
A groundbreaking discovery has been made by paleontologists in Africa with the identification of a new dinosaur species, Musankwa sanyatiensis, found in Zimbabwe. This find not only enriches our understanding of prehistoric life on the continent but also provides fresh insights into the evolutionary history of dinosaurs globally. The unearthing of this species marks a significant milestone in paleontology, offering a glimpse into the ancient ecosystems that once thrived in this region.
The Discovery of Musankwa sanyatiensis
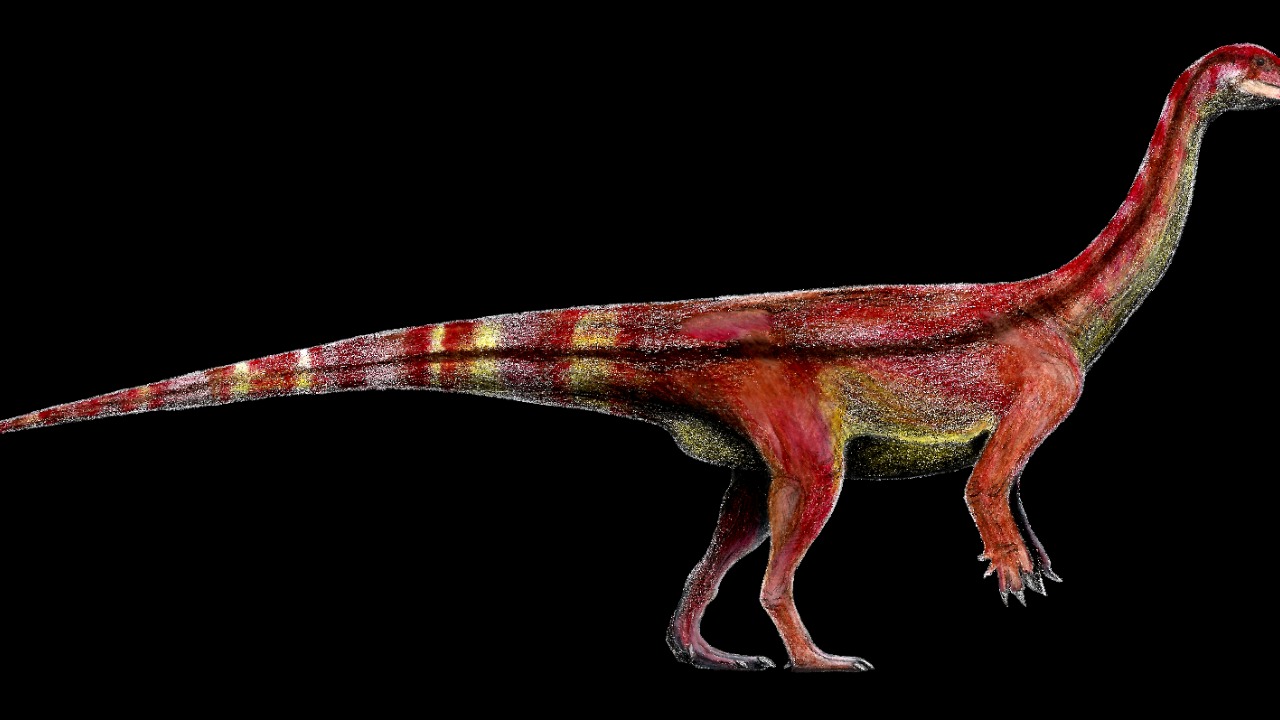

The excavation site in Zimbabwe’s Sanyati Basin has drawn considerable attention from the paleontological community. Located in a region known for its rich geological formations, the site presented a unique opportunity to uncover fossils that have been buried for millions of years. The discovery of Musankwa sanyatiensis’ fossilized remains, including a partial skeleton and distinct cranial features, was pivotal in identifying this new species. The meticulous process of excavation involved delicate techniques to ensure the preservation of these invaluable remains.
Collaboration played a crucial role in this discovery. Scientists from Zimbabwe, along with international experts, worked in tandem to piece together the fossil evidence. Their combined expertise facilitated a comprehensive analysis, leading to the official recognition of the species as Musankwa sanyatiensis. This collaborative effort underscores the importance of global teamwork in advancing our understanding of prehistoric life.
