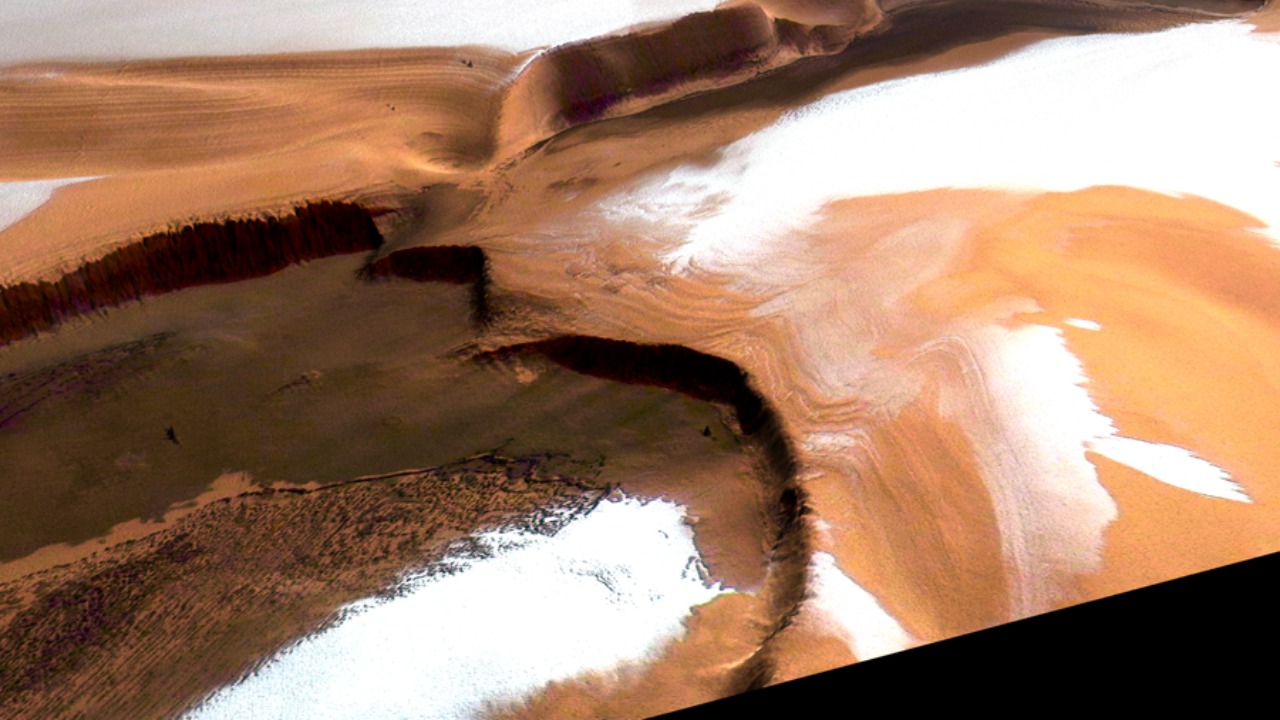
A groundbreaking discovery has been made by a NASA probe on Mars, revealing the presence of ice beneath the planet’s dusty surface. This finding has profound implications for understanding Mars’ climate history and evaluating the planet’s potential to harbor life. The discovery promises to reshape our understanding of Mars and guide future exploration missions.
The Discovery of Ice on Mars
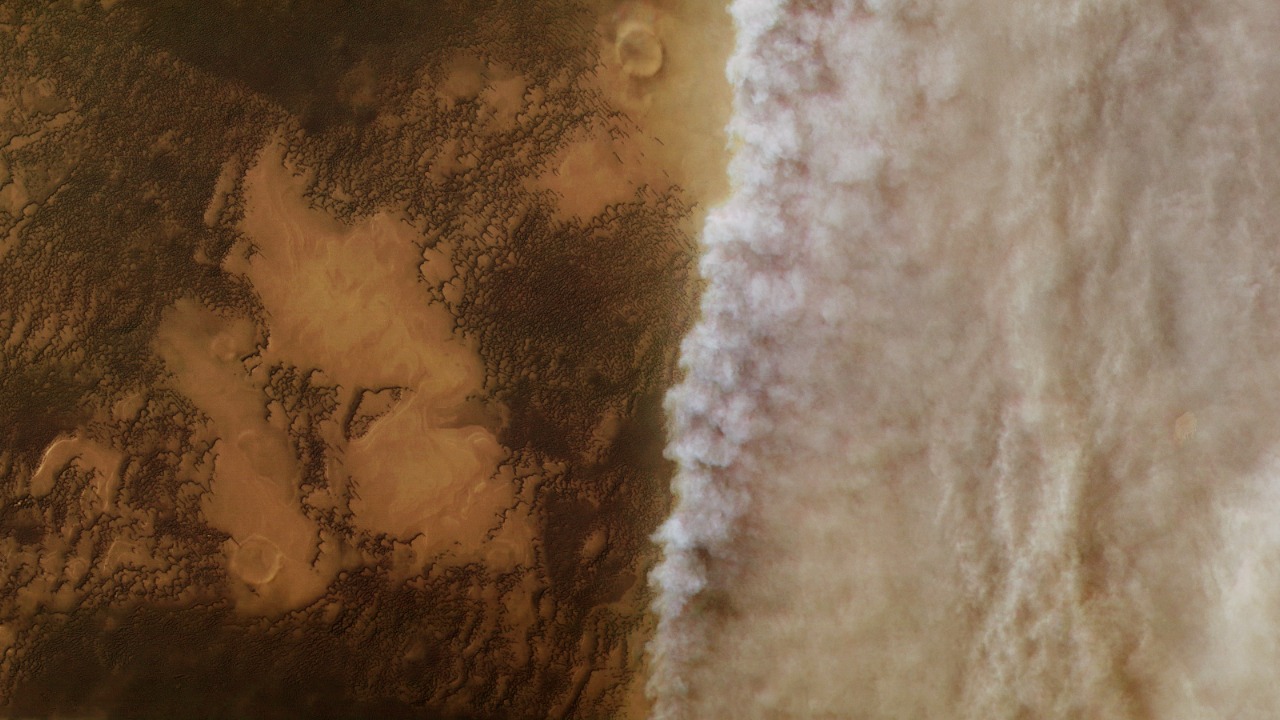

The NASA probe mission, which has been pivotal in unveiling these new findings, was designed with a specific set of objectives aimed at understanding Mars’ subsurface composition. Launched as part of the Mars Exploration Program, the mission employed cutting-edge technology to penetrate the Martian surface and detect ice deposits beneath layers of dust. This involved advanced radar systems capable of distinguishing between different subsurface materials based on their reflective properties.
