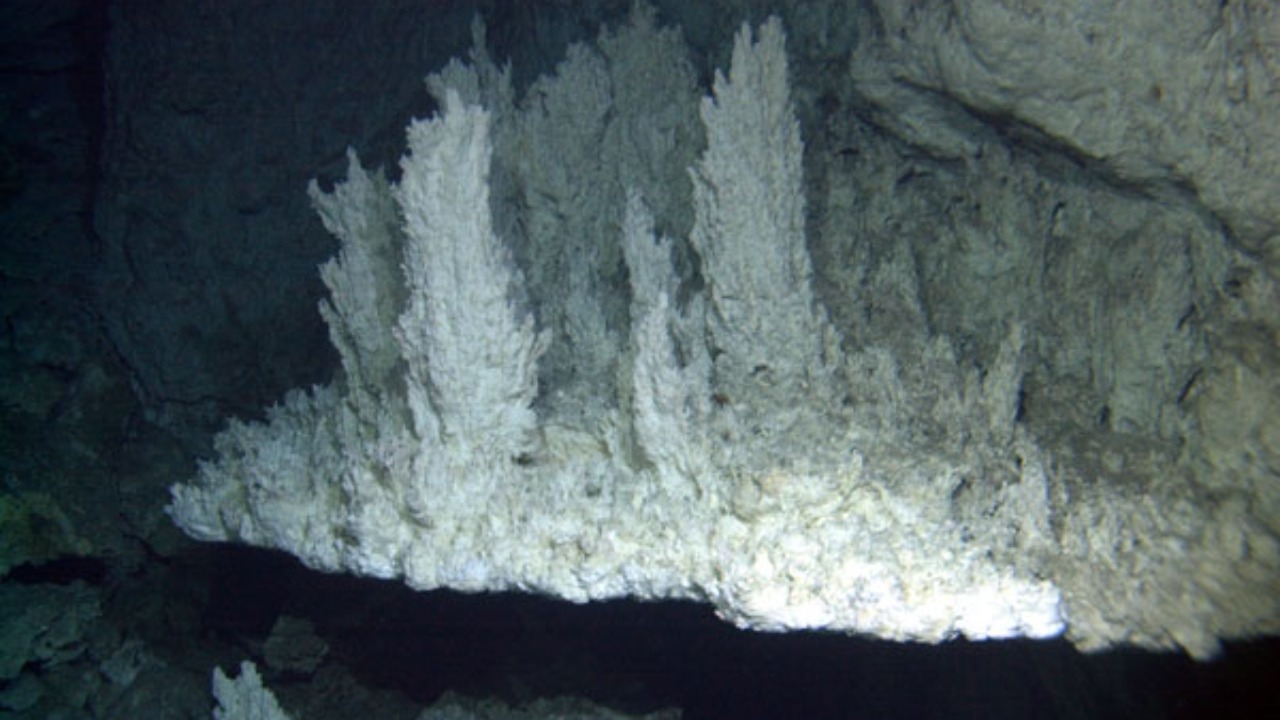

Recent discoveries at deep sea vents have unveiled a potential new branch of life, sparking excitement and intrigue among scientists and researchers alike. These findings may not only redefine our understanding of life’s diversity but also provide insights into the origins of life on Earth. The extreme environments of deep sea vents offer a unique glimpse into ecosystems that thrive under conditions once thought to be uninhabitable.
