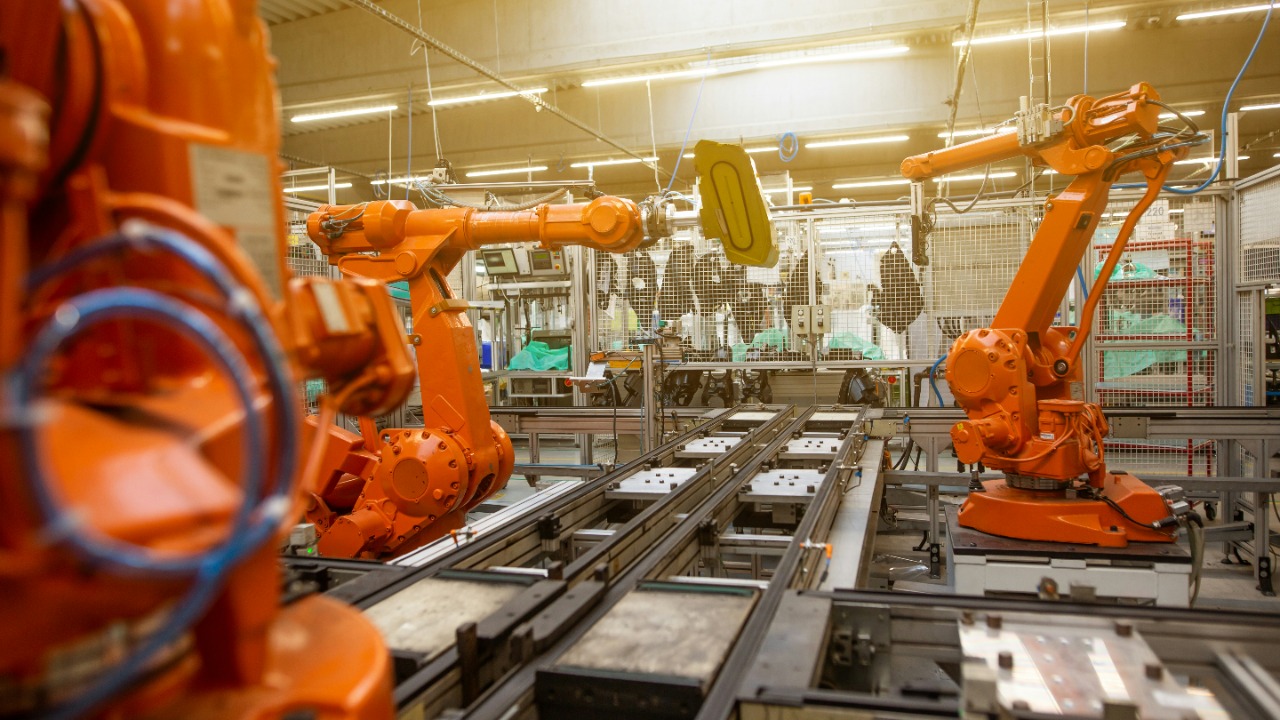

Robots have long been admired for their ability to perform tasks with high precision and consistency. These machines are increasingly integrated into various fields, proving indispensable in roles where accuracy is paramount. From healthcare to manufacturing, let’s explore eight types of robots that excel in precision tasks, often surpassing human capabilities.
