
Over the past decade, the automotive industry has seen remarkable advancements in engine technology, but not all developments have been successful. Some engines, despite their promise, have fallen short due to reliability issues, performance problems, or design flaws. Here, I delve into seven of the most disappointing engines produced in the last ten years.
Fiat MultiAir Engine

The Fiat MultiAir engine was introduced with high expectations for its innovative electro-hydraulic valve control system. This technology was supposed to improve fuel efficiency and performance, but it often led to maintenance nightmares. Owners reported frequent issues with the oil control system, which could cause engine failure if not addressed promptly. The engine was used in models like the Fiat 500 and Alfa Romeo MiTo, where these problems were most prevalent.
Despite its innovative design, the complexity of the MultiAir system often resulted in costly repairs. The engine’s sensitivity to oil quality and regular maintenance made it less reliable compared to its competitors. For those interested in understanding more about engine reliability, check out this comprehensive guide.
Ford EcoBoost 1.0L Engine
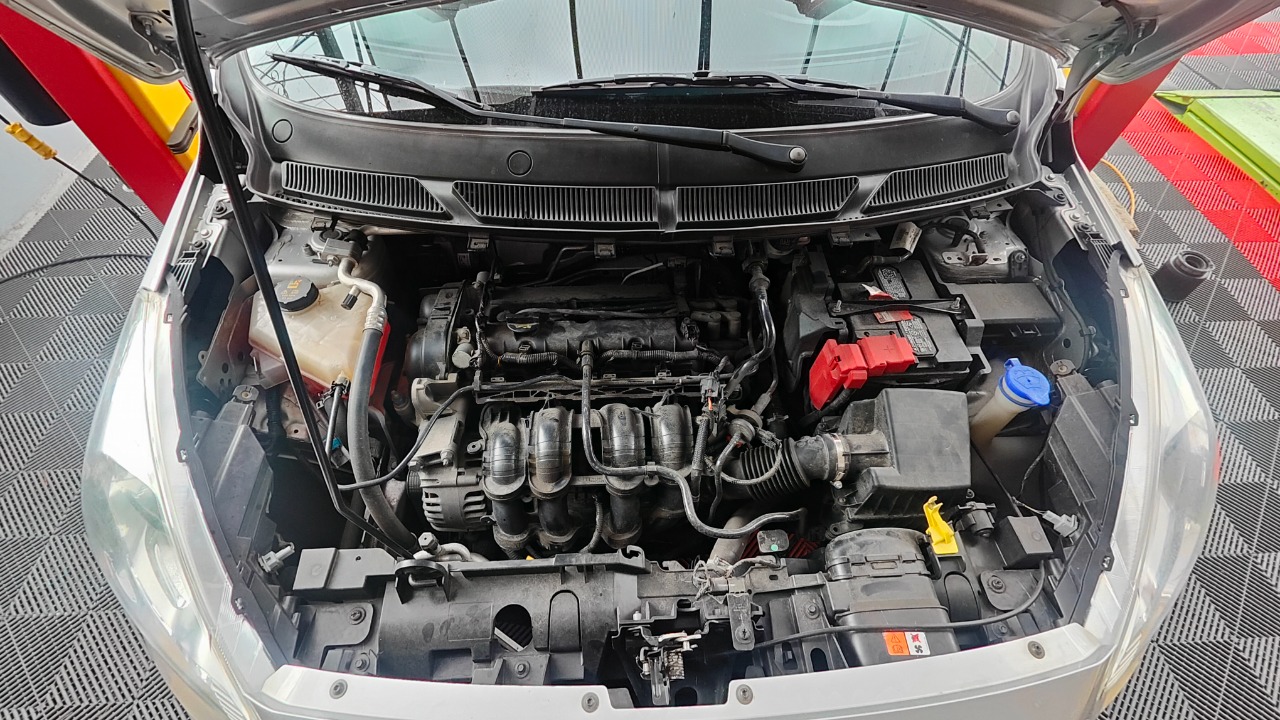
Ford’s 1.0L EcoBoost engine was hailed as a game-changer for its ability to deliver impressive power output from a small displacement. However, real-world applications, particularly in models like the Ford Fiesta and Focus, revealed significant drawbacks. Many owners experienced overheating issues that led to engine damage, often resulting in costly repairs or replacements.