Significance in the Paleontological Record
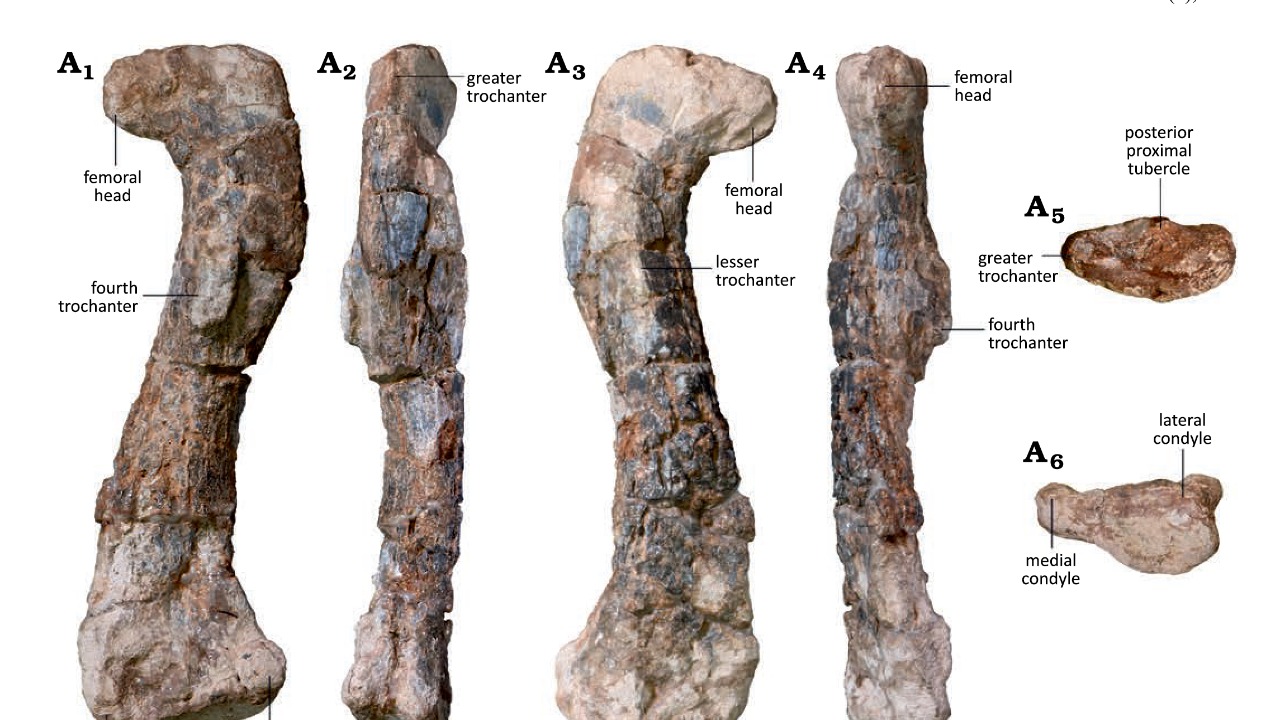
Musankwa sanyatiensis holds a distinctive place in the dinosaur family tree. As the oldest species discovered in Africa to date, it provides critical insights into the evolutionary timeline of dinosaurs on the continent. This species is believed to have roamed the Earth during the Late Triassic period, making it a key piece in the puzzle of dinosaur evolution. Its discovery challenges existing theories about how dinosaurs migrated and diversified across ancient landmasses.
The characteristics of Musankwa sanyatiensis, including its unique skeletal structure, offer valuable information about the adaptations that allowed dinosaurs to thrive in diverse environments. The implications of this find extend beyond Africa, offering clues about global dinosaur migration patterns and evolutionary strategies. By placing Musankwa sanyatiensis within the broader context of the dinosaur family tree, scientists can better understand the dynamic processes that shaped life on Earth millions of years ago.