Surgical Robots
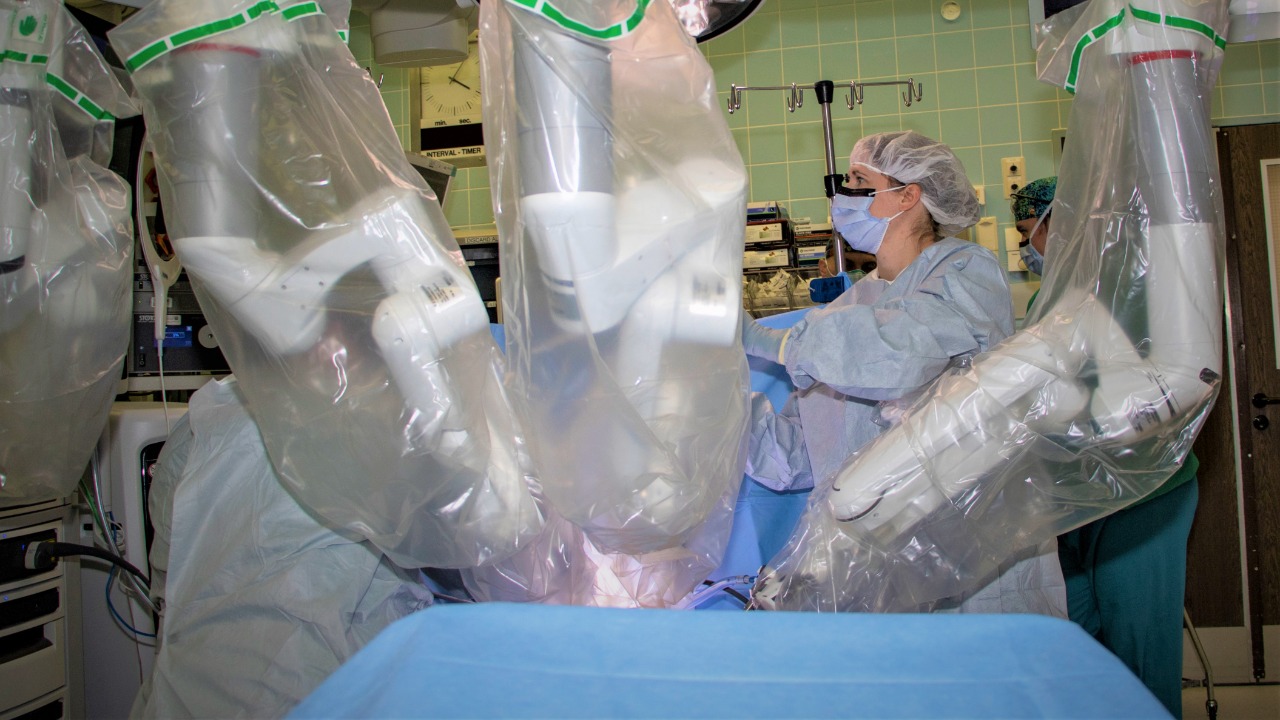
Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, are revolutionizing the medical field by enhancing the precision of surgical procedures. These robots enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive surgeries with greater accuracy and control, reducing recovery times and patient trauma. The robotic systems provide a steadier hand than humans can achieve, minimizing the risk of human error.
With advancements in robotic technology, surgical robots are becoming an essential tool in operating rooms worldwide. Their ability to execute complex tasks with pinpoint accuracy has made them a trusted ally in delicate surgeries, such as neurosurgery and cardiac procedures.
