
The presence of methane on Mars has long intrigued scientists, as it could potentially signify biological activity or geological processes. Recent studies suggest that these methane emissions may exhibit a seasonal pattern, adding a new layer of complexity to the Red Planet’s atmospheric dynamics. This article delves into the latest findings on Martian methane, exploring the implications for our understanding of Mars.
The Mystery of Martian Methane
For years, scientists have been captivated by the mysterious presence of methane on Mars. Historical detections of methane date back to the early 2000s, when telescopic observations first identified the gas in the Martian atmosphere. These early findings sparked a debate over the origins of methane, as it can be produced both biologically and geologically. Despite numerous studies, the question of whether Martian methane is a sign of life or a result of geological processes remains unanswered.
Potential sources of methane on Mars have been a significant point of discussion. On Earth, methane is often associated with biological activity, such as the decomposition of organic matter. However, geological processes can also produce methane through reactions between water and certain types of rock. The possibility that Martian methane could originate from microbial life beneath the planet’s surface is tantalizing, but the alternative explanation of geological activity also presents intriguing possibilities for understanding Mars’ history.
Detecting methane on Mars is no simple task. The thin Martian atmosphere and the presence of other gases make accurate measurements challenging. Instruments need to be incredibly sensitive to detect the trace amounts of methane present. As a result, researchers have faced difficulties in obtaining consistent data, leading to ongoing debates about the reliability of methane detections on Mars.
Seasonal Patterns in Methane Emissions

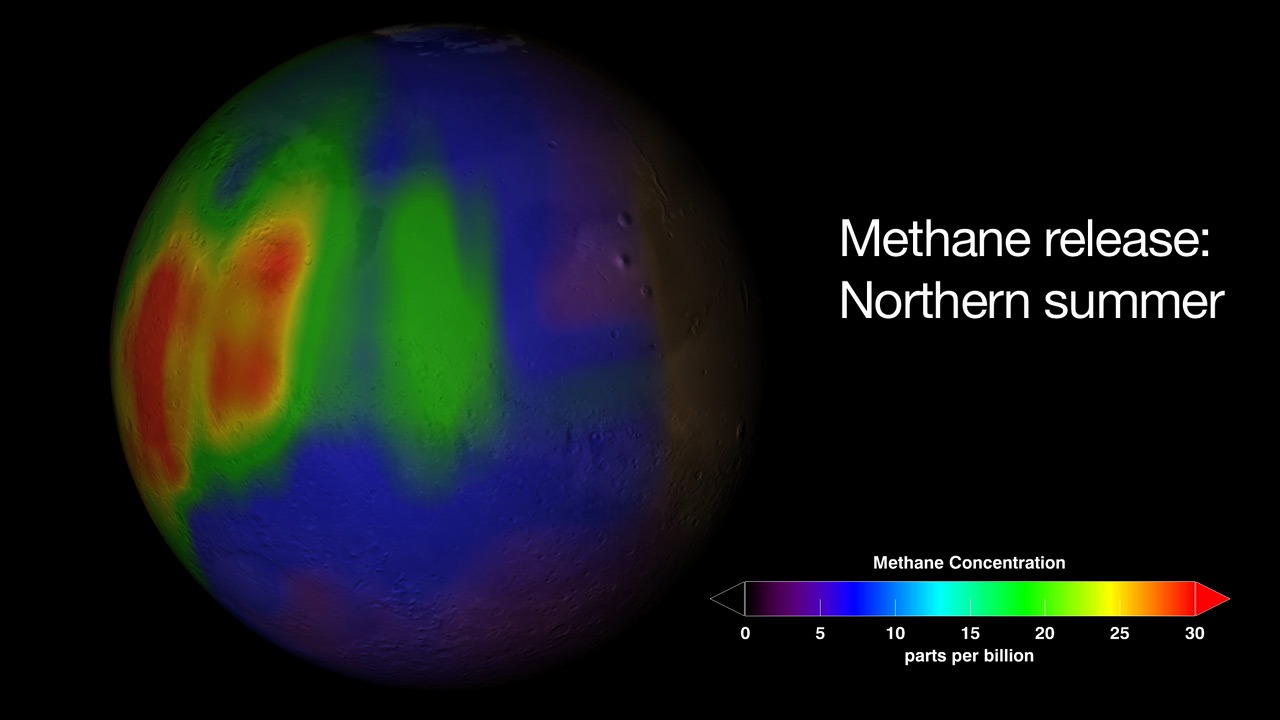
Recent studies have started to reveal that methane emissions on Mars may follow a seasonal pattern. Data from the Curiosity rover has shown that methane levels in the Martian atmosphere fluctuate with the seasons, reaching their peak during the summer months. This discovery adds a new dimension to the ongoing investigation into the sources of Martian methane. Recent research suggests these seasonal spikes could be linked to changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure, which may influence the release of methane from subsurface reservoirs.
Detecting these seasonal patterns requires sophisticated data analysis techniques. Researchers have utilized a combination of ground-based observations and satellite data to study methane fluctuations. By analyzing the variations in methane levels over time, scientists aim to better understand the processes driving these changes. This analysis is crucial for developing theories about the potential seasonal mechanisms influencing methane emissions on Mars.
Several theories have been proposed to explain why methane levels might change with the seasons. One possibility is that temperature fluctuations cause methane trapped in the Martian soil to be released into the atmosphere. Another theory suggests that seasonal changes in atmospheric pressure could play a role in methane emissions. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for determining whether the observed patterns are indicative of biological or geological processes.
Implications for Martian Life and Geology

