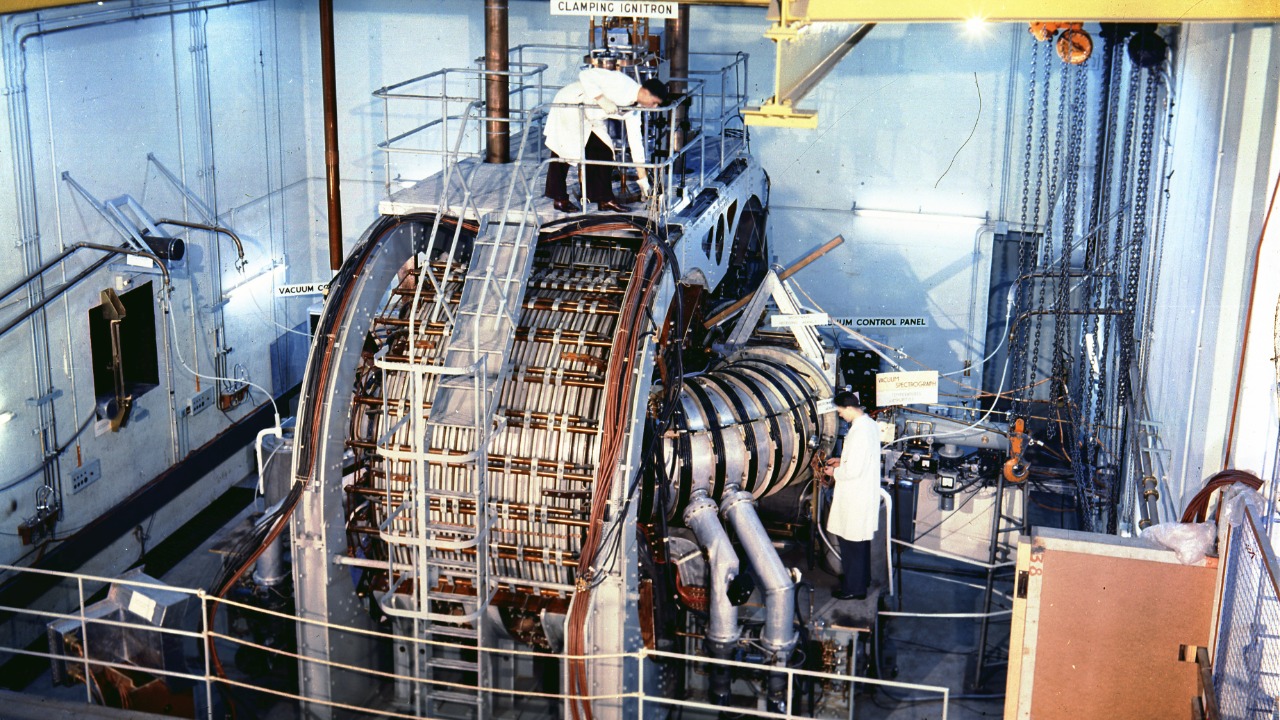
Advanced Materials and Reactor Designs
One of the key drivers of progress in nuclear fusion is the development of advanced materials and innovative reactor designs. New materials, such as high-temperature superconductors, are being used to construct more efficient and safer fusion reactors. These materials are capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures, which are essential for sustaining fusion reactions. Modern reactor designs, like those being developed by ITER and other international projects, aim to optimize plasma confinement, a crucial factor in achieving stable fusion.
Superconducting Magnets
Superconducting magnets have seen remarkable advancements, significantly boosting the energy output and stability of fusion reactions. The cutting-edge technology used in these magnets allows them to create intense magnetic fields necessary for plasma confinement without losing energy through resistance. This improvement has led to more efficient operation of fusion reactors, bringing us closer to realizing continuous and sustainable fusion power. These developments are crucial in addressing the technical challenges that have historically hindered fusion energy.
Laser Inertial Confinement Technology
Laser-driven inertial confinement has emerged as a promising method for achieving sustainable fusion reactions. This technique involves the use of powerful lasers to compress and heat a small fuel pellet, initiating fusion. Recent advancements in laser technology have improved the energy efficiency and precision of this method, making it a viable path toward commercial fusion energy. Research centers like the National Ignition Facility in the United States are at the forefront of this technology, continually pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in fusion research.
Investment and Funding Landscape