Industrial Assembly Robots
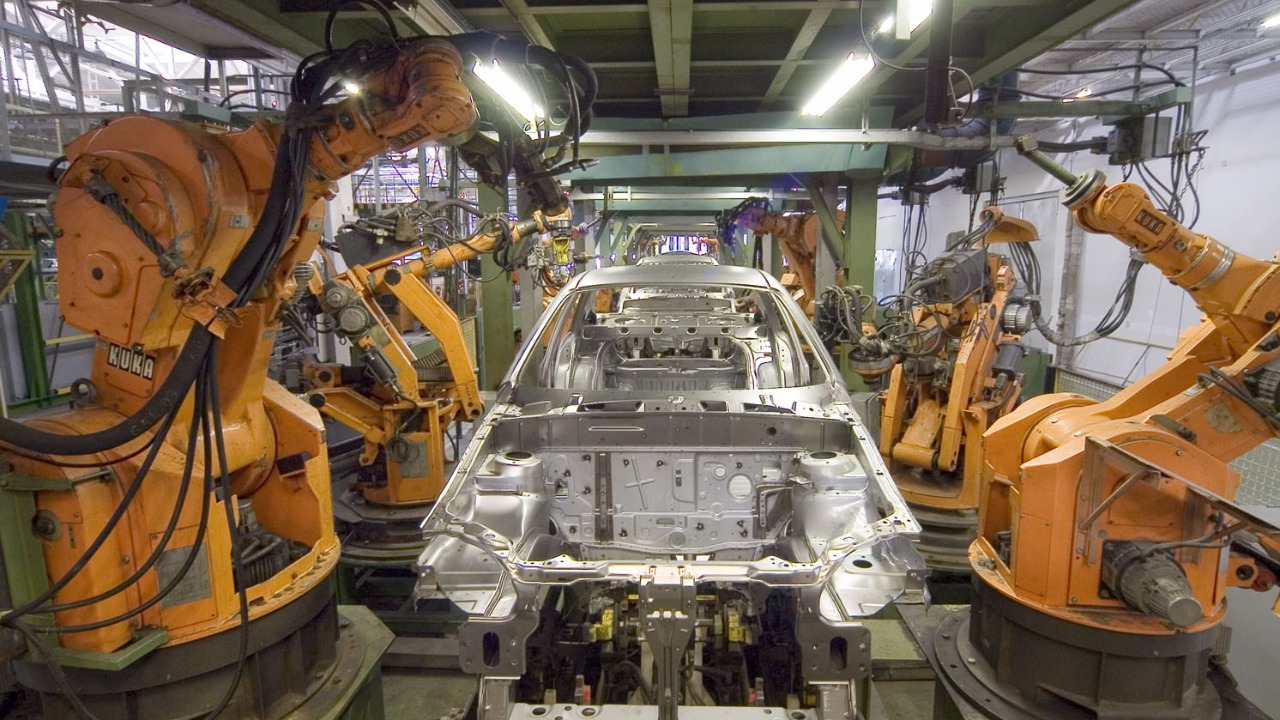

Industrial assembly robots are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, capable of assembling complex products with unmatched precision and speed. These robots are programmed to perform repetitive tasks with consistent accuracy, significantly reducing the margin of error compared to human workers. This level of precision is crucial in industries like automotive and electronics, where even minor mistakes can lead to significant issues.
In a comparative study, industrial robots have shown remarkable efficiency, boosting productivity while maintaining high-quality standards. Companies continue to invest in these robots to streamline their operations and remain competitive in a fast-paced market.
Robotic Arms for 3D Printing
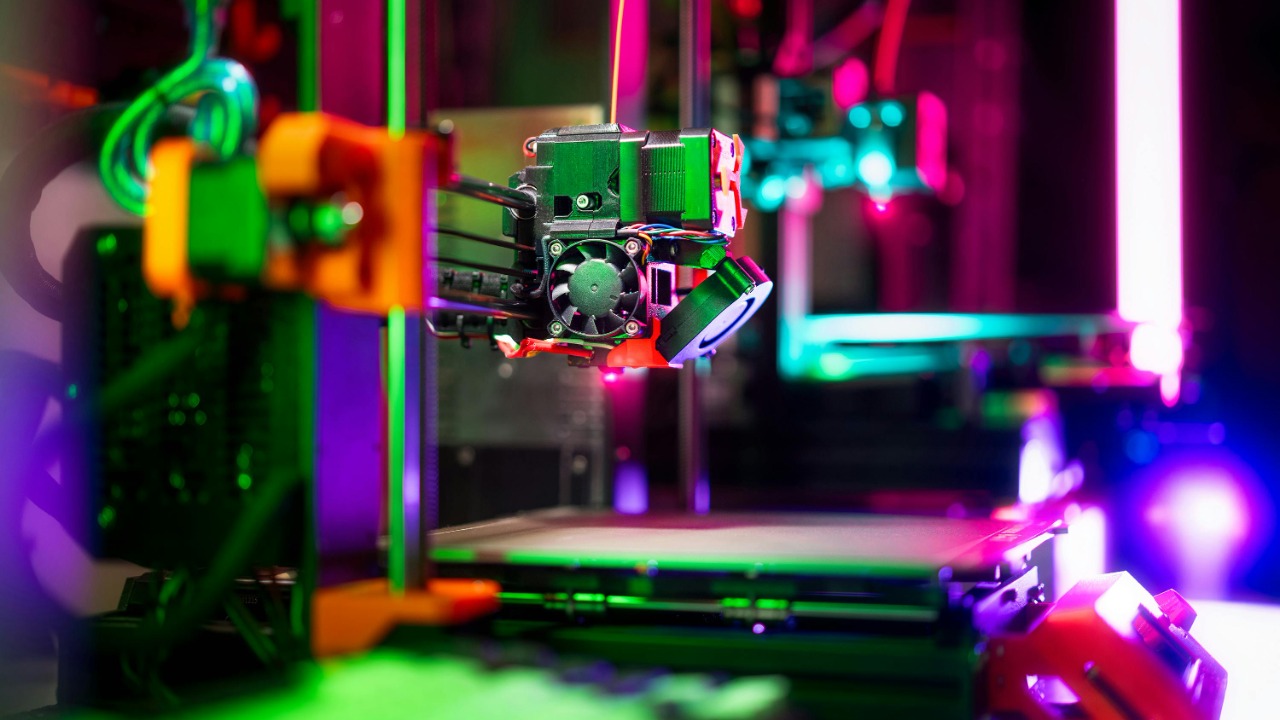

