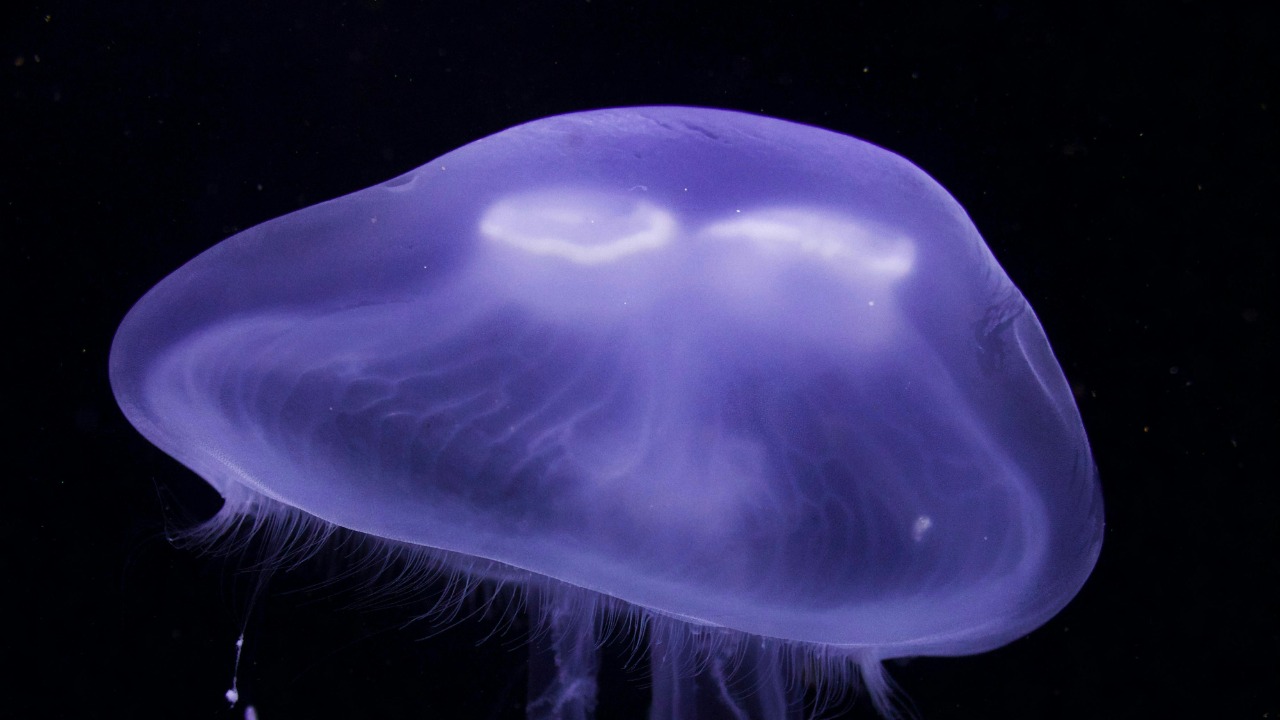

In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have identified a gene responsible for the biological immortality of the Turritopsis dohrnii, commonly known as the “immortal jellyfish.” This unique species has become a focal point for aging research, sparking hope for breakthroughs in human longevity. By unraveling the mysteries of this remarkable organism, researchers are delving into the potential applications for extending human life.
The Immortal Jellyfish Phenomenon
The Turritopsis dohrnii, often referred to as the “immortal jellyfish,” possesses an extraordinary capability that defies the typical biological constraints of aging. This small, transparent jellyfish, native to the Mediterranean Sea and found in oceans around the world, can revert its cells to an earlier state. This process, known as transdifferentiation, allows the jellyfish to transform from its adult medusa stage back into a polyp, essentially starting its lifecycle anew. This remarkable rejuvenation process challenges our conventional understanding of aging and death.
Scientifically, the jellyfish’s ability to revert to its juvenile form represents a significant deviation from the standard progression of life. While most species follow a linear lifecycle from birth to death, the immortal jellyfish can cycle through its life stages indefinitely under the right conditions. This unique trait has made it a subject of intense scientific interest, as researchers aim to uncover the genetic and cellular mechanisms underlying this biological phenomenon. Recent studies, including one published in PNAS, have begun to elucidate the complex processes that enable this jellyfish to bypass the traditional aging processes.
The Discovery of the Immortality Gene
At the heart of the immortal jellyfish’s extraordinary capability lies a specific gene, recently identified by scientists as a crucial component of its regenerative prowess. Through advanced genome sequencing techniques, researchers have pinpointed this “immortality gene” that plays a pivotal role in cellular regeneration and rejuvenation. The identification of this gene opens new avenues for understanding how some organisms achieve biological immortality and how such mechanisms might be harnessed for human benefit.
The process of isolating and studying this gene has been facilitated by significant advancements in genomic technologies. Sophisticated tools such as CRISPR and next-generation sequencing have enabled scientists to delve deeper into the jellyfish’s genetic makeup. These technologies not only help in isolating the specific gene responsible for its unique capabilities but also provide insights into its function and potential applications. A detailed exploration of these methodologies can be found in an article by Futurism, highlighting the cutting-edge techniques employed in this groundbreaking research.
Implications for Human Aging and Longevity
