
Recent advancements in nanotechnology have made their way into the food industry, promising enhanced flavors, improved nutritional profiles, and longer shelf lives. However, alongside these benefits come significant concerns about the safety and ethical implications of nanotech in our diets. Exploring the potential dangers associated with using nanotechnology in food production and consumption reveals a complex landscape of benefits and risks.
Understanding Nanotechnology in Food
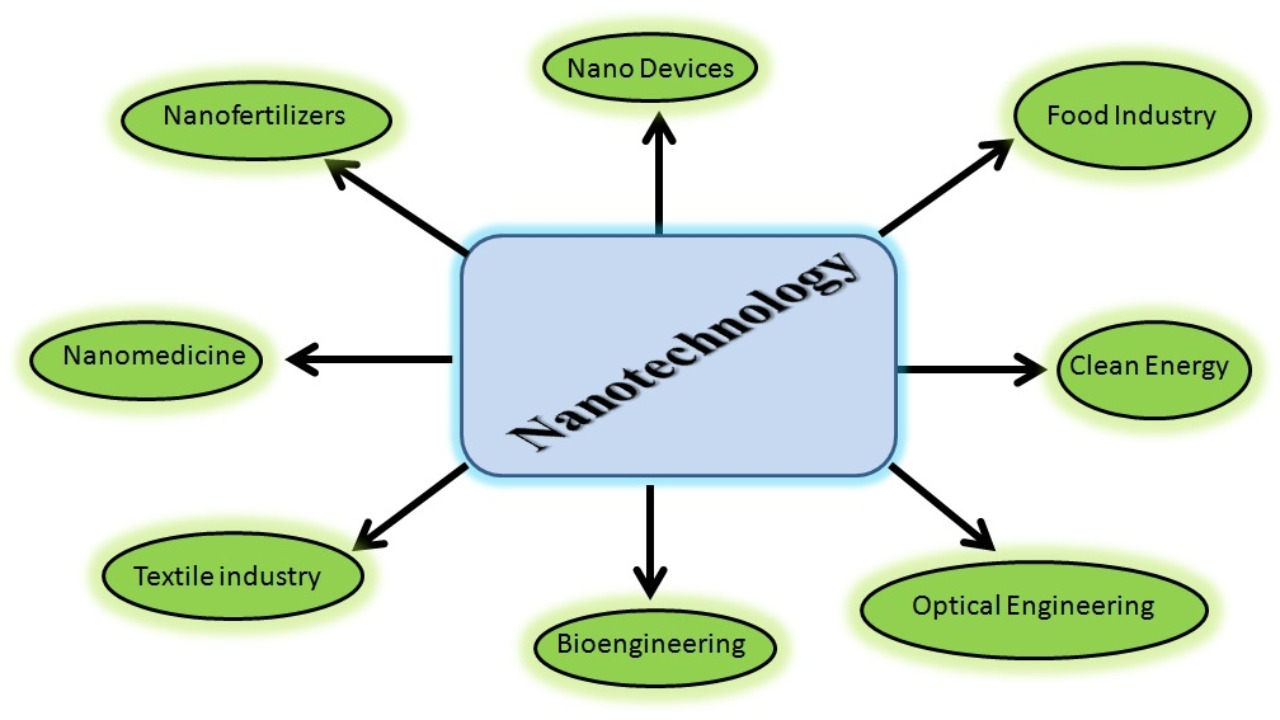
Nanotechnology in food involves manipulating matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale to improve food quality and safety. Common applications include nano-encapsulation, which enhances flavors and preserves nutrients, and nano-emulsions that improve the texture and stability of food products. These innovations promise significant improvements in food manufacturing and preservation.
The current market trends indicate a growing presence of nanotechnology in food products. Items such as dietary supplements, beverages, and processed foods are increasingly being enhanced with nanoparticles. The rise in consumer demand for fortified and functional foods has further propelled the integration of nanotech in the industry, with countries like the United States and China leading in production and consumption.
Regulatory frameworks governing nanotechnology in food vary significantly across the globe. While the European Union maintains strict regulations, requiring comprehensive risk assessments before market approval, other regions like the United States have adopted a more lenient approach. This discrepancy can create challenges in establishing uniform safety standards and ensuring consumer protection worldwide.
Health Risks and Safety Concerns

Despite the potential benefits, there are significant health risks associated with nanotechnology in food. Some studies have raised concerns about the potential toxicity of nanoparticles. For example, research has shown that certain nanoparticles may interfere with human digestion and absorption, posing risks to gut health. The small size of nanoparticles allows them to penetrate biological barriers, leading to unforeseen health complications.
Long-term health effects are also a significant concern, as there is a notable lack of comprehensive studies on the prolonged consumption of nano-enhanced foods. The absence of long-term data makes it difficult to assess the potential risks, leaving consumers and health professionals in the dark about the full implications of these technological advancements.
Additionally, the potential for bioaccumulation and environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Nanoparticles introduced into the food chain may accumulate in the human body and the environment, leading to adverse outcomes over time. As these particles persist, they may contribute to ecological imbalances, further exacerbating the health risks associated with their use.
Ethical and Social Implications

One of the most pressing ethical concerns is the lack of transparency and labeling of nano-enhanced foods. Consumers have the right to know what is in their food, yet many products do not disclose the presence of nanotechnology. This lack of transparency undermines consumer trust and raises questions about informed consent in dietary choices.
Public perception of nanotechnology in food varies, with some consumers embracing the advancements and others expressing skepticism. Trust plays a crucial role in the acceptance of new food technologies. Negative perceptions can be fueled by a lack of information or misinformation, further complicating the relationship between consumers and food manufacturers.
Socioeconomic factors also come into play, as the integration of nanotechnology in food may exacerbate existing disparities. Access to safe and nutritious food is already unevenly distributed, and the potential cost implications of nano-enhanced foods could widen the gap between different socioeconomic groups, limiting access for those who may benefit the most.
Alternatives and Future Directions

In light of these concerns, exploring natural and organic approaches that can achieve similar benefits without the associated risks is crucial. Techniques such as fermentation and fortification with natural compounds offer promising alternatives to nanotechnology, promoting food safety and sustainability.
Ongoing research is essential to address the challenges posed by nanotechnology in food. Scientists are actively investigating methods to mitigate potential risks, with studies focusing on the development of safer nanoparticle formulations and biodegradable options. These efforts aim to balance innovation with safety, ensuring that technological advancements do not compromise consumer health.
Policymakers and industry leaders play a vital role in shaping the future of nanotechnology in food. By collaborating to establish robust safety standards and transparent regulations, they can foster consumer confidence and promote responsible innovation. Such initiatives are crucial for ensuring that the benefits of nanotechnology are realized without compromising public health.
Consumer Awareness and Education
Increasing consumer awareness about the presence and safety of nanotech in food is vital. Education initiatives can empower consumers to make informed decisions, fostering a better understanding of the benefits and risks associated with nano-enhanced foods.
Providing resources and tips for consumers can aid in making informed choices. Organizations and platforms can offer guidance on identifying and evaluating nano-enhanced products, ensuring that consumers have access to reliable information. This knowledge enables individuals to navigate the complex landscape of modern food technologies.
Advocacy for stricter regulations and better transparency in the food industry is essential. Engaging with policymakers and industry leaders can drive change, promoting a more informed and equitable approach to food safety. Encouraging public dialogue and participation can help bridge the gap between consumers and producers, fostering a more transparent and trustworthy food system.