
Recent advancements in technology have enabled cameras to detect objects through walls, a concept that once seemed purely science fiction. By leveraging unique approaches such as Wi-Fi signals, thermal imaging, and advanced AI algorithms, researchers are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in surveillance and object recognition.
The Science Behind Wall-Penetrating Cameras

Wi-Fi signals, ubiquitous in modern environments, are being repurposed as a means to visualize objects through walls. Researchers have discovered that by analyzing the distortions and reflections of Wi-Fi signals, it is possible to reconstruct images of objects hidden behind walls. This process essentially turns a Wi-Fi router into a makeshift camera, offering a non-invasive method to perceive the unseen. The technique, as demonstrated in various studies, relies on the ability to interpret the interactions between radio waves and objects, converting these interactions into a visual format. More information on this can be found through a Reddit discussion about AI turning Wi-Fi routers into cameras.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of these systems. By utilizing sophisticated algorithms, AI can accurately identify and estimate the pose of objects detected through walls. This involves complex computations that analyze signal patterns and convert them into recognizable shapes and positions. The ability to discern not just the presence but the orientation of an object is a significant leap forward in the field of object recognition. Research papers, such as those available on ResearchGate, delve into the technical intricacies of this technology.
Technological Approaches and Innovations

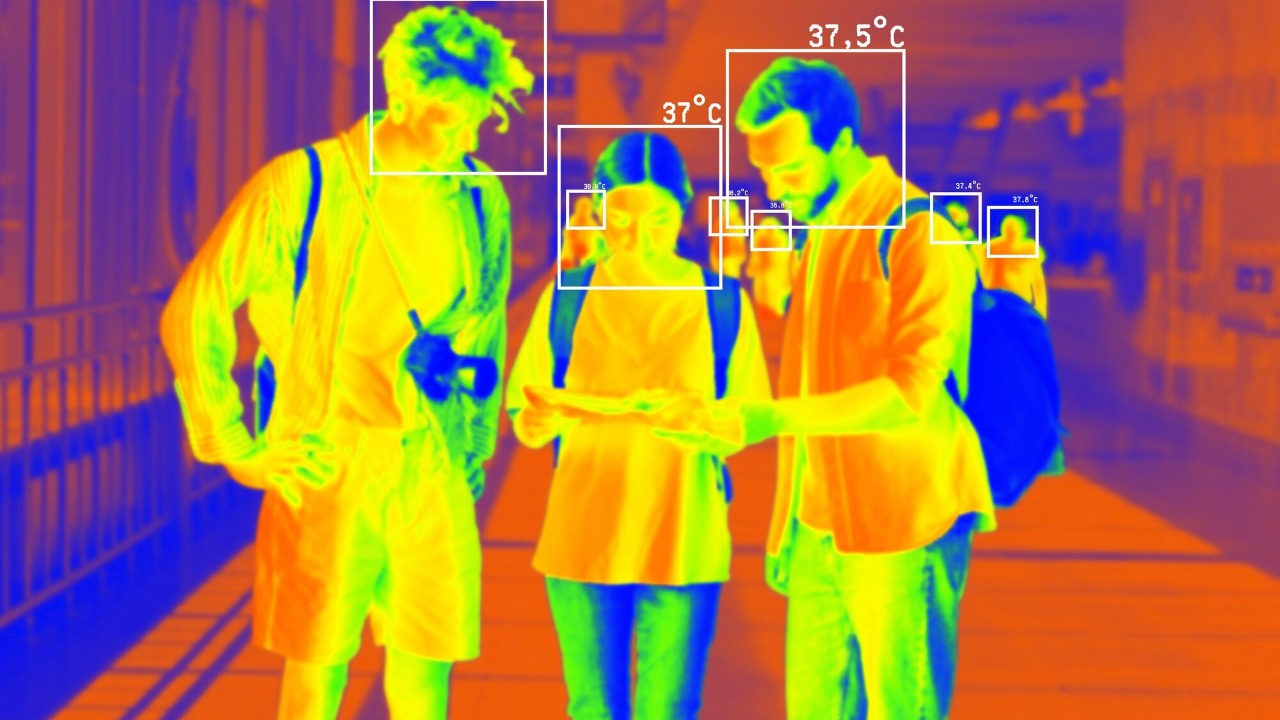
Beyond Wi-Fi, other technologies like thermal imaging and radar are pivotal in achieving through-wall vision. Thermal imaging, for instance, detects heat signatures, allowing it to see through walls by capturing the thermal radiation emitted by objects. This method is particularly useful in scenarios where live subjects, such as humans or animals, are involved, as their body heat creates a distinct signature. Radar systems, on the other hand, use electromagnetic waves to detect objects, providing another layer of data that can be used to create a comprehensive image of hidden environments. These technologies are critical in environments with low visibility or where other methods might fail.
Numerous experiments highlight the practical applications and limitations of these technologies. For instance, a fascinating experiment involving Tesla cameras showcased how car systems could perceive objects through walls, albeit with varying degrees of success. Such studies point to the potential and the current constraints of these technologies, emphasizing the need for continual refinement and innovation. Algorithmic advancements and machine learning techniques are vital for interpreting and making sense of the data captured through walls, transforming raw signals into actionable insights.
Applications and Implications

