
Astronomers have recently sparked intrigue and excitement within the scientific community with the potential discovery of a new dwarf planet. This celestial body, yet to be officially named, could deepen our understanding of the solar system’s outer reaches and the objects that inhabit it. As researchers delve into this discovery, the implications for astronomy and planetary science are profound.
The Discovery Process
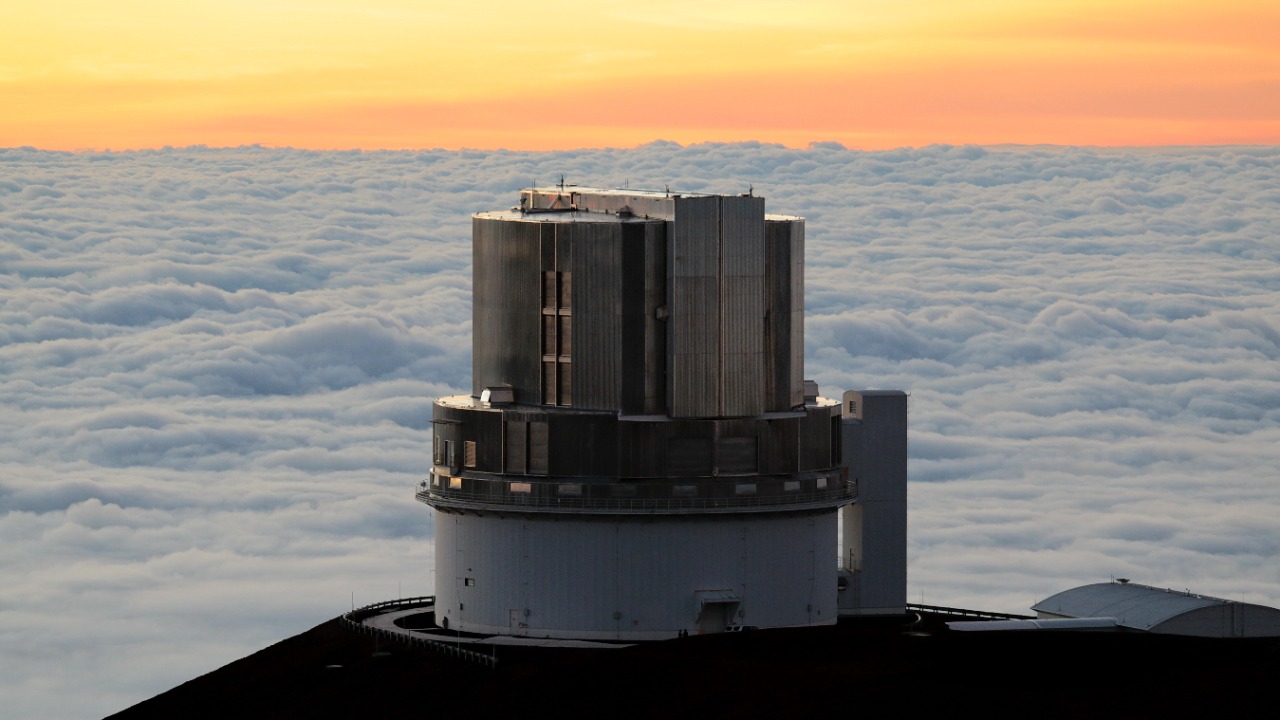

The search for celestial bodies located at the far reaches of our solar system is an intricate process that requires the use of advanced technology and observational methods. Telescopes such as the Subaru Telescope in Hawaii and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile are pivotal in these discoveries. These instruments allow astronomers to detect faint objects that are far away from Earth, using techniques like wide-field imaging and spectroscopy. The potential discovery of this new dwarf planet is a testament to the capabilities of these sophisticated tools, which provide invaluable data that might otherwise remain out of reach.
Once initial observations suggest the presence of a new object, extensive data analysis becomes crucial. Astronomers employ a variety of algorithms and specialized software to differentiate a new celestial object from other phenomena, such as asteroids or distant stars. This process involves scrutinizing vast amounts of data to identify unique characteristics of the potential dwarf planet. The role of machine learning and artificial intelligence in this realm is growing, with algorithms designed to process and analyze data more efficiently than ever before. Such advancements not only increase the accuracy of discoveries but also accelerate the timeline from initial detection to confirmation.
International collaboration among astronomers and research institutions is essential for the success of such projects. The discovery of this potential dwarf planet involved a global effort, with researchers from various countries contributing their expertise and resources. This collaborative spirit is a hallmark of modern astronomy, where shared knowledge and technology transcend borders to achieve common goals. The combined efforts of teams from different parts of the world underscore the importance of cooperation in advancing our understanding of the universe.
Characteristics of the Potential Dwarf Planet