The engine’s turbocharger, while efficient, was prone to failure under certain conditions. Moreover, the cooling system was not robust enough to handle the engine’s heat output, leading to frequent recalls. For a detailed technical analysis, this SAE technical paper offers valuable insights.
Volkswagen EA888 Engine
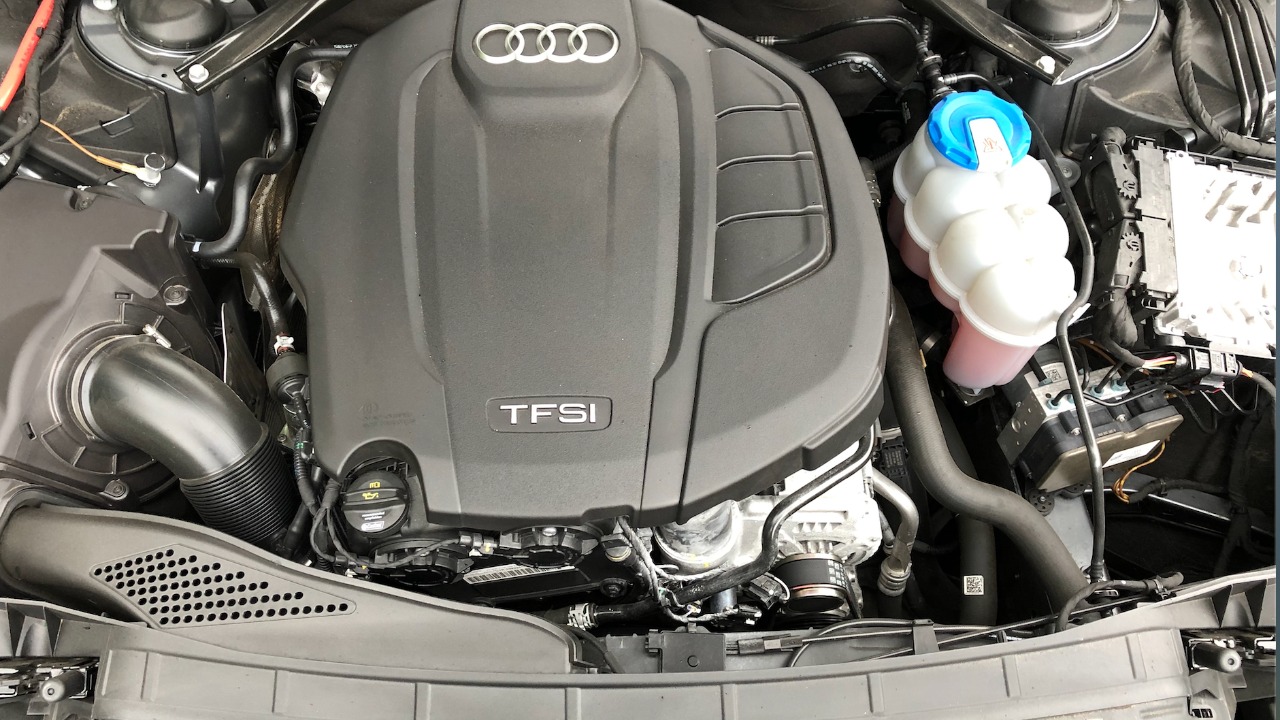

The Volkswagen EA888 engine, used in numerous models including the Audi A4 and VW Golf, faced criticism for its excessive oil consumption. Owners frequently reported the need to add oil between changes, a problem attributed to the engine’s piston rings not sealing correctly. This issue often led to premature engine wear and, in severe cases, engine failure.
Despite updates to the design, the EA888’s reputation was marred by these persistent problems. The oil consumption issue also raised environmental concerns due to increased emissions. More details on engine design challenges can be found in this scientific article.