Private Sector Investments
The role of private sector investments in accelerating fusion development cannot be overstated. Companies like Google have poured significant resources into fusion startups, driving innovation and reducing the time to market. This influx of capital has allowed for rapid advancements in technology and has helped startups like Commonwealth Fusion Systems make strides in achieving practical fusion energy. The involvement of tech giants not only provides financial backing but also brings in valuable expertise and a culture of rapid iteration and innovation.
Government Support and International Collaborations
Government funding and international collaborations have also played a crucial role in advancing fusion technology. Projects like ITER, a consortium of 35 countries, exemplify how global cooperation can accelerate technological breakthroughs. Diverse expertise and shared resources have allowed for significant progress, particularly in addressing complex engineering challenges. This collaborative approach ensures that lessons learned and technological advancements are shared across borders, speeding up the journey to commercialization.
Economic Incentives and Market Potential
The economic incentives for investing in fusion technology are becoming increasingly apparent. As the world shifts towards sustainable energy sources, fusion offers a compelling solution with its potential for virtually limitless and clean energy. The market potential is enormous, with applications ranging from electricity generation to industrial processes. Investors are recognizing the long-term value of fusion, and with continued technological advancements, the cost of fusion energy is expected to become competitive with other renewable sources, making it a viable option in the global energy market.
Regulatory and Safety Advancements

Evolving Regulatory Frameworks
The regulatory landscape for fusion energy is rapidly evolving to address the unique challenges posed by this emerging technology. Regulatory bodies are developing new safety standards and guidelines to ensure the safe deployment of fusion reactors. These frameworks are crucial for gaining public trust and facilitating the integration of fusion energy into existing power grids. By addressing safety and regulatory concerns proactively, the fusion industry aims to avoid the pitfalls faced by traditional nuclear energy.
Safety Improvements
Advancements in safety measures have made fusion a more attractive energy option compared to traditional nuclear fission. Fusion reactions produce minimal radioactive waste, and the absence of chain reactions eliminates the risk of catastrophic meltdowns. These safety improvements are pivotal in gaining public and regulatory acceptance, paving the way for wider adoption of fusion energy. As a result, fusion presents an opportunity to redefine nuclear energy as a safe and sustainable power source.
Environmental Benefits
Fusion energy offers significant environmental advantages, including reduced radioactive waste and minimal carbon emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, fusion does not produce greenhouse gases, making it an environmentally friendly alternative. The shift towards fusion energy could play a critical role in mitigating climate change and achieving global sustainability goals. As awareness of these benefits grows, support for fusion energy is likely to increase, further driving its development and commercialization.
Commercialization and Industrial Applications

Grid Compatibility and Energy Storage
Integrating fusion energy into existing power grids is a critical aspect of its commercialization. Fusion reactors can be designed to produce a steady supply of energy, complementing intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind. Additionally, advancements in energy storage technologies are essential for maximizing the potential of fusion energy. Efficient storage solutions will allow for the balancing of supply and demand, ensuring a reliable energy supply even when fusion reactors are offline for maintenance.
Industrial and Commercial Uses
The potential applications of fusion energy extend beyond electricity generation. Industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, and transportation could benefit from the high energy density and continuous power supply provided by fusion. For example, fusion energy could enable more efficient production processes in manufacturing or power long-duration space missions. The versatility and scalability of fusion make it an attractive option for a wide range of industrial applications, further increasing its commercial viability.
Cost Competitiveness
The cost trajectory of fusion energy is a critical factor in its ability to compete with other renewable sources. Continued technological advancements and economies of scale are expected to drive down costs, making fusion an economically viable option. As the technology matures and more reactors come online, the cost of fusion energy is likely to decrease further, enhancing its competitiveness in the energy market. This potential for cost reduction is a key incentive for continued investment and development in the fusion sector.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Remaining Technical Challenges
Despite the significant progress made, several technical challenges remain on the path to widespread commercial adoption of fusion energy. Achieving sustained and stable fusion reactions requires overcoming issues related to plasma confinement and reactor materials. Researchers are actively working to address these challenges, leveraging advancements in computational modeling and experimental techniques to optimize reactor designs. Continued investment in research and development is crucial for overcoming these hurdles and bringing fusion energy to market.
The Path Forward
The roadmap for future developments in fusion technology involves a collaborative effort among researchers, governments, and private companies. Key milestones include achieving net positive energy output and demonstrating the reliability of fusion reactors in real-world conditions. Projects like ITER and developments in laser inertial confinement are paving the way for these achievements. With continued support and innovation, the timeline for significant breakthroughs is becoming increasingly optimistic.
Global Impact and Energy Transition
Nuclear fusion has the potential to be a catalyst for a global energy transition, offering a sustainable and scalable solution to meet rising energy demands. As countries strive to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, fusion could play a pivotal role in achieving these goals. The widespread adoption of fusion energy could usher in a new era of clean energy, transforming the global energy landscape and contributing to a more sustainable future. The world stands on the brink of a fusion-powered future, with the potential to redefine how we generate and consume energy.