The estimated size and composition of the potential dwarf planet offer fascinating insights into its nature. While exact measurements are still pending, preliminary data suggests that it could be comparable in size to other known dwarf planets like Pluto and Eris. Its mass and density provide clues about its composition, which could range from a mixture of ice and rock to more exotic materials. Understanding these characteristics helps astronomers draw comparisons with other bodies in the solar system and refine their models of planetary formation.
The orbital path of this celestial object is another area of keen interest. Located in the distant regions of the Kuiper Belt or possibly beyond, its orbit could provide vital information about the structure and dynamics of these outer solar system regions. By studying its trajectory, astronomers can infer its distance from the sun and how it interacts with other objects in its vicinity. This knowledge contributes to redefining our understanding of the solar system’s boundaries and the diverse population of bodies that inhabit its outskirts.
Speculating on the surface features and atmosphere of such a distant object is challenging due to the limitations of current observational technology. However, based on existing data, researchers can make educated guesses about its surface characteristics. It might possess a thin atmosphere composed of volatile compounds, similar to what has been observed on Pluto. Alternatively, its surface could be covered in frozen gases, creating a reflective, icy shell. Continued observations and future missions will be crucial in confirming these hypotheses and expanding our knowledge of such enigmatic worlds.
Significance of the Discovery
The potential discovery of a new dwarf planet has profound implications for planetary science. It challenges existing theories about the solar system’s formation and evolution, particularly concerning the Kuiper Belt. This region, a vast expanse beyond the orbit of Neptune, is home to countless icy bodies that could hold clues about the early solar system. By studying new discoveries in this area, scientists can refine their understanding of how planets form and evolve over time.
Moreover, this finding could significantly impact future research priorities and missions. As researchers gain more knowledge about the potential dwarf planet, it could become a target for future space missions. The prospect of exploring such distant objects inspires the development of new technologies and methodologies for space exploration. This discovery serves as a catalyst, encouraging scientists to push the boundaries of what is possible and explore the outer reaches of our solar system in greater detail.
Beyond the scientific community, discoveries like this one capture the public’s imagination and foster interest in astronomy. They highlight the importance of science education in helping people understand the universe and our place within it. As interest in space exploration grows, it is crucial to inspire future generations to pursue careers in STEM fields, ensuring that the quest for knowledge continues to thrive. Public engagement with these topics can lead to increased support for scientific research and exploration, ultimately benefiting society as a whole.
Challenges and Next Steps

Before the object can be officially classified as a dwarf planet, it must undergo a verification process based on criteria set by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). This process involves confirming its characteristics, such as size and orbital dynamics, to meet the established standards for dwarf planet classification. The IAU’s guidelines ensure consistency in how celestial bodies are categorized, but they also require considerable time and effort from the scientific community to satisfy.
Further study of the potential dwarf planet poses technological and financial challenges. The development and deployment of missions to explore distant regions of the solar system require significant investment and innovation. Agencies like NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) must weigh the costs and benefits of such endeavors, balancing them against other priorities in space exploration. Despite these hurdles, the scientific rewards of studying a new dwarf planet could justify the resources required, providing valuable insights into the solar system’s outer reaches.
Continued monitoring of the object is essential to refine our understanding and gather more data. Ongoing observations will help astronomers track its orbit, study its surface properties, and determine its composition more accurately. As technology advances and new techniques become available, the ability to observe and analyze distant celestial bodies will improve, offering more precise information and enhancing our knowledge of the universe.
Broader Implications for Astronomy

The discovery of a new dwarf planet could prompt discussions about planetary definitions and classifications within the astronomical community. As we uncover more objects in the solar system’s outer regions, the criteria for what constitutes a planet may evolve. This dialogue is crucial for ensuring that our understanding of the universe remains accurate and up-to-date, reflecting the latest discoveries and insights.
Such discoveries also have the power to inspire future generations of astronomers and scientists. By revealing the mysteries of the universe, they encourage curiosity and innovation, driving the pursuit of knowledge and exploration. Young people interested in space science may find their passion ignited by the prospect of discovering new worlds, leading them to pursue careers in astronomy and related fields.
Ultimately, the potential discovery of a new dwarf planet reminds us of the vast, largely unexplored universe awaiting discovery. Each new celestial body we uncover adds to our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. As we continue to explore the farthest reaches of the solar system and beyond, the possibilities for discovery are boundless, offering endless opportunities for learning and exploration.