Detecting ice beneath the Martian dust is of immense significance. Ice serves as both a record of climatic changes and a potential resource for future human missions. The presence of ice reveals information about Mars’ geological history and provides clues to the water cycle on the planet. As scientists analyze these findings, they gain a deeper understanding of how Mars evolved and how similar or different its processes are compared to Earth.
Implications for Martian Climate and History
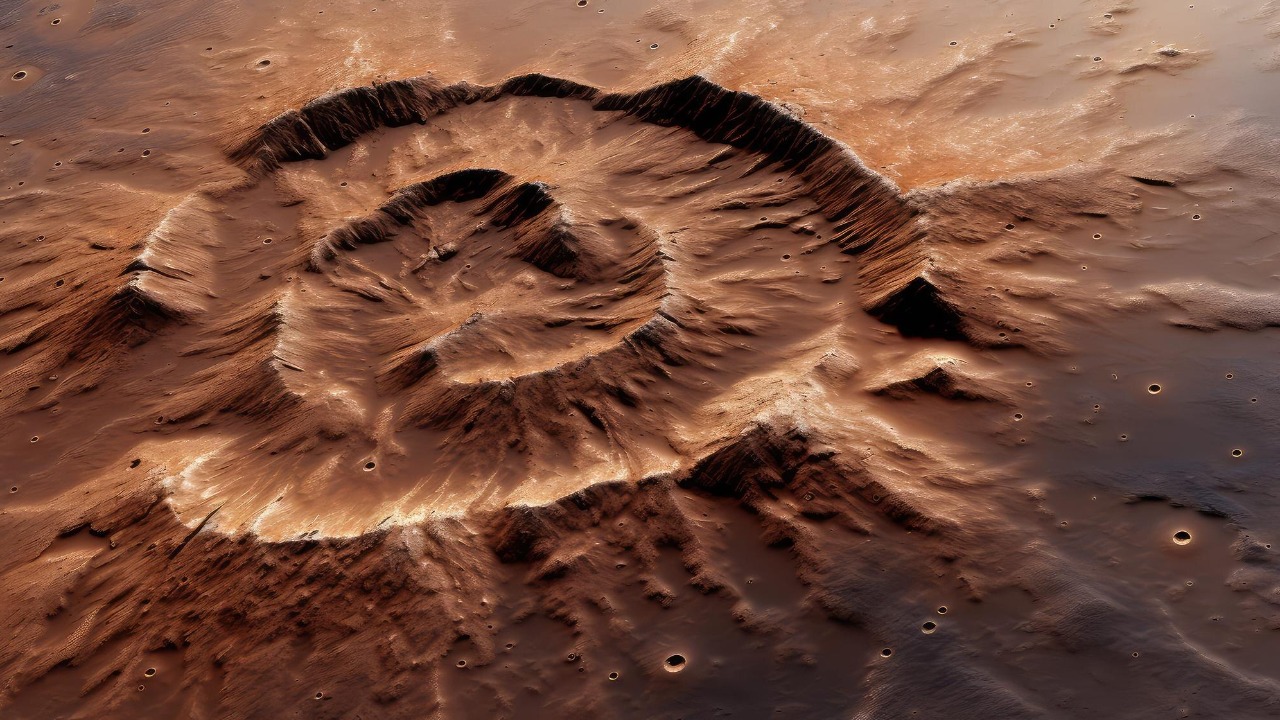

The presence of subsurface ice is crucial for reconstructing the historical climate of Mars. By examining the ice layers, researchers can infer past climatic conditions and detect shifts in temperature and atmospheric pressure over millions of years. This knowledge is essential for understanding how water once flowed on Mars and the extent to which it shaped the planet’s surface.
