
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have unearthed the remains of an ancient child who challenges our understanding of human evolution. Initial analyses suggest this child wasn’t fully human but a hybrid of different hominid species, offering a tantalizing glimpse into our complex ancestry. This finding could redefine the evolutionary tree and our perception of what it means to be human.
The Discovery of the Ancient Child
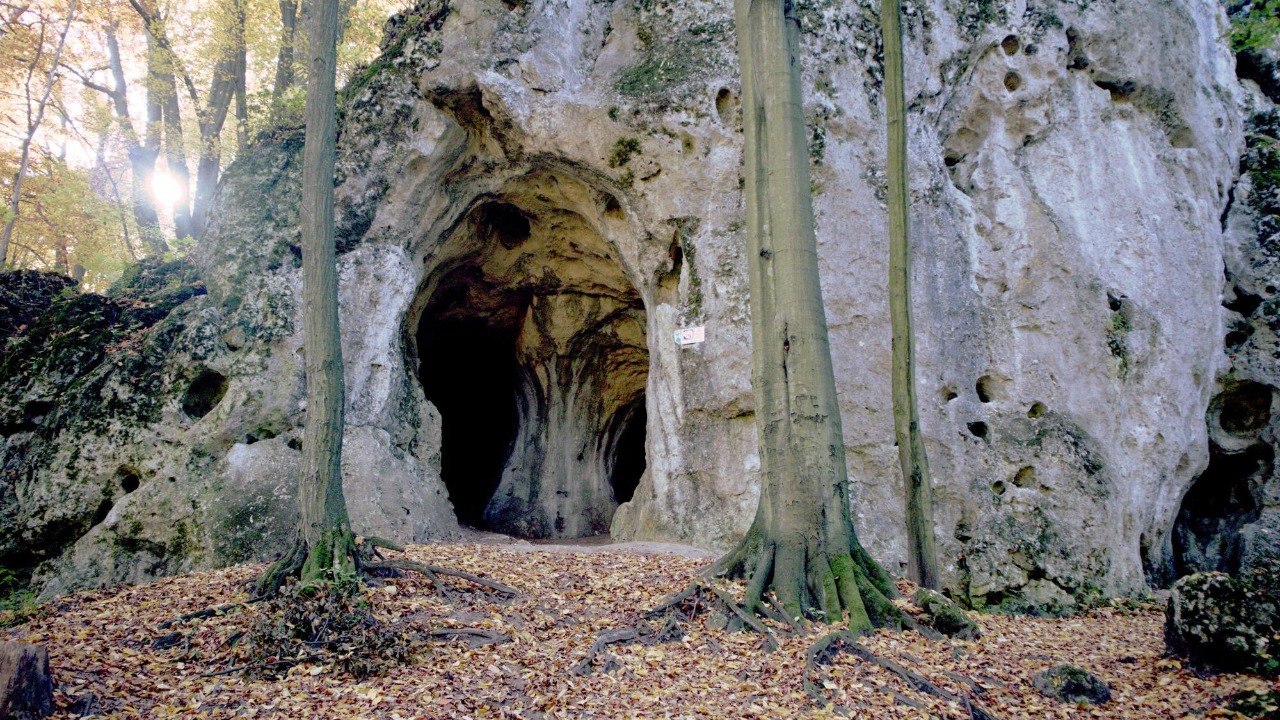

The remains of this ancient child were discovered in a remote region that has long been a treasure trove for archaeologists. The site, located in the Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains of Siberia, provides a unique window into the past due to its exceptional preservation conditions. The cave’s stable temperature and humidity levels have kept the remains remarkably intact, allowing researchers to conduct detailed analyses. It was here that the remains of a child, estimated to be around 90,000 years old, were found, sparking immediate interest among the scientific community.
Initial analysis of the remains involved dating techniques such as radiocarbon dating and stratigraphic analysis. These methods helped establish a timeline for the child’s existence, confirming that she lived during a period when various hominid species coexisted. The significance of this site cannot be overstated, as it offers critical insights into the interactions and cohabitation of ancient human ancestors. The discoveries at this site have consistently challenged our understanding of how different hominid species evolved and interacted with each other.
Unraveling the Genetic Mystery