BMW N63 V8 Engine
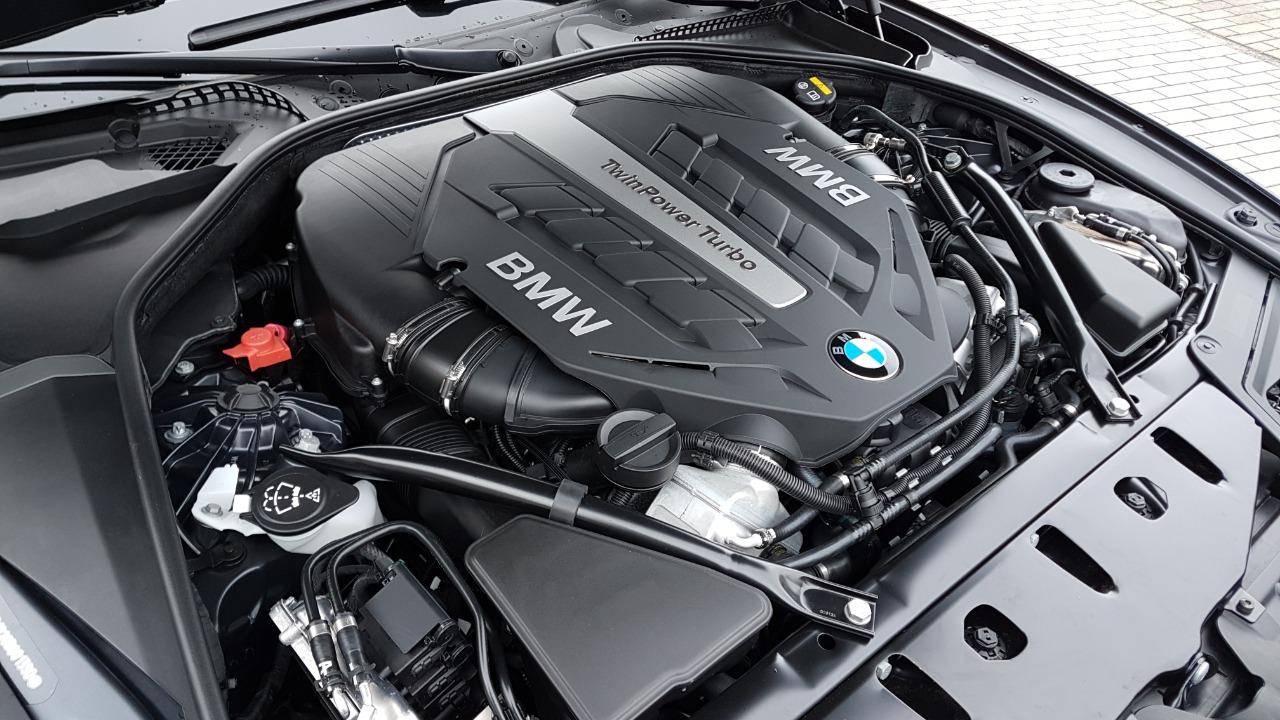

The BMW N63 V8 engine, featured in luxury models like the BMW 5 Series and 7 Series, faced significant reliability issues. Known for its twin-turbocharging and direct injection, the engine suffered from problems such as high oil consumption, timing chain failures, and cooling system inadequacies. These issues often led to costly repairs and diminished performance.
BMW attempted several fixes and issued extended warranties to address these concerns, but the engine’s reputation remained tarnished. For a visual breakdown of the engine’s complexities, watch this informative video.
Subaru FB20 Engine

Subaru’s FB20 engine, found in models like the Subaru Impreza and Forester, was designed to offer improved fuel efficiency and performance. However, it was plagued by issues such as excessive oil consumption and head gasket failures. These problems were particularly troubling for owners who relied on the vehicles for daily commuting and long drives.
The engine’s problems often led to significant repair costs and reduced reliability, tarnishing Subaru’s reputation for durability. Subaru has made efforts to address these problems in newer models, but the legacy of the FB20 remains a cautionary tale.