Robotic arms designed for 3D printing are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in additive manufacturing. These robots can produce intricate designs with a degree of precision that is challenging to achieve manually. By precisely controlling the deposition of materials, they create complex structures layer by layer, ensuring consistency and accuracy at every step.
The integration of robotic arms in 3D printing has opened up opportunities in various sectors, including aerospace, healthcare, and consumer goods. As technology advances, these robots continue to improve, offering greater flexibility and efficiency in producing customized and detailed objects.
Autonomous Drone Systems
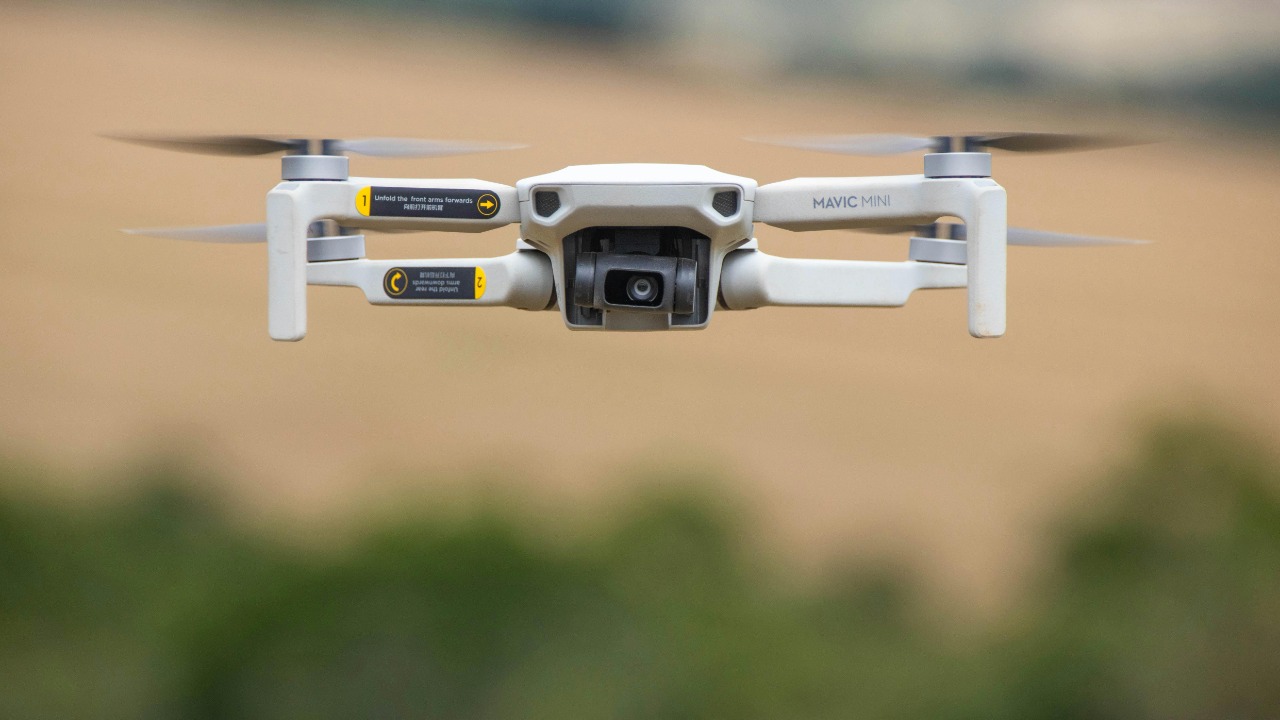

Autonomous drone systems are enhancing precision in tasks ranging from aerial photography to agricultural monitoring. These drones are equipped with advanced sensors and GPS