
The universe is full of mysteries, and meteorites are some of the most intriguing objects that scientists study. While these space rocks often offer valuable insights into the cosmos, some meteorites present challenges that make researchers hesitate to study them. Here are five meteorites that have puzzled scientists and continue to spark curiosity and caution.
1. The Tunguska Mystery

In 1908, a massive explosion occurred over the Tunguska region in Siberia, flattening over 2,000 square kilometers of forest. Despite the devastation, no impact crater was found, leading scientists to believe that the explosion was caused by an airburst of a meteoroid. The Tunguska Event remains a scientific enigma, primarily because there is no physical meteorite to study.
Researchers have long speculated about the composition and origins of the object that caused the explosion. Some theories suggest it was made of ice, similar to a comet, while others propose a rocky asteroid. The lack of concrete evidence makes any definitive conclusion elusive. Despite over a century of research, the Tunguska Mystery remains unsolved, leaving scientists both fascinated and cautious about drawing conclusions without more evidence.
2. The Chicxulub Enigma
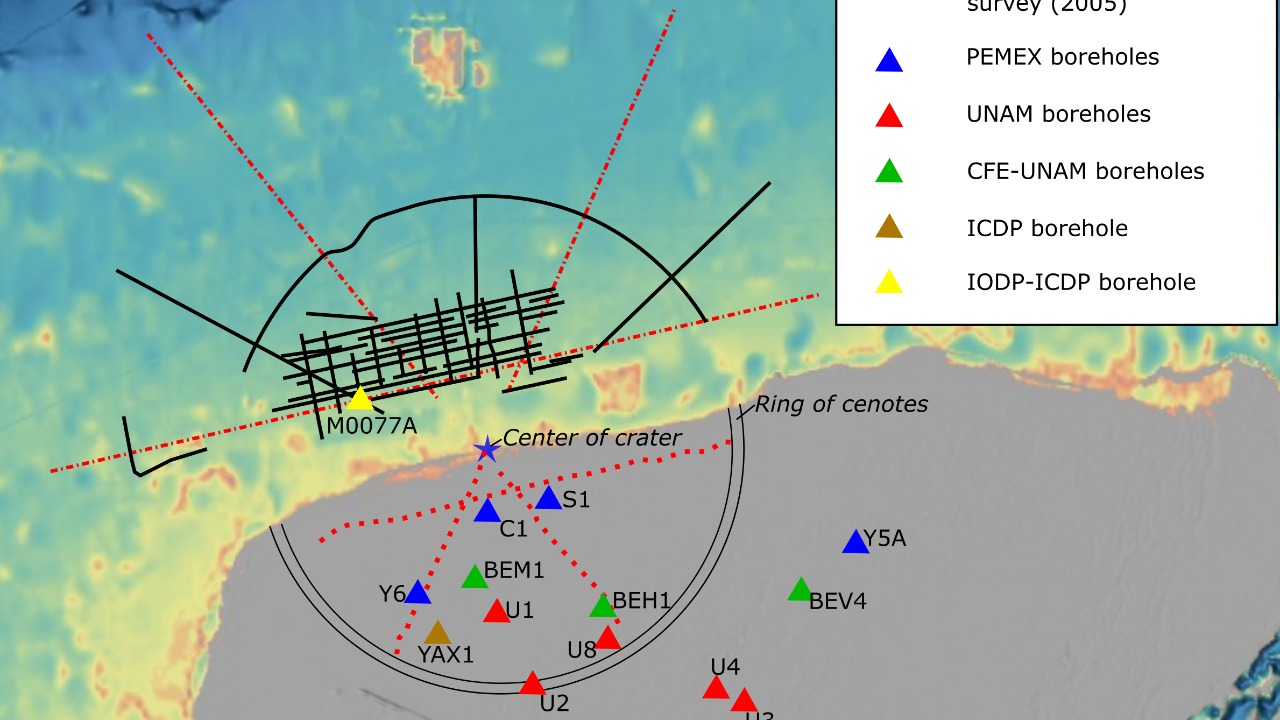
Sixty-six million years ago, a massive asteroid struck the Yucatán Peninsula, leading to the extinction of the dinosaurs. The impact created the Chicxulub crater, which is over 180 kilometers in diameter. While the extinction event is well-documented, the exact nature of the asteroid remains uncertain.
