
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping various sectors, and healthcare is no exception. With AI’s potential to outperform humans in specific tasks, the question arises: could AI replace doctors sooner than we think? The factors contributing to this possibility and the implications for the future of healthcare are worth exploring.
Technological Advancements in AI
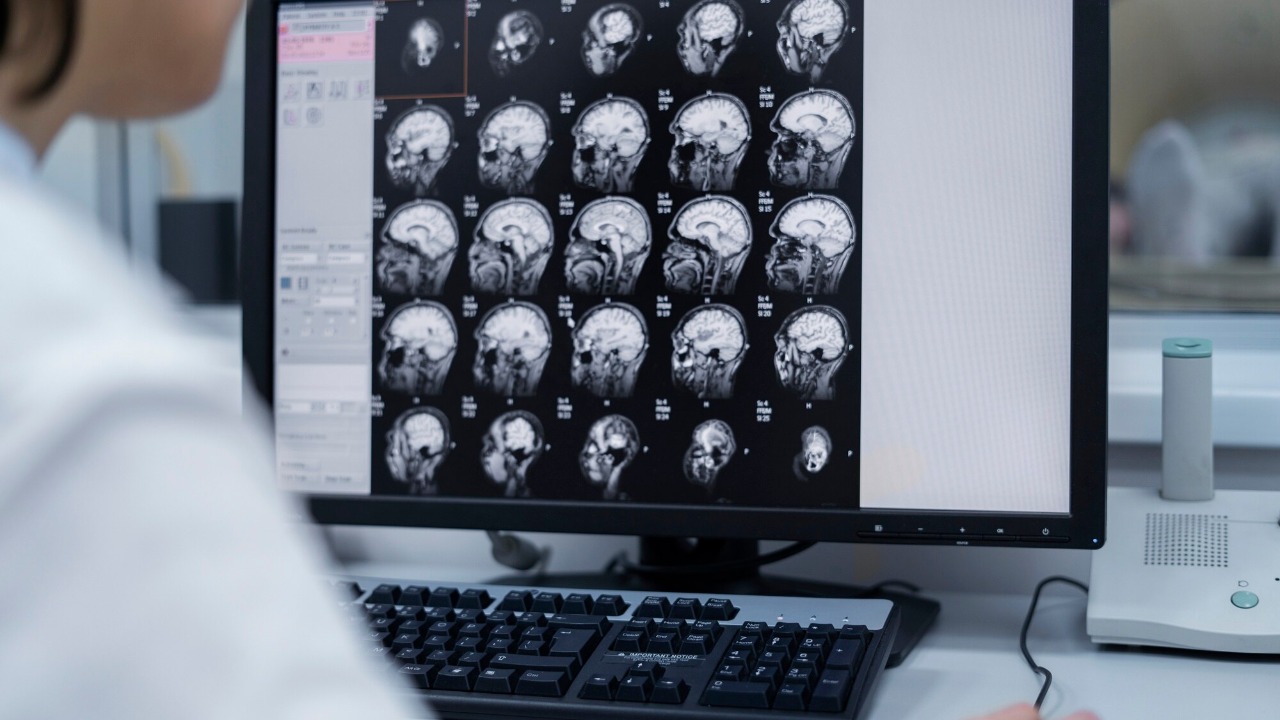
One of the most compelling areas where AI is making significant strides is in diagnostic accuracy. AI systems, such as Google’s DeepMind and IBM’s Watson, have demonstrated the capability to analyze medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with a precision that often surpasses human doctors. For instance, AI algorithms have been utilized to detect early signs of retinal diseases and breast cancer, reducing the chances of misdiagnosis and ensuring timely interventions. This enhanced accuracy not only improves patient outcomes but also builds trust in AI-driven diagnostics among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Moreover, the integration of AI with wearable technology is transforming patient monitoring. Devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch are equipped with AI-driven features that allow continuous health tracking. These wearables can monitor vital signs such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity levels, which can be crucial for early detection of health issues. AI algorithms analyze this data in real-time, alerting users and healthcare providers to potential health concerns before they escalate. This proactive approach to health management represents a significant shift from traditional reactive healthcare models.
In addition to diagnostics and monitoring, AI’s advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) are revolutionizing patient interactions and administrative efficiency. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle routine inquiries, schedule appointments, and provide medication reminders, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex tasks. Furthermore, NLP technology enables AI to analyze vast amounts of unstructured data, such as patient notes and clinical records, providing valuable insights for personalized treatment plans and improving overall healthcare delivery.
Economic and Efficiency Factors

The economic implications of AI in healthcare are profound. AI systems offer a level of cost-effectiveness that is transforming the industry. By automating routine tasks such as data entry, billing, and appointment scheduling, AI reduces the administrative burden on healthcare staff, allowing them to concentrate on direct patient care. Additionally, AI’s ability to minimize human error in diagnostics and treatment planning can lead to significant cost savings by reducing the need for unnecessary tests and procedures.