One of the most fascinating aspects of this discovery lies in the genetic analysis of the child’s remains. Researchers employed advanced techniques such as high-throughput DNA sequencing to extract and analyze ancient DNA from the bones. Extracting viable DNA from remains this old is no small feat, considering the degradation that typically occurs over millennia. Nevertheless, the researchers succeeded in obtaining genetic material that provided groundbreaking insights.
The genetic evidence revealed that the child was a hybrid, possessing DNA from both Neanderthals and another extinct hominid group known as the Denisovans. This finding adds a new layer of complexity to our understanding of human evolution, suggesting that interbreeding between different hominid species was more common than previously thought. Such hybridization events could have played a significant role in shaping the genetic diversity of modern humans. The implications for the human family tree are profound, as this discovery highlights the intricate web of interactions that contributed to our evolutionary history.
The Child’s Place in Evolutionary History
Comparing the child’s genetic and anatomical features with those of known hominid species reveals intriguing similarities and differences. The hybrid nature of her DNA suggests that she possessed characteristics from both Neanderthals and Denisovans, while also potentially exhibiting unique traits not found in either group. These findings challenge existing notions of distinct evolutionary lineages and underscore the complexity of human evolution.
Current theories on human evolution and migration are being reevaluated in light of this discovery. The presence of hybrid individuals like this child suggests that the migration patterns of ancient hominids were more intertwined than previously believed. This raises questions about the extent of interbreeding and its influence on the genetic makeup of ancient populations. Furthermore, the role of hybridization in evolution must be reconsidered, as it may have facilitated the exchange of beneficial traits and adaptations among different groups, ultimately contributing to the development of modern humans.
The Broader Impact on Science and Society

This discovery has significant implications for scientific paradigms in anthropology and human genetics. It challenges the longstanding view of human evolution as a linear progression and instead presents a more intricate picture of interconnected evolutionary pathways. The realization that hybridization played a crucial role in our evolutionary history has prompted a reevaluation of the criteria used to define species and has spurred debates within the scientific community.
Beyond the scientific implications, this discovery also raises ethical considerations regarding the study of ancient human remains. Researchers must navigate the delicate balance between advancing scientific knowledge and respecting the cultural and ethical concerns associated with excavating and studying human ancestors. The responsibility of scientists extends to ensuring that their work is conducted with sensitivity and respect for the communities and cultures connected to these ancient remains.
In the realm of public interest, discoveries like this capture the imagination of people worldwide, influencing perceptions of science and history. The media coverage surrounding this find has been extensive, highlighting the enduring fascination with our origins and the mysteries of human evolution. Such discoveries have the power to inspire a new generation of scientists and foster a deeper appreciation for the complexity of our shared heritage. For more insights, read more about the impact of this discovery on society.
Future Directions for Research

The discovery of this ancient child opens new avenues for research and collaboration among scientists worldwide. Ongoing studies aim to delve deeper into the genetic and anatomical characteristics of hybrid individuals, shedding light on the extent and impact of interbreeding among ancient hominid species. Collaborative efforts between archaeologists, geneticists, and anthropologists are crucial in unraveling the complexities of our evolutionary history.
Technological advancements in archaeology and genetics play a pivotal role in driving future research. Emerging techniques, such as more refined DNA extraction methods and advanced imaging technologies, hold the potential to uncover even more details about ancient human species and their interactions. As these technologies continue to evolve, they offer the promise of new discoveries that could reshape our understanding of human evolution.
Looking ahead, the potential for future discoveries remains vast. Scientists speculate on the existence of additional hybrid individuals and unknown hominid groups that could further illuminate the intricate web of human evolution. Each new finding has the potential to rewrite chapters of our history, offering fresh perspectives on the journey that led to the rise of modern humans. For those interested in exploring the broader implications of these discoveries, this review delves into the complexities of human evolution and the role of hybridization.