Studying the Chicxulub impactor presents challenges due to the crater’s depth and the mixture of different geological materials at the site. Drilling projects have provided some clues, but the precise composition and origins of the asteroid are still debated. Scientists must carefully consider the environmental and logistical challenges of further excavation, making the Chicxulub impactor a complex subject of study.
3. The Orgueil Enigma
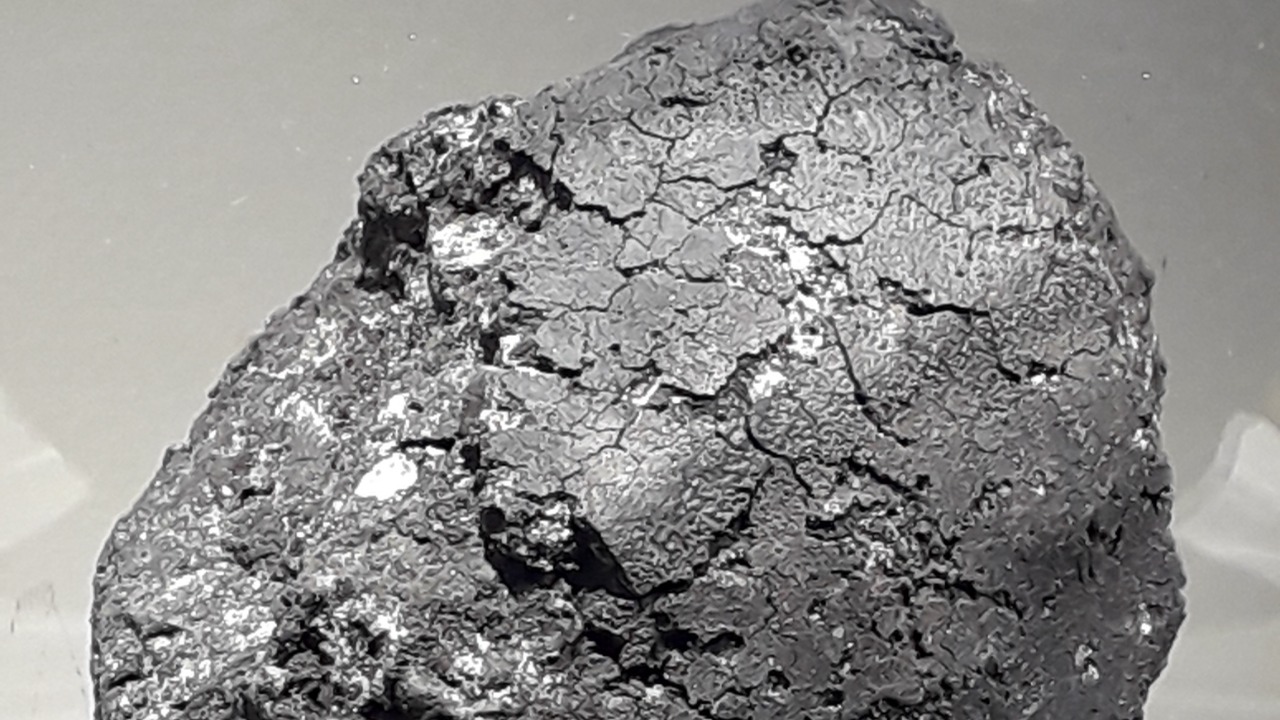

In 1864, a meteorite fell in Orgueil, France, and has since become one of the most studied carbonaceous chondrites. The Orgueil meteorite is rich in organic compounds, sparking interest in its potential to provide insights into the early solar system and the origins of life. However, the controversy surrounding its organic matter has made scientists wary.