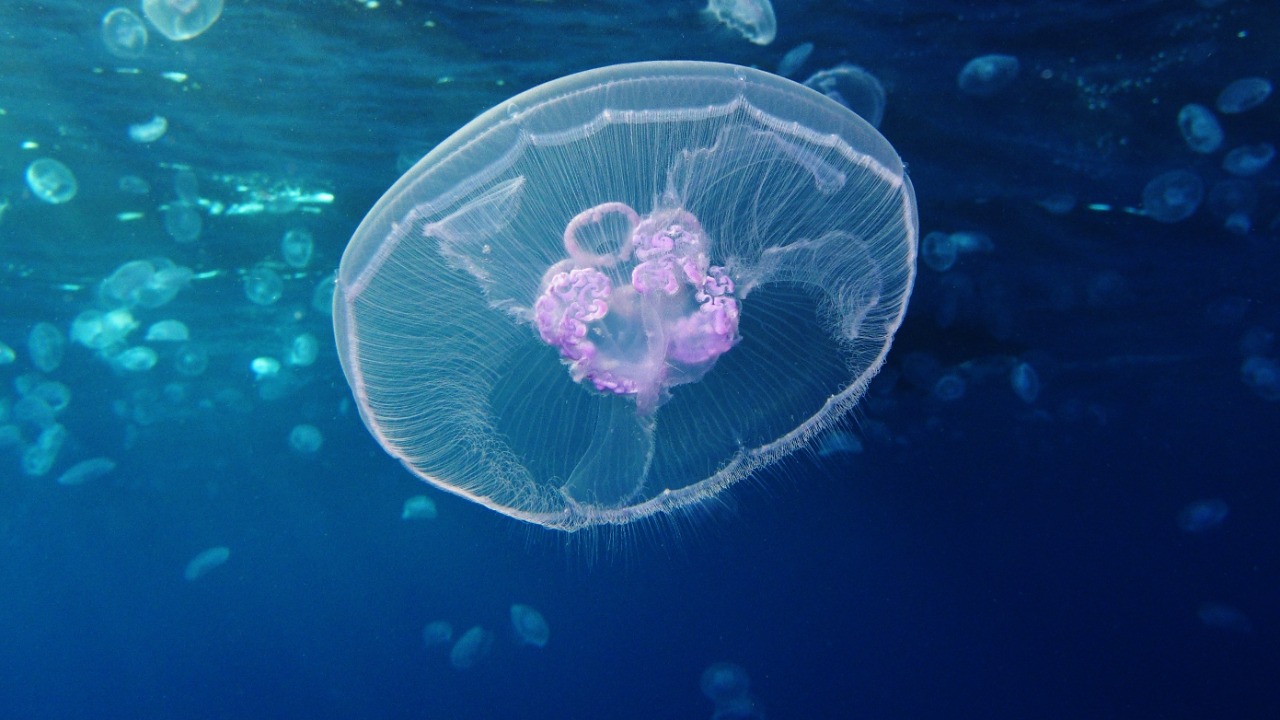

The discovery of the immortality gene in the immortal jellyfish has profound implications for the field of anti-aging research. By understanding the genetic basis of the jellyfish’s regenerative abilities, scientists hope to uncover new strategies for combating human aging and age-related diseases. This could potentially revolutionize the development of therapies aimed at prolonging human life, improving the quality of life, and delaying the onset of age-associated conditions. The potential for such applications is discussed in a feature by Reuters, which explores the future of anti-aging science.
However, the translation of these findings from jellyfish to humans is fraught with challenges. The biological differences between humans and jellyfish are vast, and the complexities of applying jellyfish genetics to human physiology are significant. Ethical considerations also come into play, as extending human lifespan raises questions about overpopulation, resource distribution, and the societal impacts of a potentially longer-lived population. Ongoing research is essential to address these challenges, and future studies will need to explore these ethical dimensions alongside scientific advancements.
Broader Scientific and Environmental Significance

Beyond its implications for human aging, the study of the immortal jellyfish also holds significance for ecological and conservation efforts. As a species with unique regenerative capabilities, the jellyfish plays a vital role in marine ecosystems. Understanding its ecological impact and ensuring its conservation is crucial, given the increased scientific interest and potential environmental pressures. Conservation efforts are being prompted to protect this species from over-exploitation and habitat loss.
Moreover, the insights gained from jellyfish research contribute to the broader field of regenerative medicine. The potential applications extend beyond anti-aging to include breakthroughs in tissue regeneration and repair. By studying the cellular processes in jellyfish, scientists can develop innovative medical technologies that could revolutionize treatments for injuries and degenerative diseases. An exploration of these contributions can be found in resources like Texas A&M University, which delves into the broader implications of jellyfish research on regenerative medicine.
In conclusion, the discovery of the immortality gene in the Turritopsis dohrnii represents a significant milestone in scientific research. While challenges remain in translating these findings to human applications, the potential benefits for anti-aging therapies and regenerative medicine are immense. As researchers continue to explore this remarkable jellyfish, the possibilities for extending and enhancing human life become increasingly tangible, paving the way for future breakthroughs in understanding and manipulating the aging process.