technology, enabling them to navigate complex environments and gather data with remarkable accuracy. Their ability to fly in predefined patterns ensures consistent coverage, whether monitoring crop health or capturing high-resolution images.
With continuous improvements in bio-mimetic robotic technology, drones are becoming more adept at performing precise tasks autonomously. Their precision and reliability make them invaluable tools in fields where accuracy and efficiency are critical.
CNC Machining Robots
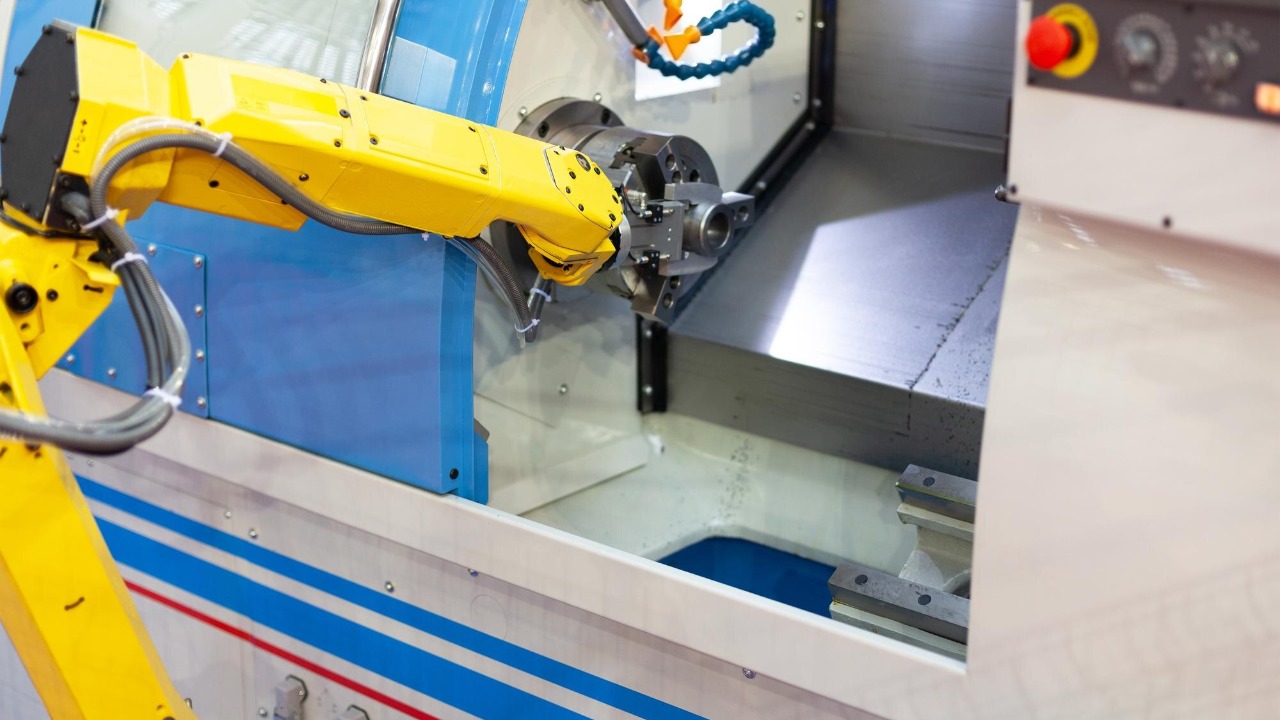

CNC machining robots are transforming the manufacturing landscape by delivering unparalleled precision in cutting and shaping materials. These robots are programmed to execute complex machining tasks with a high degree of accuracy, making them ideal for producing intricate components in industries like aerospace and automotive.