AI is also playing a crucial role in increasing healthcare accessibility. In remote or underserved areas where access to medical professionals is limited, AI tools can provide essential medical expertise. Telemedicine platforms powered by AI facilitate virtual consultations, enabling patients to receive timely care without the need for travel. This technology bridges the gap in healthcare access, ensuring that more people can benefit from quality medical services regardless of their geographical location.
Furthermore, AI’s scalability is unmatched. AI systems can process vast amounts of data and manage multiple patients simultaneously, addressing a critical constraint faced by human practitioners. This scalability is particularly valuable during healthcare crises, such as pandemics, where the demand for services can overwhelm traditional healthcare systems. AI’s ability to efficiently triage patients and allocate resources ensures that healthcare facilities can maintain high standards of care even under pressure.
Ethical and Legal Considerations

As AI becomes more integrated into healthcare, ethical and legal challenges must be addressed. One major concern is determining accountability and liability in AI-driven healthcare decisions. When an AI system makes a medical error, it remains unclear who should be held responsible—the developers, the healthcare providers, or the technology itself. This lack of clarity presents significant challenges for regulators and could complicate the adoption of AI technologies in clinical settings.
Data privacy is another critical issue. AI systems rely on large datasets to function effectively, raising concerns about patient privacy and data security. Ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA is essential to protect sensitive health information. Healthcare providers must implement robust data protection measures to maintain patient trust and prevent unauthorized access to personal health records.
Moreover, the issue of bias and fairness in AI systems cannot be overlooked. AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data is biased, the AI system will likely produce biased outcomes, potentially leading to disparities in healthcare delivery. Addressing these biases is crucial to ensure that AI technologies provide equitable healthcare outcomes for all populations, regardless of race, gender, or socioeconomic status.
Current Limitations and Challenges
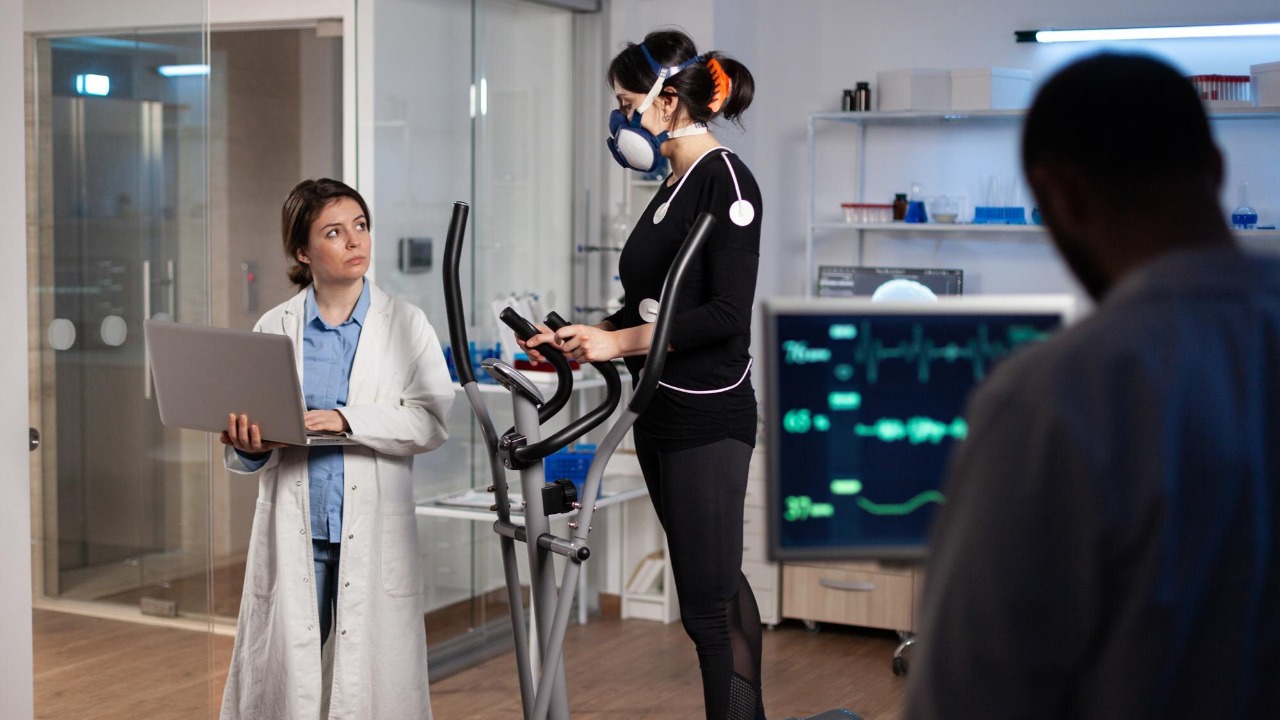

Despite the promising advancements, AI still faces significant limitations in healthcare. One of the most notable is the lack of empathy. While AI can analyze data and make recommendations, it cannot replicate the human touch and emotional intelligence that are vital in patient care. The ability to empathize, understand patient concerns, and provide emotional support is an intrinsic part of the doctor-patient relationship that AI cannot replace.