The discovery of seasonal methane spikes has significant implications for the possibility of life on Mars. If methane is being produced biologically, the seasonal patterns could suggest the presence of microbial life that becomes more active during certain times of the year. While this is a compelling hypothesis, more evidence is needed to support the idea of life on Mars. Nevertheless, the potential for seasonal biological activity is an exciting avenue for future research.
From a geological perspective, the seasonal methane fluctuations provide valuable insights into Mars’ subsurface activity. If methane emissions are primarily geological, this could indicate active processes such as serpentinization, where water reacts with minerals to produce methane. Understanding these geological processes is crucial for piecing together the history of Mars and its potential for habitability.
Comparing Mars’ methane cycles to those on Earth offers important context. On Earth, methane is a well-studied greenhouse gas with known biological and geological sources. By examining Earth’s methane dynamics, scientists can develop models to better understand the Martian environment. This comparative approach helps to frame the possible scenarios for methane production on Mars and their implications for life and geology.
The Role of Atmospheric Pressure and Temperature

Atmospheric pressure changes on Mars are thought to play a significant role in the release of methane. During certain seasons, variations in pressure could cause methane stored in the Martian soil to escape into the atmosphere. This phenomenon is similar to how gases are released from permafrost on Earth when temperatures rise. By studying these pressure changes, researchers can gain insight into the potential mechanisms driving methane emissions.
Temperature also affects methane stability and release. As temperatures rise during the Martian summer, methane trapped in the soil may become more volatile, leading to increased emissions. This seasonal warming could explain the observed spikes in methane levels. Understanding how temperature influences methane release is vital for developing a comprehensive model of Martian methane dynamics.
In addition to pressure and temperature, other atmospheric components may interact with methane. The presence of oxidizing agents, for example, could influence the breakdown of methane in the atmosphere. These interactions are complex and require further study to determine their impact on methane behavior. By examining the interplay of different atmospheric elements, scientists can better understand the factors affecting methane on Mars.
Future Research and Exploration
As the mystery of Martian methane continues to unfold, future missions are being planned to investigate this phenomenon further. Upcoming missions aim to deploy new technologies and instruments capable of more precise methane detection and analysis. These advancements are critical for resolving the ongoing debates about the sources and implications of methane on Mars.
Technological advancements are paving the way for improved methane detection and analysis. Innovations in spectrometry and remote sensing are expected to enhance our ability to measure methane concentrations accurately. By employing these new tools, researchers hope to gather more consistent and reliable data to better understand the seasonal patterns and potential sources of Martian methane.
The long-term goals of understanding Martian methane extend beyond scientific curiosity. Insights gained from studying methane could inform future exploration and colonization efforts on Mars. By unraveling the mysteries of Martian methane, we move closer to understanding the planet’s past, present, and potential for supporting life. The quest to comprehend methane’s role on Mars is a critical step toward preparing for humanity’s future on the Red Planet.