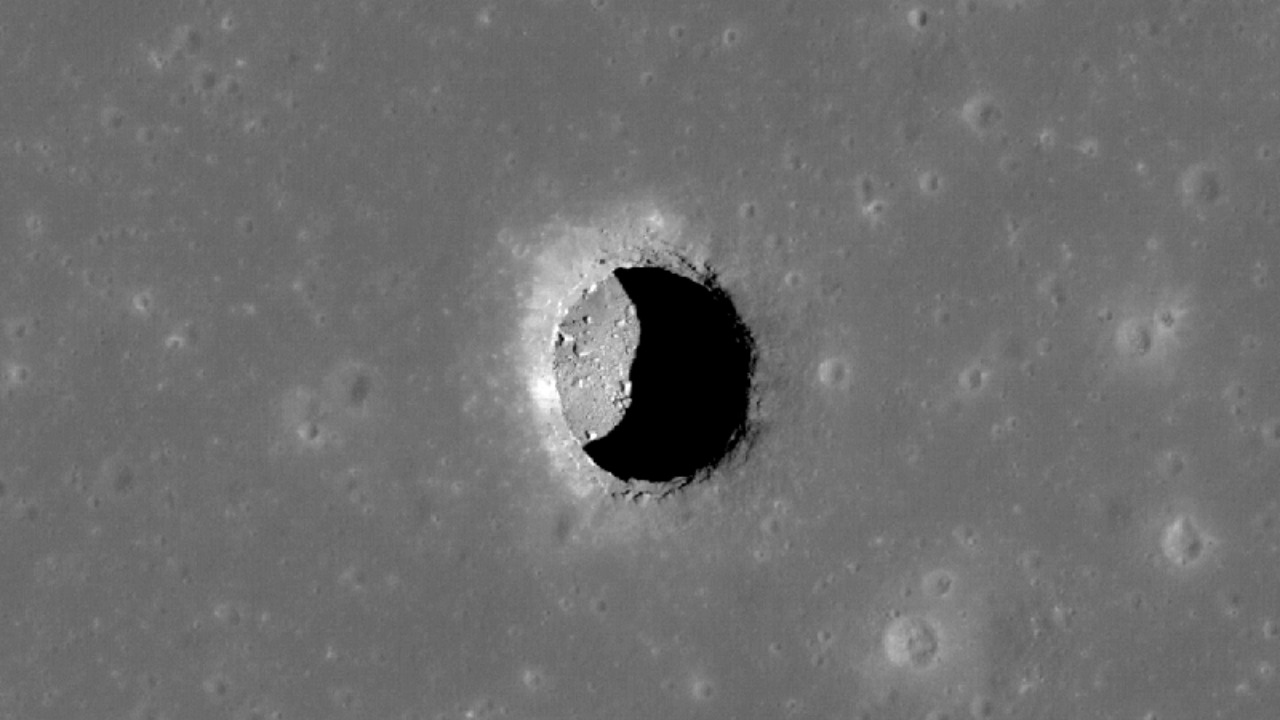

Recent discoveries have unveiled a network of caves beneath the lunar surface, potentially providing safe havens for future astronaut missions. These subterranean structures, formed by ancient volcanic activity, could offer significant advantages over traditional surface habitats on the Moon. The potential of these lunar caves has significant implications for the future of space exploration.
The Discovery of Lunar Caves
The formation of lunar caves is a result of ancient volcanic activity that occurred billions of years ago. As volcanic lava flowed across the Moon’s surface, it created hollow tubes when the outer layer of lava cooled and solidified while the hot inner lava continued to flow. When the flow ceased, it left behind empty tunnels or caves. These geological formations are now being explored for their potential to house future lunar missions.
Detection of these lunar caves has been made possible through advanced technologies and missions. Lunar orbiters equipped with high-resolution imaging systems, such as the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, have played a crucial role in mapping these subterranean structures. Additionally, radar and thermal imaging from orbiters have helped identify potential cave locations and assess their sizes and depths. Recent studies have confirmed the existence of these caves, highlighting their vastness and potential for human habitation.
Advantages of Moon Caves for Astronauts

One of the most significant advantages of lunar caves is their ability to protect astronauts from harmful cosmic and solar radiation. The thick layers of rock provide a natural shield, a crucial consideration given the lack of atmosphere on the Moon to filter out such radiation. This protection is essential for long-term missions where exposure to radiation is a primary concern.
In addition to radiation protection, lunar caves offer a stable thermal environment. Unlike the harsh temperature fluctuations experienced on the lunar surface, which can range from extreme heat to freezing cold, the caves maintain a more constant temperature. This temperature stability is beneficial for both astronauts’ comfort and the longevity of equipment and habitats. Moreover, these caves may be located near areas with water ice, providing a potential resource for water supply and oxygen production.
Challenges and Considerations for Habitation

While the potential of lunar caves is promising, there are significant challenges to overcome. Accessing these caves involves logistical hurdles, including the transportation of astronauts and equipment from the lunar surface to the cave entrances. Developing infrastructure to support these missions will be crucial, involving technologies like advanced rovers and possibly vertical transportation systems.
Another concern is the structural integrity of the caves. While the rock formations are ancient, they must be thoroughly assessed for stability to ensure they can safely house humans. Engineering solutions will be necessary to reinforce areas that might be prone to collapse or erosion. Additionally, life support systems must be developed to sustain human life within these environments. This includes reliable air, water, and power supplies to enable long-term habitation.
Future Missions and Research

There are several upcoming missions by space agencies aimed at further exploring these lunar caves. For instance, NASA and other international partners are planning robotic missions to study the caves’ properties and assess their suitability for human habitation. These missions will provide valuable data to pave the way for future manned missions.
International collaboration will play a vital role in advancing lunar exploration. The shared use of cave habitats could lead to cost-sharing and the pooling of resources among countries, enhancing the feasibility of sustained lunar presence. In the long term, lunar caves could serve as stepping stones for missions to Mars and beyond, offering a testing ground for technologies and life support systems necessary for deep space exploration.
Implications for Space Exploration

Utilizing lunar caves could significantly impact mission costs by reducing the need for extensive habitat construction on the Moon’s surface. These natural structures provide a ready-made shelter, potentially lowering the financial barrier to long-term lunar missions. Furthermore, they offer unique scientific opportunities for geological and astrobiological research, which could lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
The possibility of living in lunar caves also holds inspirational value, igniting interest in space exploration among the next generation of scientists and explorers. As we look to the future, the exploration and utilization of lunar caves could mark a significant milestone in humanity’s journey into the cosmos, offering a glimpse into the potential of living beyond our home planet.