Another challenge is the complexity of medical decision-making. While AI excels at processing large datasets and identifying patterns, some medical decisions require human judgment and experience. The nuances of patient history, lifestyle, and preferences can influence treatment decisions, necessitating a level of discernment that AI systems currently lack. Moreover, successful AI integration in healthcare requires interdisciplinary collaboration. Technologists and healthcare professionals must work together to ensure that AI tools are designed to meet clinical needs and enhance patient outcomes.
Future Implications for Healthcare Professionals
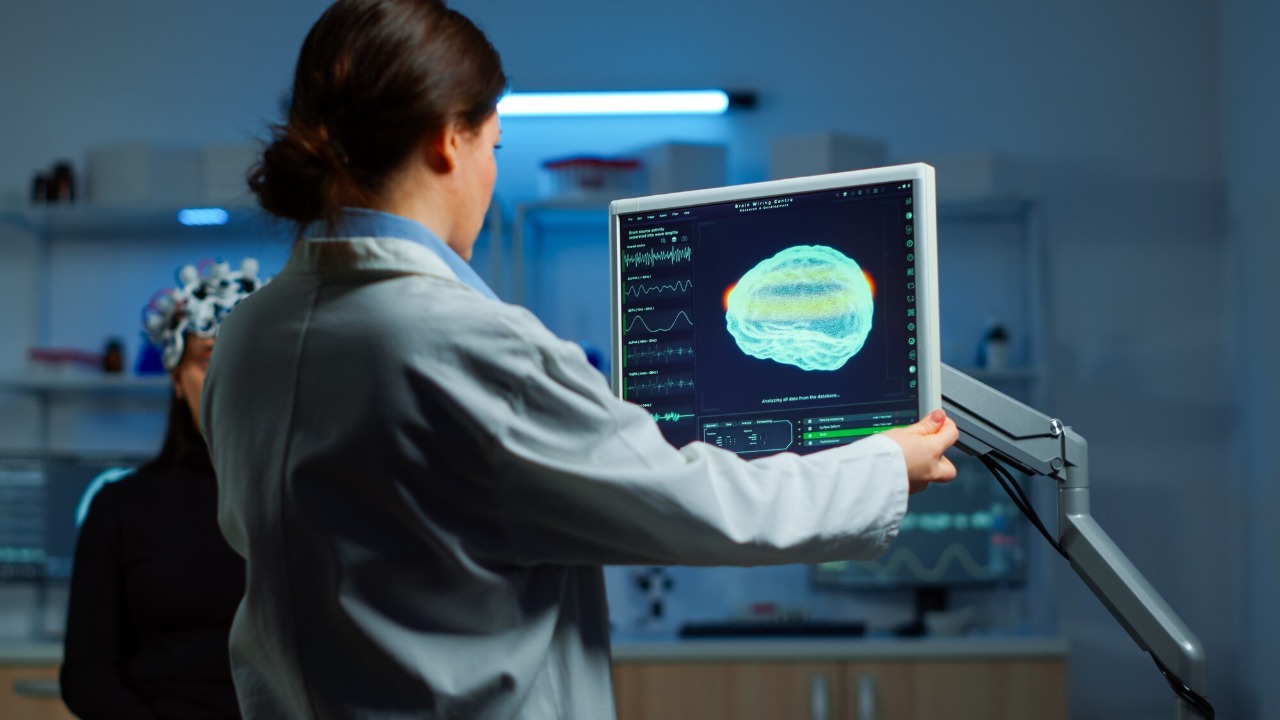

The rise of AI in healthcare is reshaping the roles of healthcare professionals. As AI takes over routine tasks, doctors and nurses may find themselves focusing more on complex cases and direct patient interaction. This shift allows healthcare professionals to apply their expertise where it is most needed, enhancing the overall quality of care.
Continuous learning and adaptation will be crucial for medical professionals as they navigate this evolving landscape. Keeping up-to-date with AI technologies and understanding how to integrate new tools into clinical practice will become essential skills. Educational programs and training initiatives will play a vital role in equipping healthcare workers with the knowledge needed to thrive in an AI-enhanced environment.
While there are concerns about job displacement, AI also presents opportunities for new roles in healthcare. Positions related to AI management, data analysis, and technology integration are likely to emerge, creating demand for skills that blend medical expertise with technological proficiency. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, professionals who embrace AI will be well-positioned to lead the way in delivering innovative and effective patient care.