The precision of CNC machining robots not only enhances product quality but also reduces waste and production time. As manufacturers continue to seek ways to optimize their processes, these robots remain at the forefront of precision engineering, ensuring products meet stringent quality standards.
Agricultural Harvesting Robots
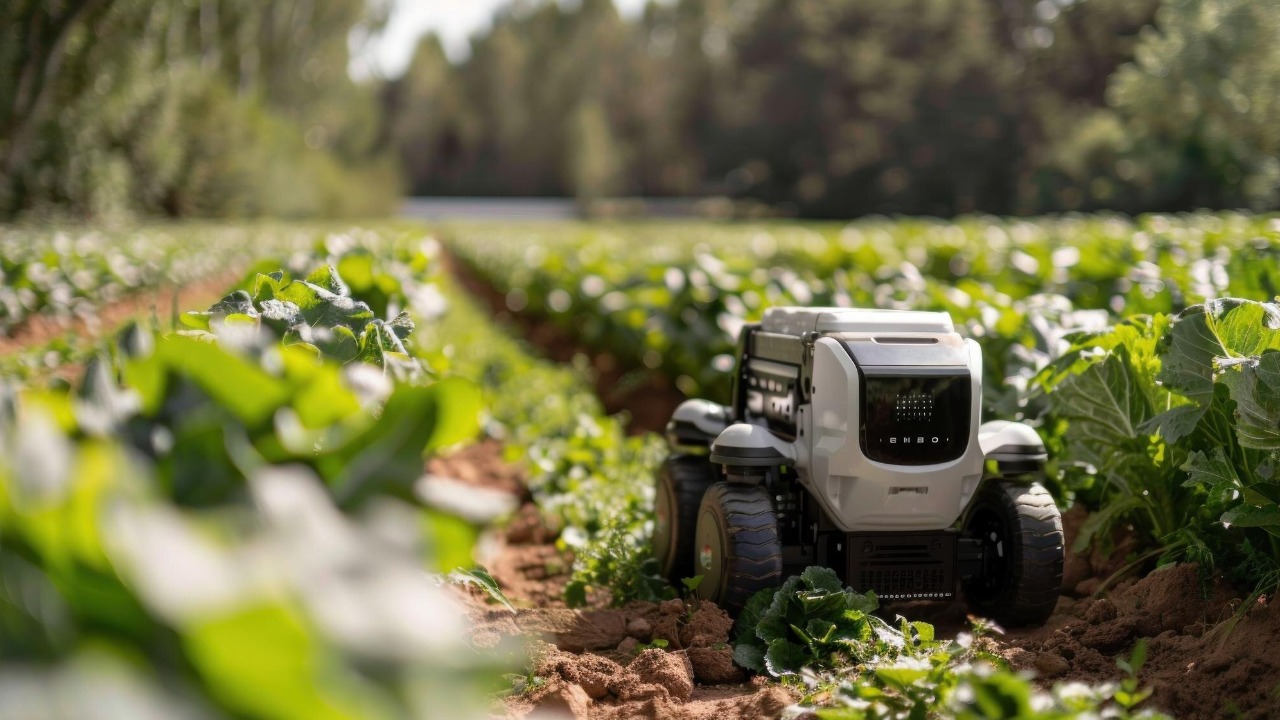

Agricultural harvesting robots are designed to perform the delicate task of picking fruits and vegetables with precision, reducing damage to crops and increasing yield. These robots use advanced vision systems and machine learning algorithms to identify ripe produce and harvest it with care.