Geologically, ice has played a significant role in sculpting the Martian landscape. The erosive and depositional processes driven by ice movements have led to the formation of valleys and basins similar to those found on Earth. Comparing these geological formations with Earth’s helps scientists draw parallels and distinctions, offering insights into planetary evolution and the potential for past life.
Potential for Life in Martian Ice

The discovery of ice on Mars opens up possibilities regarding the potential for microbial life. Conditions beneath the ice, shielded from harsh surface radiation, may offer a hospitable environment for life. If microorganisms can exist in such extreme conditions on Earth, similar life forms might be present on Mars. Previous studies have suggested that microbial habitats could exist within the ice, thriving on nutrients and energy sources available beneath the surface.
Studying potential life forms on Mars presents numerous challenges. The need for sterile equipment to prevent contamination, coupled with the technical difficulty of drilling through ice, complicates these missions. Nonetheless, the implications for astrobiology missions are profound, as they could provide answers to one of humanity’s most compelling questions: Are we alone in the universe?
Future Missions and Exploration
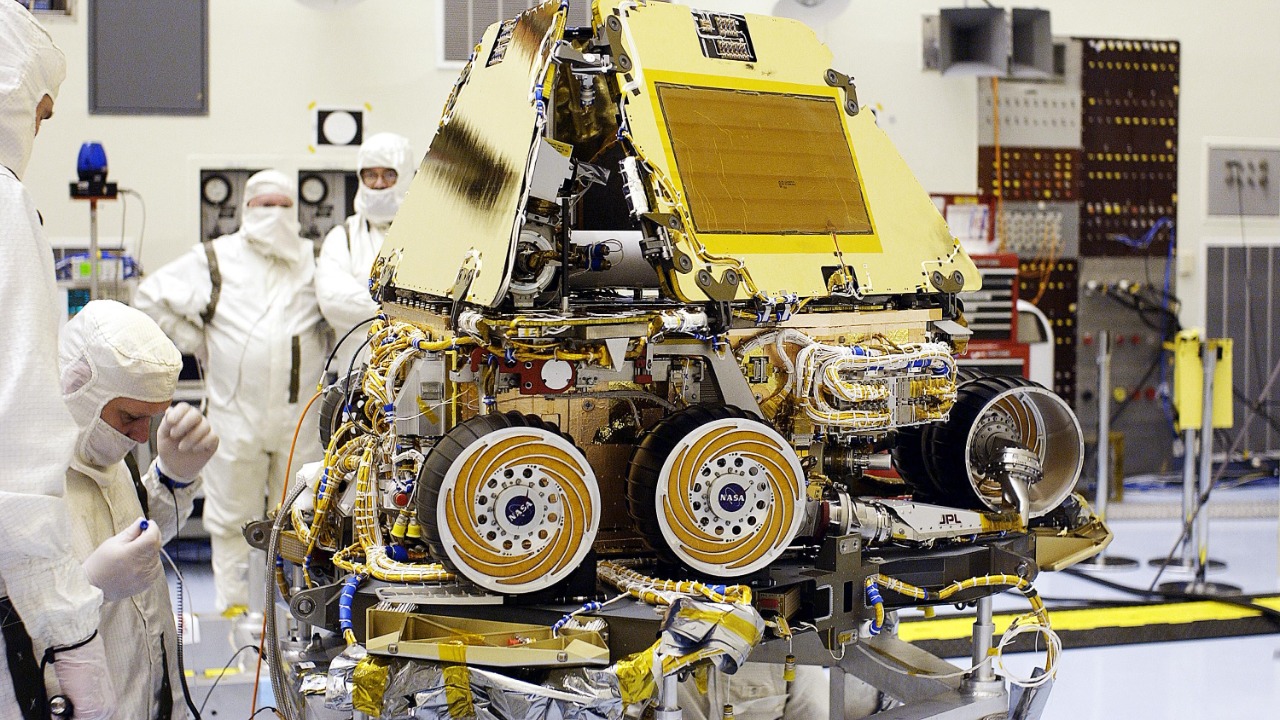
NASA has several upcoming missions targeting Martian ice. These missions aim to explore the depth, distribution, and composition of ice deposits. With advancements in technology, such as enhanced drilling techniques and more sensitive instruments, future missions are better equipped to analyze Martian ice.
International collaboration plays a crucial role in Mars exploration. Agencies worldwide are contributing expertise and resources to study Mars’ ice deposits. Efforts like the European Space Agency’s ExoMars program and contributions from countries such as India and China underscore the global interest in unraveling Mars’ mysteries. These partnerships are vital for maximizing the scientific yield and ensuring the success of missions aimed at understanding Mars’ potential to harbor life.