Some researchers argue that the organic materials could be terrestrial contaminants rather than extraterrestrial. This possibility complicates the interpretation of data gathered from the meteorite. To avoid drawing inaccurate conclusions, scientists approach the Orgueil meteorite with caution, meticulously analyzing samples and cross-referencing findings.
4. The Hypatia Stone Conundrum
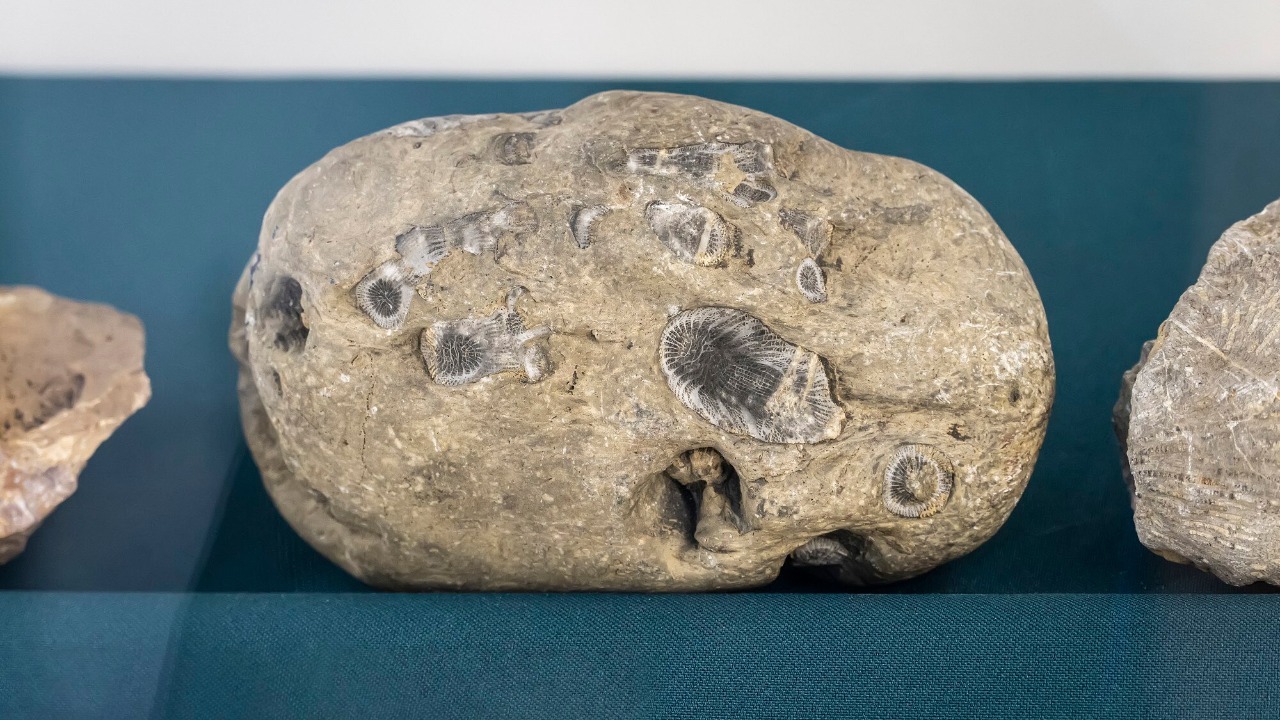

Discovered in Egypt, the Hypatia stone is unique due to its unusual mineral composition that doesn’t match any known meteorite or earthly material. Its extraterrestrial origins are clear, but its formation remains a mystery. The stone’s exotic structure suggests it might predate the solar system itself, raising questions about its journey through space.