The Discovery at Deep Sea Vents
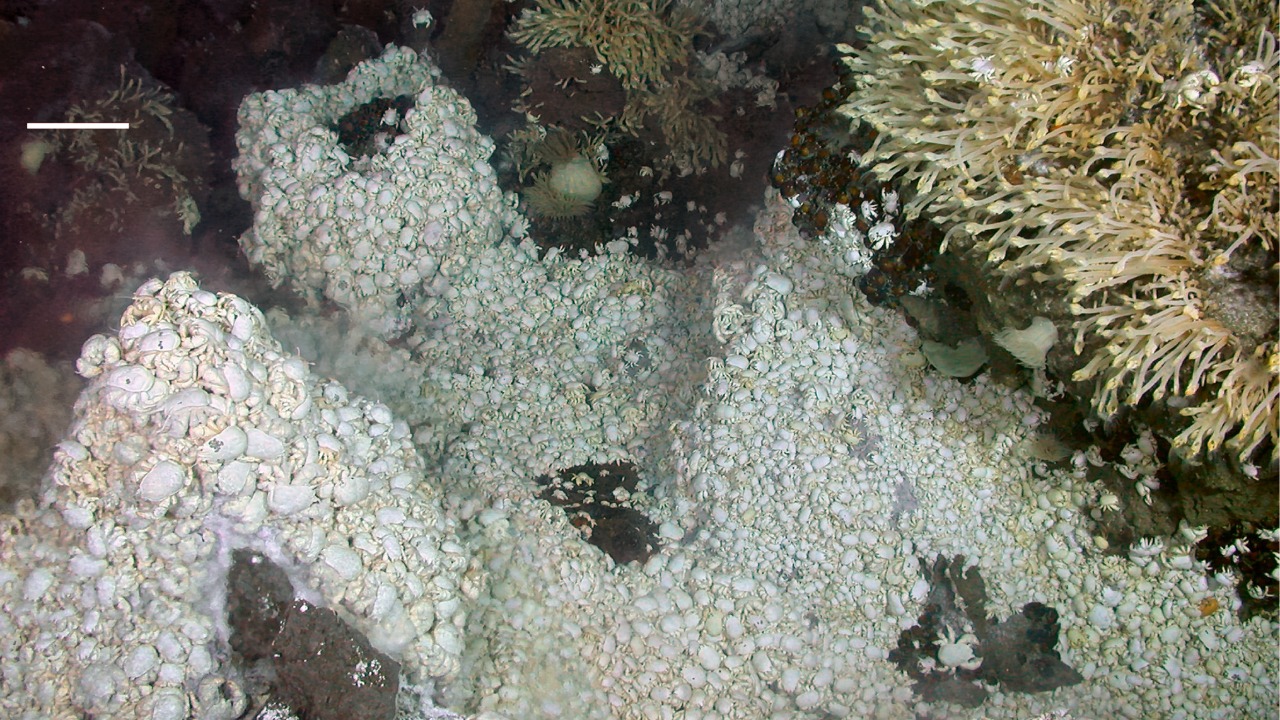

The latest expedition to the ocean’s abyssal depths has uncovered a fascinating potential new branch of life. The research team, tasked with exploring these uncharted territories, stumbled upon organisms that exhibit characteristics unlike any known life forms. The mission, brimming with the promise of new discoveries, has yielded results that could significantly alter our understanding of biological diversity.
Deep sea vents are known for their extreme conditions, including high pressure, darkness, and geothermal heat. These environments, often considered inhospitable, provide a unique habitat where life can flourish in unexpected ways. The vents’ unique chemical properties create an ecosystem unlike any other, facilitating the development of life forms that challenge our traditional biological categorizations.
The scientific community has been abuzz with reactions to this groundbreaking discovery. Researchers are both excited and cautious as they begin to analyze the implications of this potential new branch of life. The findings have sparked debates and discussions about how life can adapt and thrive under such extreme conditions, leading to a reevaluation of existing biological classifications.
Characteristics of the New Life Form
These newly discovered organisms demonstrate a range of physical and biological traits that set them apart from established life forms. Their unique adaptations to the harsh deep-sea environment include specialized metabolic processes and resilience to extreme pressure and temperature variations. These characteristics provide valuable insights into the potential for life’s adaptability and evolution.
More fascinating are the results of the genetic analyses conducted on these organisms. The genetic makeup of these life forms reveals significant differences from known species, suggesting a separate evolutionary path. This discovery could lead to a redefinition of the broader tree of life, as scientists work to understand the implications of these genetic divergences.
Such findings open up the possibility of introducing new classifications in biology. As researchers continue to study these organisms, they may need to establish new categories to accommodate the unique features and evolutionary history of these deep-sea dwellers. This discovery highlights the dynamic nature of biological classification and the continuous evolution of our understanding of life.