Challenges and Methods in Dinosaur Excavation
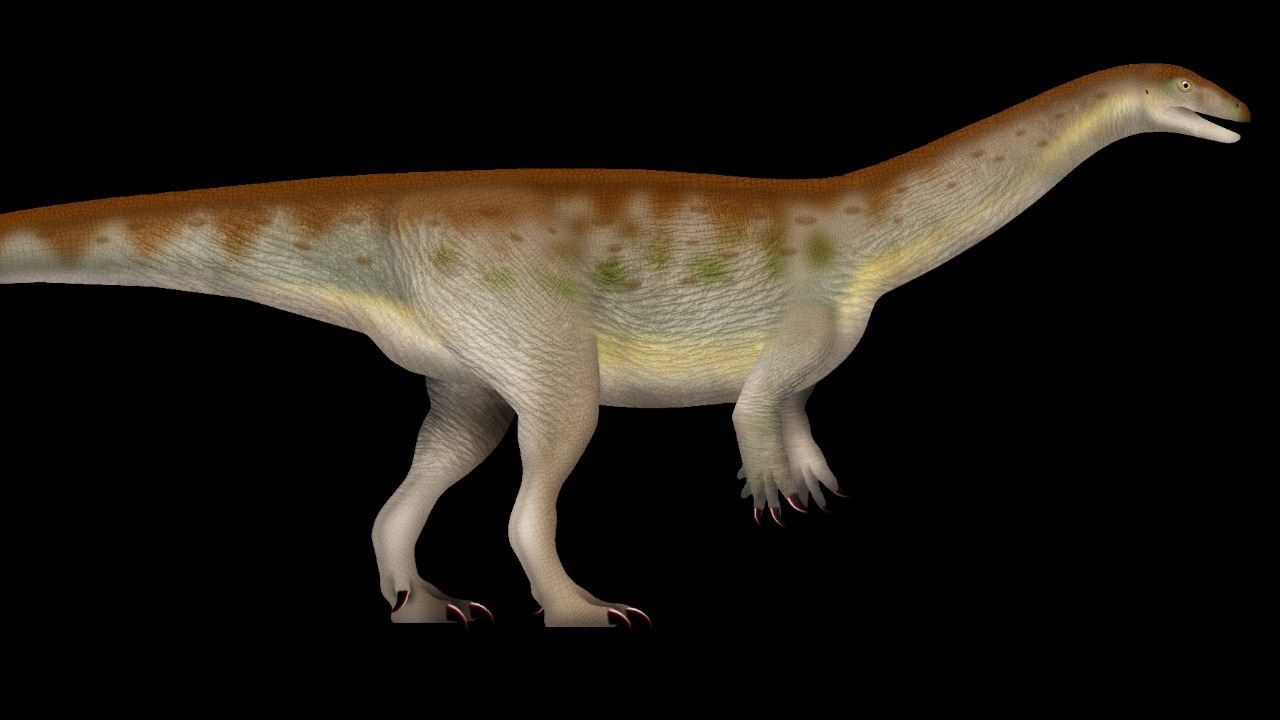

Excavating dinosaur fossils is a complex endeavor that requires a combination of traditional methods and modern technology. In the case of Musankwa sanyatiensis, paleontologists employed ground-penetrating radar and 3D modeling to locate and analyze the fossil sites. These tools enabled researchers to visualize the extent of the fossil beds and plan their excavation strategies accordingly. Such technological advancements are increasingly vital in overcoming the challenges posed by Africa’s varied and often unforgiving terrain.
Despite these innovations, paleontologists face numerous obstacles, including harsh weather conditions and remote locations that are difficult to access. The Sanyati Basin, for instance, is characterized by rugged landscapes that make transportation and excavation logistics challenging. However, the dedication and expertise of the research team ensured the successful recovery of the fossils. Their efforts highlight the perseverance required in the field of paleontology, where every discovery involves overcoming significant hurdles.
Impact on Local Communities and Scientific Community

The discovery of Musankwa sanyatiensis has the potential to significantly impact local communities in Zimbabwe. By attracting attention from tourists and researchers alike, the region stands to benefit economically and educationally. The presence of such a significant fossil find can enhance local tourism, drawing visitors eager to learn about the ancient history of the area. Moreover, educational programs centered around the discovery can inspire future generations to pursue careers in science and paleontology.
On a broader scale, this discovery contributes to the global scientific community by enriching our understanding of dinosaur evolution. It encourages further research and exploration in Africa, a continent that holds many untapped paleontological treasures. Leading scientists involved in the research have expressed optimism about the potential for new discoveries. According to recent reports, the collaborative framework established during this project serves as a model for future international research initiatives.
Future Prospects and Research Directions

The discovery of Musankwa sanyatiensis opens the door to numerous future prospects in paleontological research. Plans are already underway for further excavations in Africa, aiming to uncover more species that could shed light on the continent’s prehistoric life. The integration of new technologies, such as advanced imaging techniques and AI-driven analysis, promises to revolutionize the field. These innovations will enable researchers to conduct more detailed studies and analyses, potentially leading to groundbreaking discoveries.
International collaboration remains a cornerstone of future research efforts. By fostering partnerships with scientists from around the world, researchers can pool their resources and knowledge to explore Africa’s rich fossil record. The importance of such collaborations cannot be overstated, as they are essential for tackling the complex questions surrounding dinosaur evolution and extinction. As new findings emerge, the scientific community can continue to build upon the legacy of discoveries like
Musankwa sanyatiensis, ensuring that our understanding of the ancient world continues to grow.
In conclusion, the identification of Musankwa sanyatiensis is a remarkable achievement that highlights the importance of both local and international efforts in paleontology. This discovery not only enriches our understanding of dinosaur evolution but also underscores the potential for future research in Africa. As scientists continue to explore the continent’s ancient landscapes, the prospects for new and exciting discoveries remain vast.