Scientists are intrigued by the potential insights Hypatia could provide about the early universe. However, studying this meteorite is challenging due to its fragile nature and the difficulty in obtaining uncontaminated samples. Researchers fear that mishandling could destroy crucial evidence, so the Hypatia stone remains a delicate puzzle for scientists to unravel.
5. The Canyon Diablo Puzzle
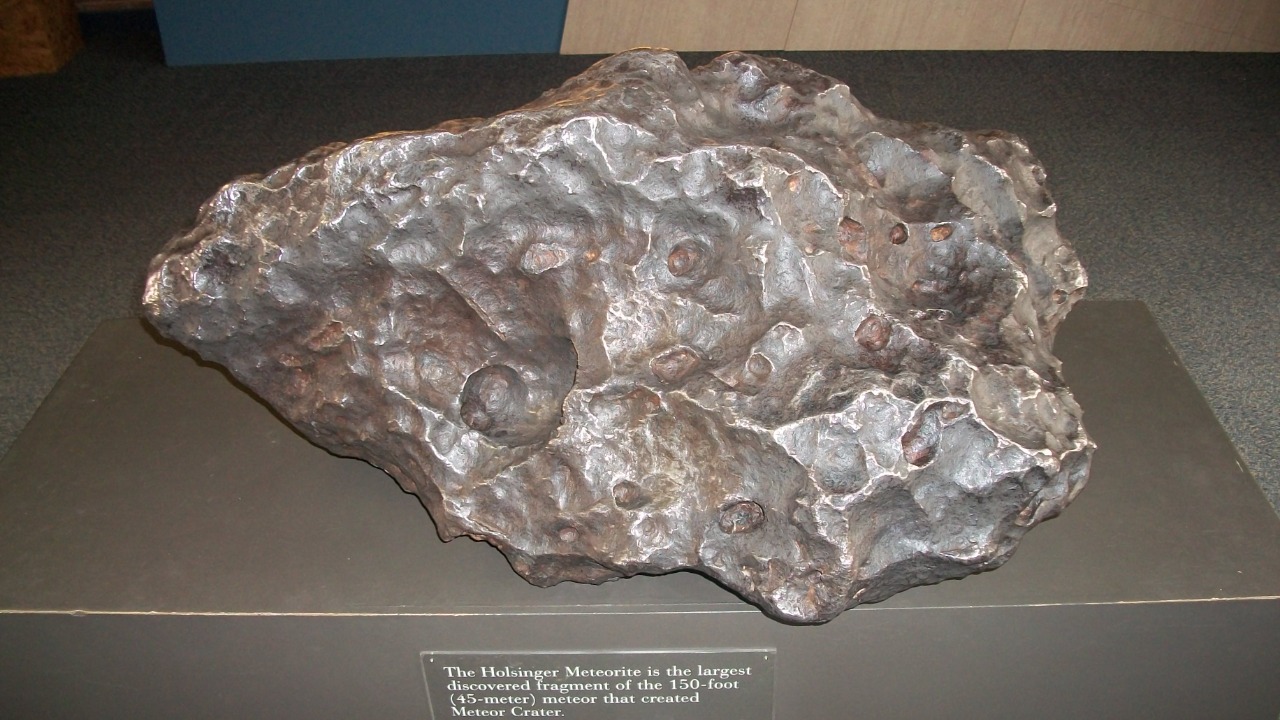

The Canyon Diablo meteorites are fragments from the asteroid that created the famous Meteor Crater in Arizona. Known for their high nickel-iron content, these meteorites have been key to understanding the composition of iron meteorites. Yet, the Canyon Diablo meteorites also present a dilemma. While they have been extensively studied, some aspects of their isotopic composition remain puzzling. Scientists are particularly interested in the presence of rare isotopes, which could provide clues about the solar system’s formation. However, the complexity of these isotopic patterns makes interpretation difficult, requiring advanced techniques and cautious analysis to avoid erroneous conclusions.