Implications for the Origin of Life Theories
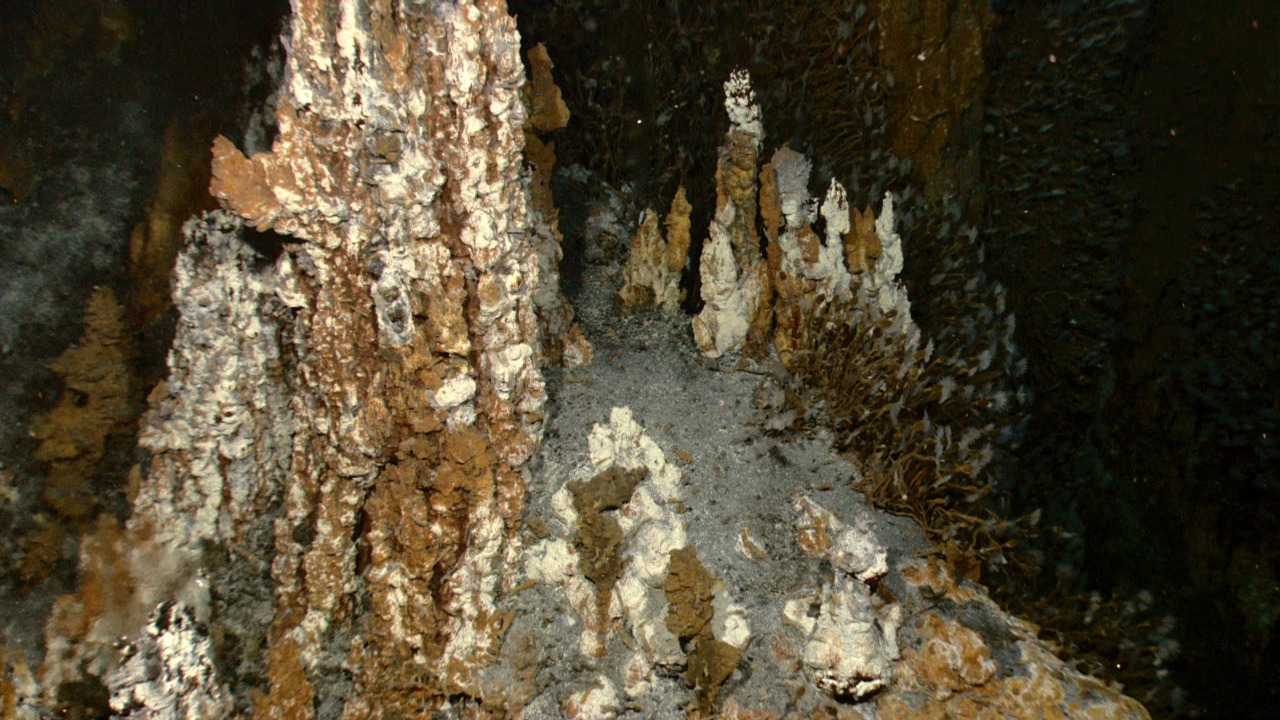

The discovery of these unique organisms at deep sea vents prompts a reexamination of existing theories regarding the origin of life. Some theories suggest that life on Earth may have originated in such environments, where the combination of heat, pressure, and chemical availability could have fostered the emergence of life. The presence of these novel life forms lends credence to the hypothesis that deep sea vents played a crucial role in life’s beginnings.
This discovery also has broader implications for the field of astrobiology. The ability of life to thrive in such extreme conditions expands the possibilities for finding life beyond Earth. If organisms can exist in the harsh environments of deep sea vents, similar life forms might be found on other planets or moons with comparable conditions.
As scientists continue to explore these theories, the discovery of new life forms at deep sea vents underscores the importance of considering alternative environments when studying the origins of life. This newfound understanding encourages a more comprehensive approach to researching life’s beginnings, both on our planet and beyond.