In a world where food demand continues to rise, the precision and efficiency of harvesting robots are becoming increasingly important. Their ability to work tirelessly and accurately makes them a valuable asset to farmers seeking to improve productivity and sustainability.
Laboratory Automation Robots
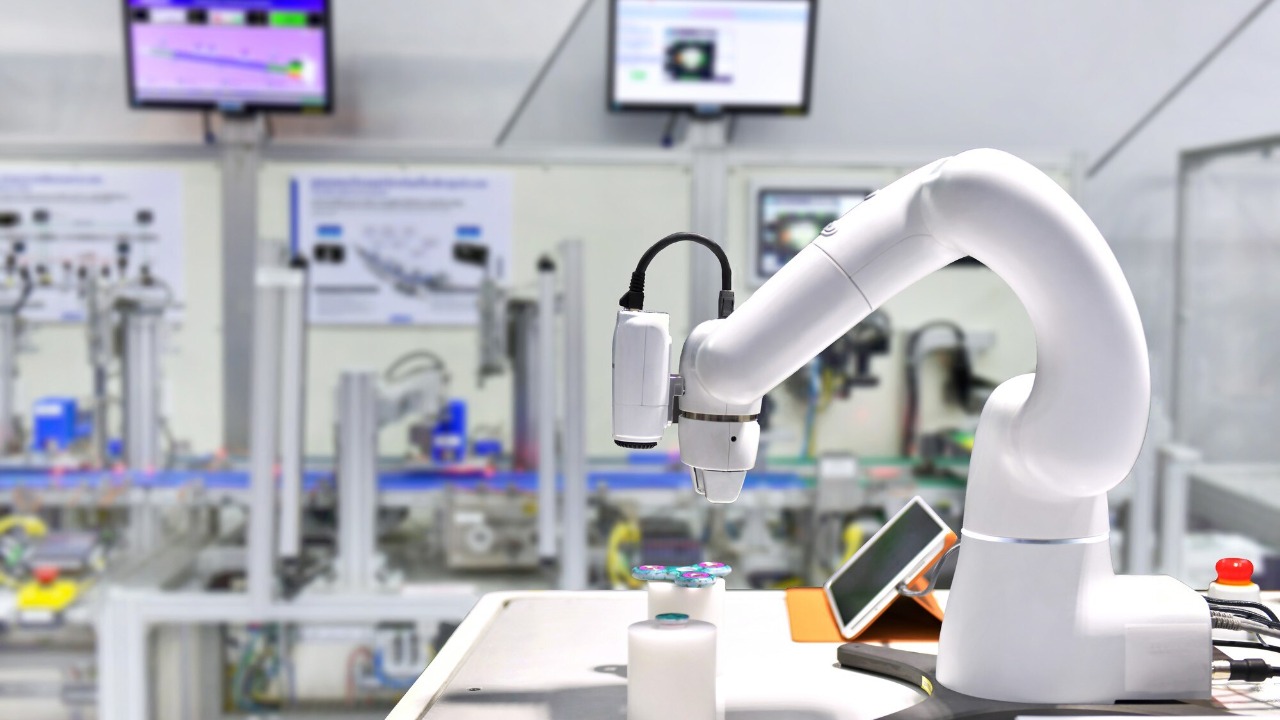

Laboratory automation robots enhance precision in research and diagnostic laboratories by performing repetitive tasks with consistent accuracy. These robots automate processes such as pipetting, sample analysis, and data recording, ensuring reliable and reproducible results.