The ability to see through walls has profound implications across various sectors. In security and surveillance, such technology could enhance the monitoring of sensitive areas, providing law enforcement and security personnel with valuable intelligence without physical intrusion. In emergency response, first responders could use through-wall vision to locate trapped individuals in disaster scenarios, significantly improving rescue operations. The potential benefits of these applications are enormous, offering new tools for safety and efficiency.
However, these advancements also raise significant privacy and ethical concerns. The ability to see through walls could lead to increased surveillance, raising questions about individual rights and freedoms in an era where privacy is already under threat. Balancing the benefits of enhanced security with the need to protect personal privacy is a critical challenge that society must navigate as this technology becomes more widespread. Industries such as construction and archaeology could also benefit from through-wall detection, allowing for non-invasive inspections and analyses that could revolutionize current practices.
Challenges and Limitations

Despite its potential, through-wall detection technology faces several technical challenges. Resolution and accuracy remain significant hurdles, as the current systems often struggle to produce clear and detailed images. This limitation can impede the technology’s effectiveness, particularly in complex environments where precision is crucial. Furthermore, environmental factors such as wall materials and signal interference can dramatically affect performance. For instance, dense or metallic walls can significantly degrade signal quality, making it difficult to obtain reliable data.
Another major consideration is the cost and scalability of these technologies. Implementing sophisticated through-wall systems on a large scale can be prohibitively expensive, limiting their accessibility and use in broader applications. As a result, ongoing research and development are essential to refine these technologies, reduce costs, and enhance their practicality. The IEEE provides insights into the technical challenges and potential solutions in this field.
The Future of Through-Wall Vision
Looking ahead, the future of through-wall vision technology is promising. Ongoing research aims to overcome current challenges, focusing on improving resolution, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. As these technologies continue to evolve, the integration of multiple approaches, such as combining thermal imaging with Wi-Fi signal analysis, could provide more comprehensive and reliable solutions. The potential to merge these technologies with advancements in AI and machine learning offers exciting possibilities for enhanced functionality and application.
Societal shifts and adaptations will likely accompany the adoption of through-wall detection technology. As it becomes more prevalent, new regulations and standards will be necessary to address privacy concerns and ensure ethical use. Industries will need to adapt to leverage these advancements effectively, transforming how tasks are approached and executed. The ongoing dialogue between technologists, ethicists, and policymakers will be crucial in shaping a future where through-wall vision is both beneficial and responsible. Innovative approaches, such as those discussed in the ICCV paper, highlight the potential for creative solutions in overcoming existing limitations.