Technological Advances in Deep Sea Exploration
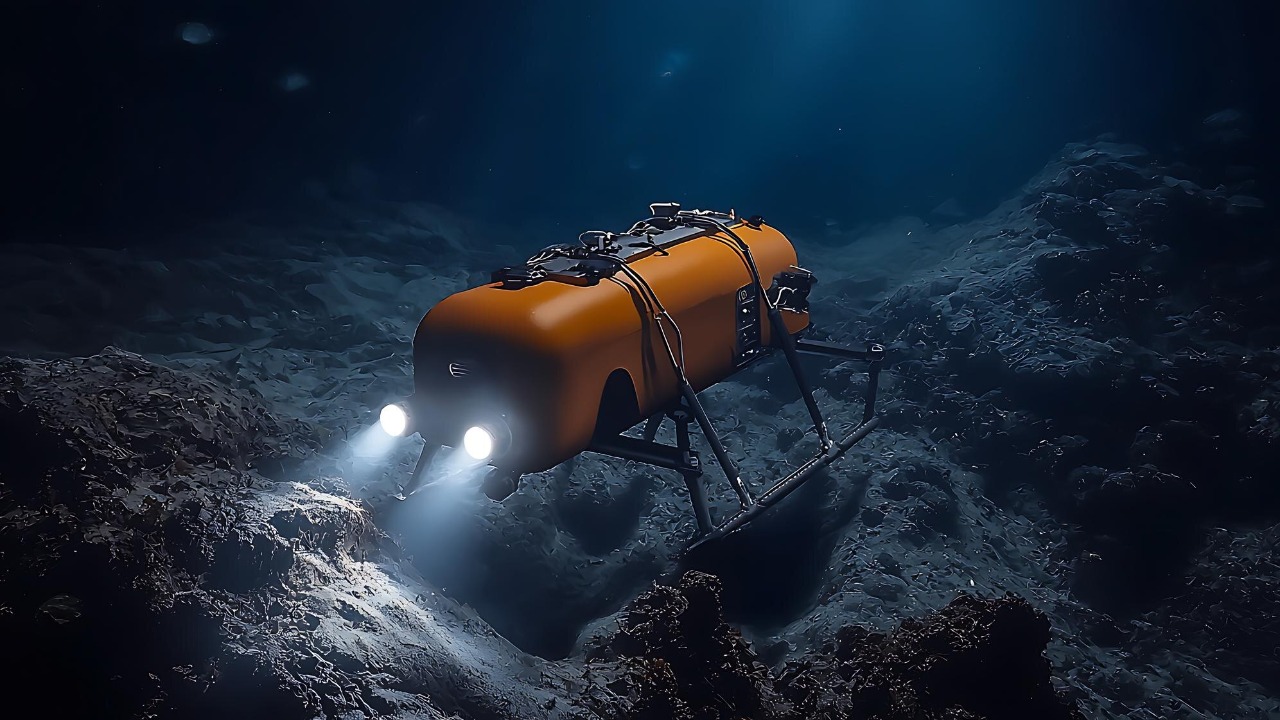

The recent discoveries at deep sea vents were made possible by significant advancements in deep-sea exploration technology. Innovations such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and advanced submersibles have allowed scientists to reach previously inaccessible depths. These tools are equipped with high-definition cameras and sampling equipment that can withstand the harsh conditions of the deep ocean.
Despite these advancements, exploring the deep sea remains a challenging endeavor. The extreme pressure, low temperatures, and complete darkness make it difficult to conduct research and gather data. Scientists often face logistical and technical challenges when planning and executing deep-sea missions. However, these obstacles are gradually being overcome as technology continues to improve.
Looking ahead, future exploration missions are being planned to further investigate deep sea vents and their unique ecosystems. These missions aim to deepen our understanding of the complex interactions within these environments and to uncover more secrets about the origins and adaptability of life. The continued exploration of the deep sea holds the promise of new discoveries and insights that could redefine our understanding of life on Earth.
The Future of Marine Biology and Ecology

The discovery of a potential new branch of life at deep sea vents has profound implications for our understanding of marine ecosystems. These findings challenge conventional views of ecological interactions and biodiversity, highlighting the complexity and resilience of life in extreme environments. As researchers delve deeper into the study of these ecosystems, they may uncover new relationships and processes that were previously unknown.
With these discoveries comes an increased awareness of the need to protect deep sea environments. Conservation efforts are crucial to preserving these unique ecosystems, which are increasingly threatened by human activities such as deep-sea mining and climate change. Protecting these habitats is essential to ensuring the survival of the diverse life forms that inhabit them.
Interdisciplinary collaboration will be key to advancing our understanding of these findings. Marine biologists, ecologists, and other scientists must work together to study and preserve these ecosystems. By combining expertise from various fields, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the deep sea and its inhabitants.
Public Engagement and Education

The discovery of potential new life forms at deep sea vents has captured the public’s imagination, sparking interest in deep-sea research. Such discoveries serve as a reminder of the vast and unexplored mysteries of our planet. Public engagement in scientific discoveries is critical, as it fosters a greater appreciation for the natural world and the importance of preserving it.
Educational programs and outreach initiatives can play a significant role in disseminating information about these findings. By incorporating the discoveries into educational curricula, schools and institutions can inspire students to pursue careers in science and marine biology. Engaging the public through lectures, documentaries, and interactive exhibits can also raise awareness about the importance of ocean conservation.
Encouraging the next generation of scientists is vital to the future of marine biology and related fields. Initiatives aimed at inspiring young people to explore scientific careers can have a lasting impact. By fostering curiosity and a love for discovery, these efforts can help cultivate the scientists and researchers who will continue to explore the mysteries of the deep sea and beyond.