By integrating automation technology into laboratory workflows, researchers can focus on more complex tasks, improving overall efficiency and productivity. The precision offered by these robots is essential for maintaining high standards in scientific research and medical diagnostics.
Robotic Exoskeletons for Rehabilitation
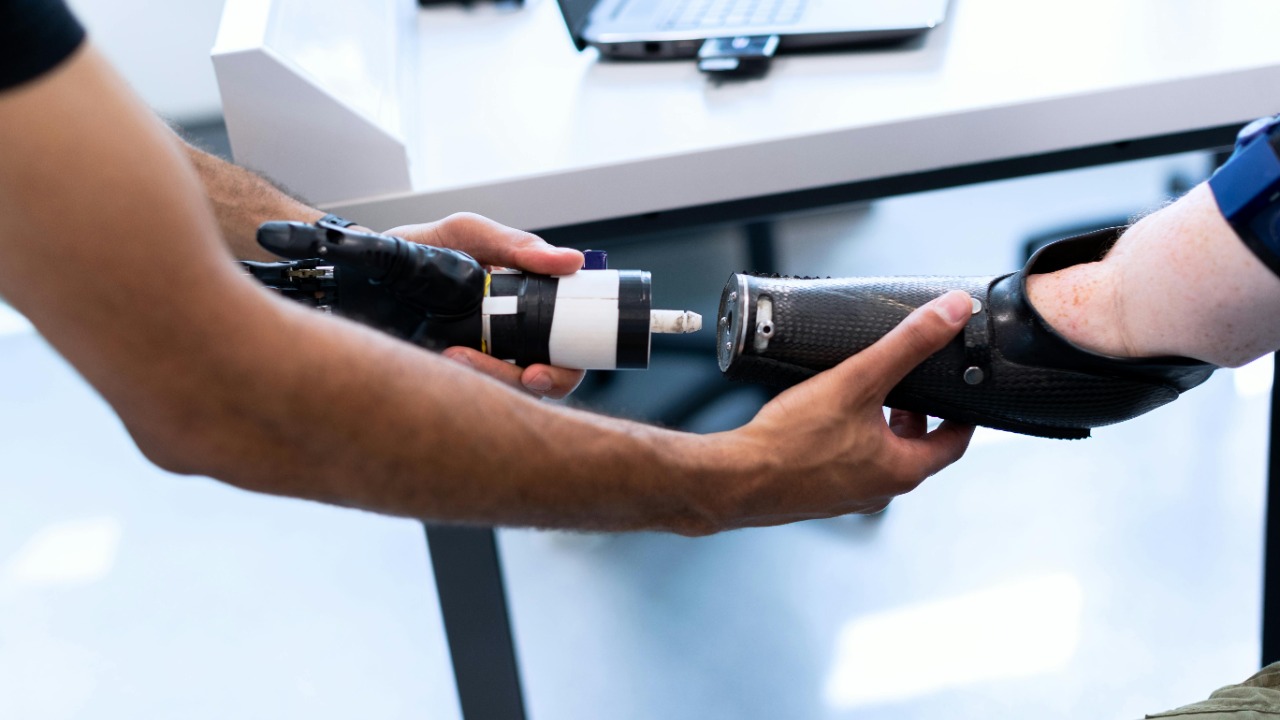

Robotic exoskeletons are revolutionizing rehabilitation by providing patients with precise and controlled movements during physical therapy. These exoskeletons support and guide patients’ limbs, enabling them to practice walking and other movements with proper alignment and consistency.
The precision of robotic exoskeletons is crucial in helping patients regain mobility and strength. As technology advances, these devices are becoming more accessible and effective, offering new hope to individuals recovering from injuries or living with mobility impairments.