
Recent research has unveiled a fascinating connection between Neanderthal DNA and autism, offering new insights into the genetic underpinnings of the condition. This breakthrough discovery could reshape our understanding of autism’s origins and open up possibilities for innovative approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
The Discovery: Unraveling the Genetic Link

The groundbreaking study that linked Neanderthal DNA to autism was conducted by a team of geneticists who employed cutting-edge analysis techniques. By examining the genomes of individuals with autism and comparing them to those of Neanderthal ancestry, researchers discovered specific genetic variants that might contribute to autistic traits. This analysis involved large-scale data interpretation and the use of advanced bioinformatic tools to identify these ancient genetic markers.
The methodologies used in this research were robust and multifaceted. Geneticists utilized genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to pinpoint the Neanderthal variants present in modern human DNA. These variants were then analyzed for their potential impact on neurological development and associated behaviors. The study’s findings have sparked interest in further exploring these genetic connections and how they may manifest in individuals with autism.
Understanding Neanderthal DNA’s Role in Modern Humans
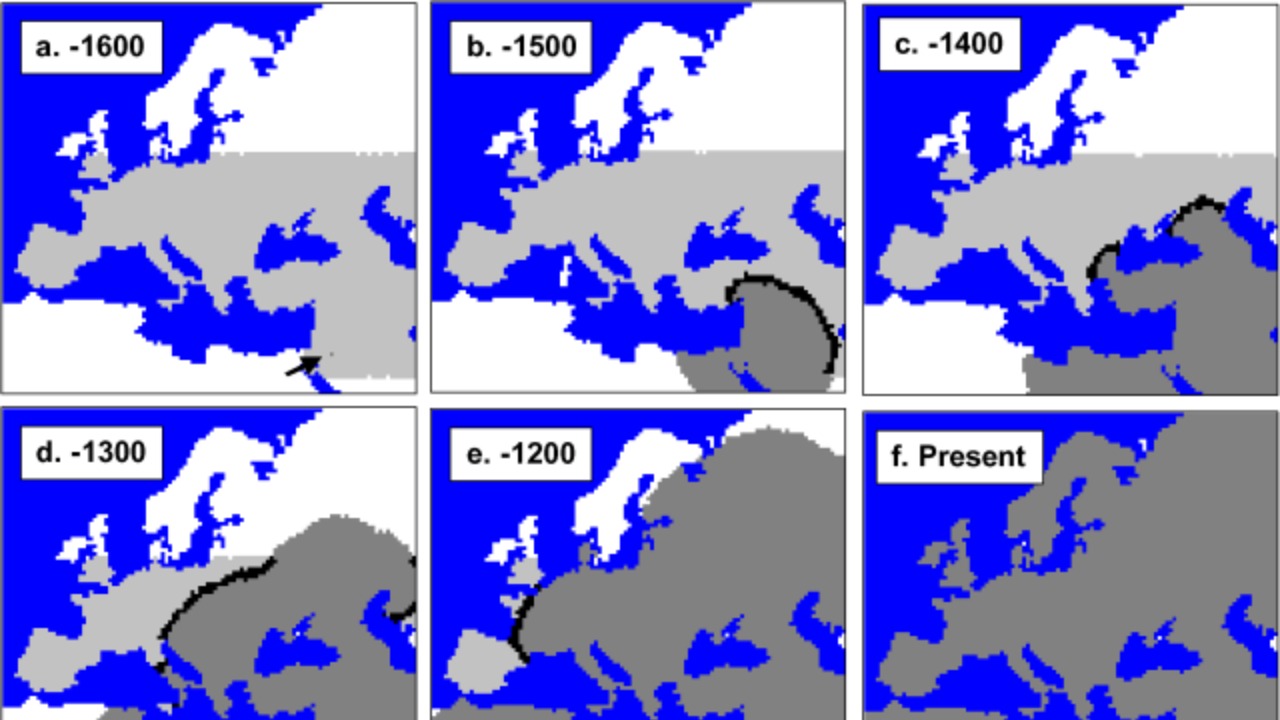
Neanderthal DNA integration into the modern human genome has a complex history. When Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa approximately 60,000 years ago, they encountered Neanderthals in Europe and Asia, resulting in interbreeding events. As a result, most people of European and Asian descent carry about 1-2% Neanderthal DNA. This ancient genetic legacy has been linked to various human traits and health conditions, such as immune response and skin pigmentation.
Research has shown that Neanderthal genetic sequences can influence neurological functions and development. These findings are consistent with the recent discovery connecting these ancient genes to autism. Scientists are now delving deeper into how specific Neanderthal variants may impact brain structure and function, providing new insights into the evolutionary aspects of neurological conditions.
Implications for Autism Research and Treatment

This discovery could significantly shift the focus of autism research, emphasizing genetic and evolutionary perspectives. By exploring the ancient genetic roots of autism, researchers may develop more targeted diagnostic tools and treatments. For instance, understanding the role of Neanderthal DNA in autism could lead to personalized therapies that address the specific genetic components contributing to the condition.
Future research will likely prioritize interdisciplinary collaboration, combining genetics, neuroscience, and anthropology to unravel the complexities of autism. As researchers continue to explore these genetic links, they may uncover new pathways for treatment and intervention. The potential for developing innovative diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies makes this area of research particularly promising.
Broader Impact on Human Genetic Diversity and Disease
The implications of this study extend beyond autism research, offering insights into the broader context of human genetic diversity. Neanderthal DNA contributes to a wide range of human diseases and traits, highlighting the intricate relationship between ancient and modern genetics. Studies have identified Neanderthal genetic variants that influence conditions like depression, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic disorders.
Understanding the role of Neanderthal DNA in human diversity also raises ethical considerations in genetic research. As scientists continue to uncover the genetic basis of diseases, it is essential to consider the societal implications of these findings. Ethical discussions surrounding genetic diversity research must address the potential for discrimination and the equitable application of scientific discoveries. The global DNA study identifying numerous genetic variants emphasizes the need for ongoing ethical dialogue.
The Future of Genetic Research in Understanding Autism

Advancements in genetic research techniques hold promise for uncovering further links between ancient DNA and modern conditions. As technology evolves, scientists can leverage big data and artificial intelligence to accelerate discoveries in genetic research. These tools enable the analysis of vast genomic datasets, potentially revealing new insights into the genetic underpinnings of autism and other neurological conditions.
Public awareness and education play a crucial role in translating scientific findings into societal benefits. By fostering a deeper understanding of genetic research, society can better appreciate the complexities of human diversity and the potential for personalized medicine. Encouraging informed discussions about the ethical implications of genetic discoveries will help ensure that scientific advancements are used to benefit all individuals.
In conclusion, the discovery of a link between Neanderthal DNA and autism represents a significant milestone in genetic research. By unraveling the genetic connections between ancient and modern humans, scientists are gaining new insights into the origins of autism and other neurological conditions. With continued research and interdisciplinary collaboration, the potential for groundbreaking advancements in diagnosis and treatment is vast. As we move forward, the integration of technology and public engagement will be essential in harnessing the full potential of genetic research to improve human health and well-being.