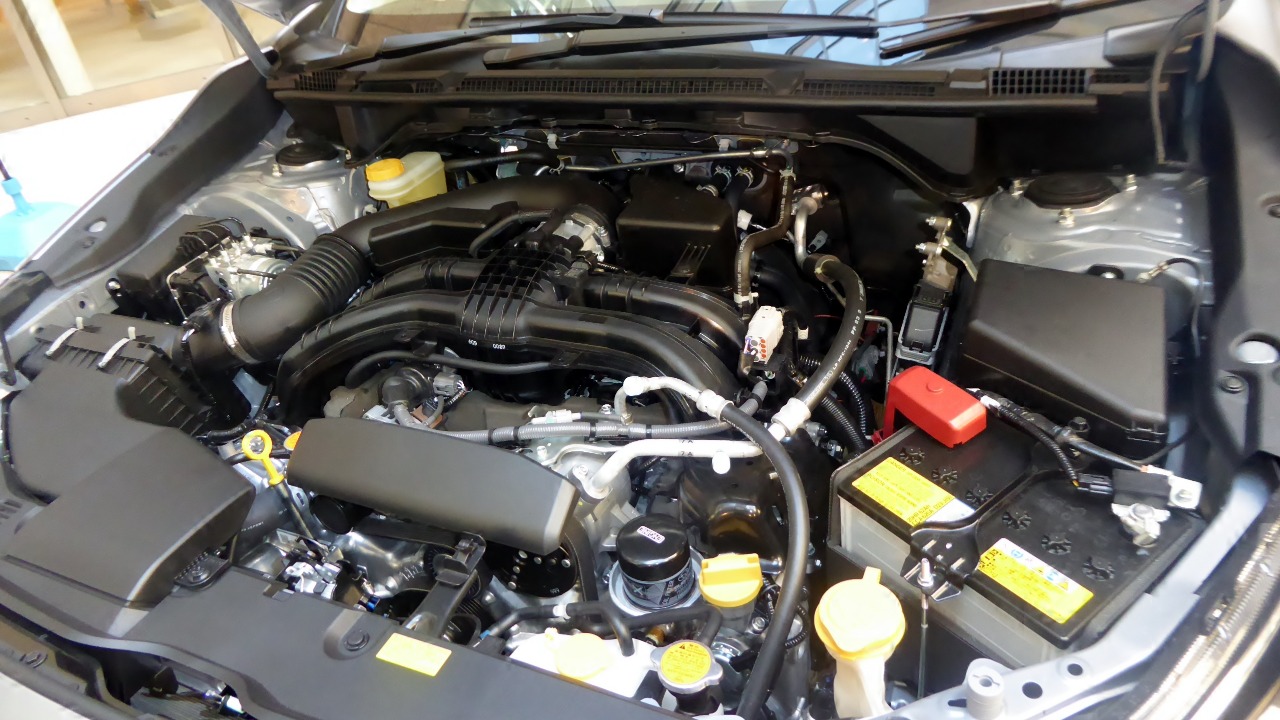
Nissan MR20DE Engine

The Nissan MR20DE engine, used in the Nissan Sentra and Rogue, has been criticized for its lack of durability. Common issues included timing chain problems and excessive oil consumption, which often resulted in engine damage if not promptly repaired. These issues not only compromised performance but also led to high maintenance costs for owners.
Despite being marketed as a reliable workhorse, the engine’s frequent mechanical failures resulted in dissatisfaction among Nissan’s customer base. For a visual assessment of the engine’s performance, this video analysis provides valuable insights.
GM 2.4L Ecotec Engine

General Motors’ 2.4L Ecotec engine, found in various models like the Chevrolet Equinox and GMC Terrain, faced numerous reliability issues. The most notable problem was excessive oil consumption, which often led to engine damage or failure. Owners also reported issues with the timing chain and balance shaft chain, which required expensive repairs.
GM addressed some of these issues through recalls and extended warranties, but the engine’s reputation was already damaged. The 2.4L Ecotec’s legacy serves as a reminder of the importance of robust engineering and thorough testing in automotive design.