
NASA’s Voyager spacecraft have been traveling through space for over four decades, providing humanity with invaluable insights into the solar system’s remote boundaries. Recently, these intrepid explorers have sent back data revealing mysterious phenomena at the very edge of our solar system, sparking both intrigue and scientific inquiry.
What NASA has uncovered in this distant celestial frontier is shaping our understanding of the universe in profound ways.
The Quest of the Voyager Spacecraft
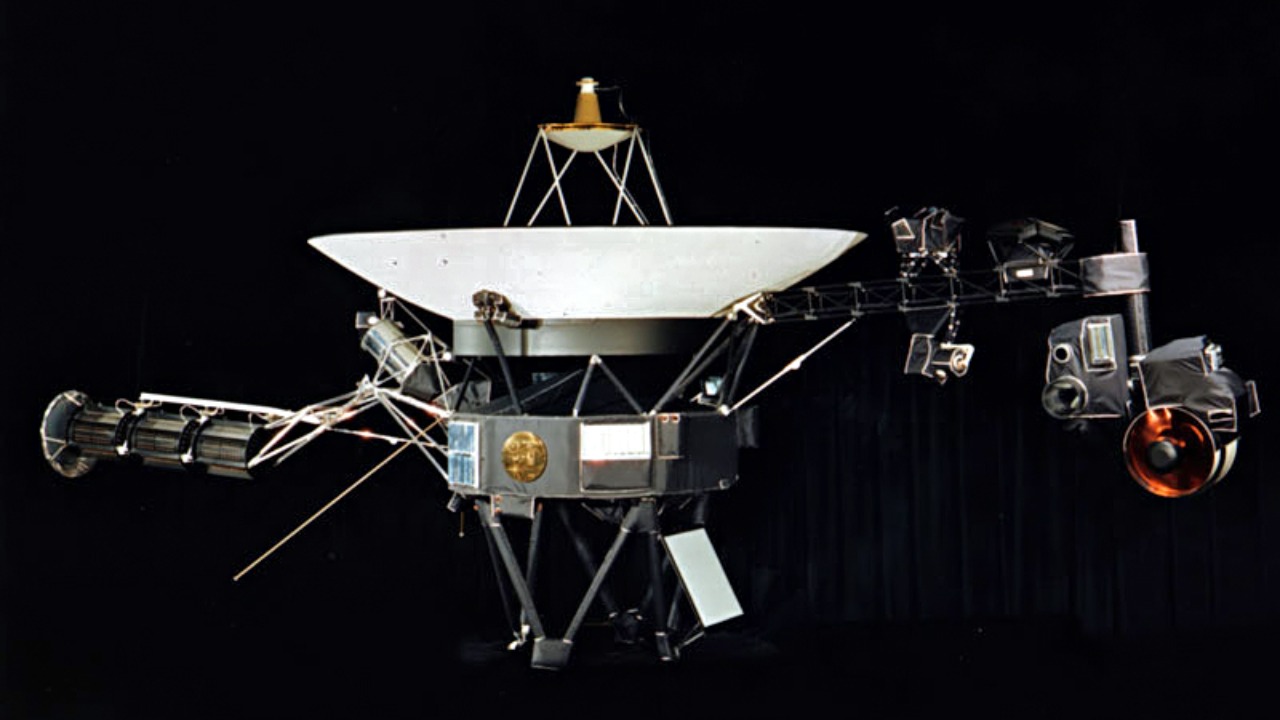
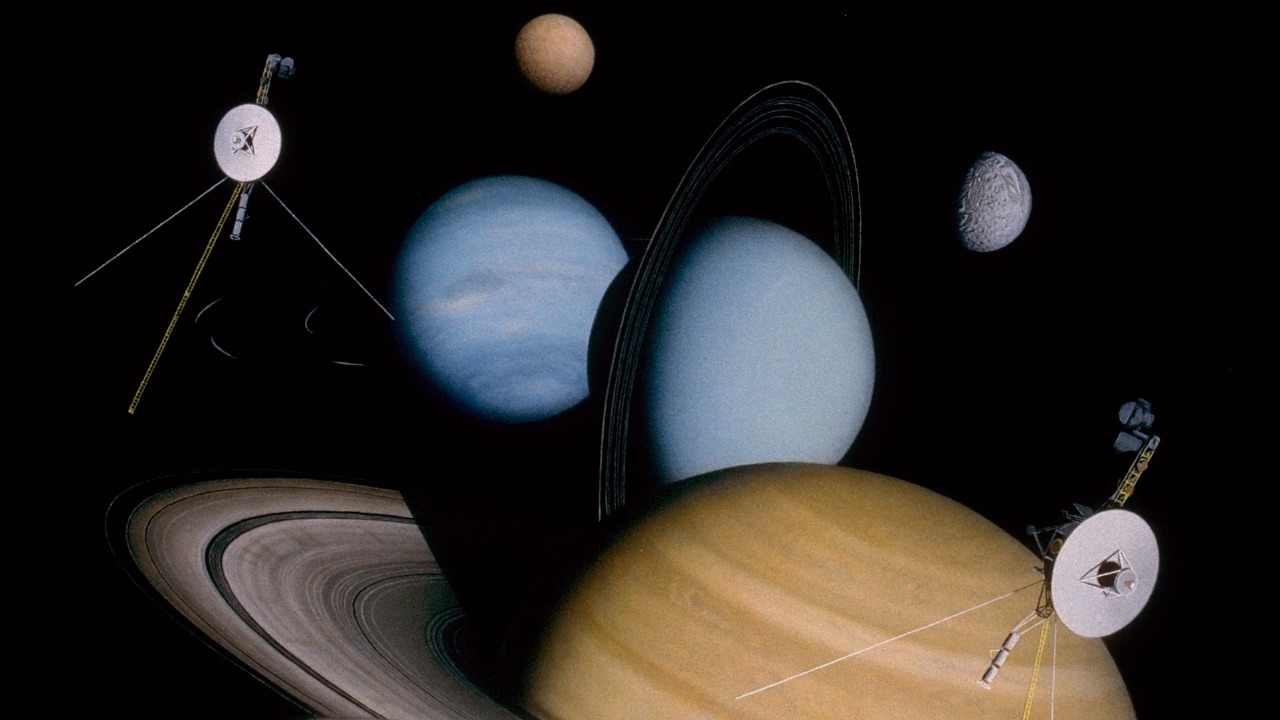
The Voyager missions, consisting of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, were launched in 1977 with the primary objective of exploring the outer planets of our solar system. These spacecraft have since exceeded their original missions and continued to send data from the farthest reaches of space. As pioneers, they provided humanity with our first close-up views of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, along with their moons and rings.
Among their most notable milestones, both Voyager spacecraft have crossed into interstellar space, with Voyager 1 achieving this historic feat in 2012, followed by Voyager 2 in 2018. This marked the first time human-made objects entered this uncharted territory, revealing groundbreaking data about the heliosphere’s boundary and the interstellar medium. The significance of these discoveries cannot be overstated; they have profoundly enhanced our understanding of the solar system and the broader universe, providing a context for future explorations.
Mysterious Phenomena at the Solar System’s Edge

One of the intriguing findings from the Voyager spacecraft is the detection of a “wall” of hydrogen. This region, located at the edge of our solar system, is where the solar wind slows down and accumulates against interstellar space. The hydrogen wall serves as a barrier of sorts, providing vital information about how our solar system interacts with the surrounding cosmos.
In addition to the hydrogen wall, NASA’s supercomputer simulations have revealed a strange spiral structure at the solar system’s edge. This feature could potentially influence the movement of cosmic rays and has sparked new questions about the dynamics at play in this distant region. These discoveries have significant implications for space physics, as they offer a glimpse into the complex interactions between solar and interstellar phenomena.
Challenges of Exploring the Distant Frontier
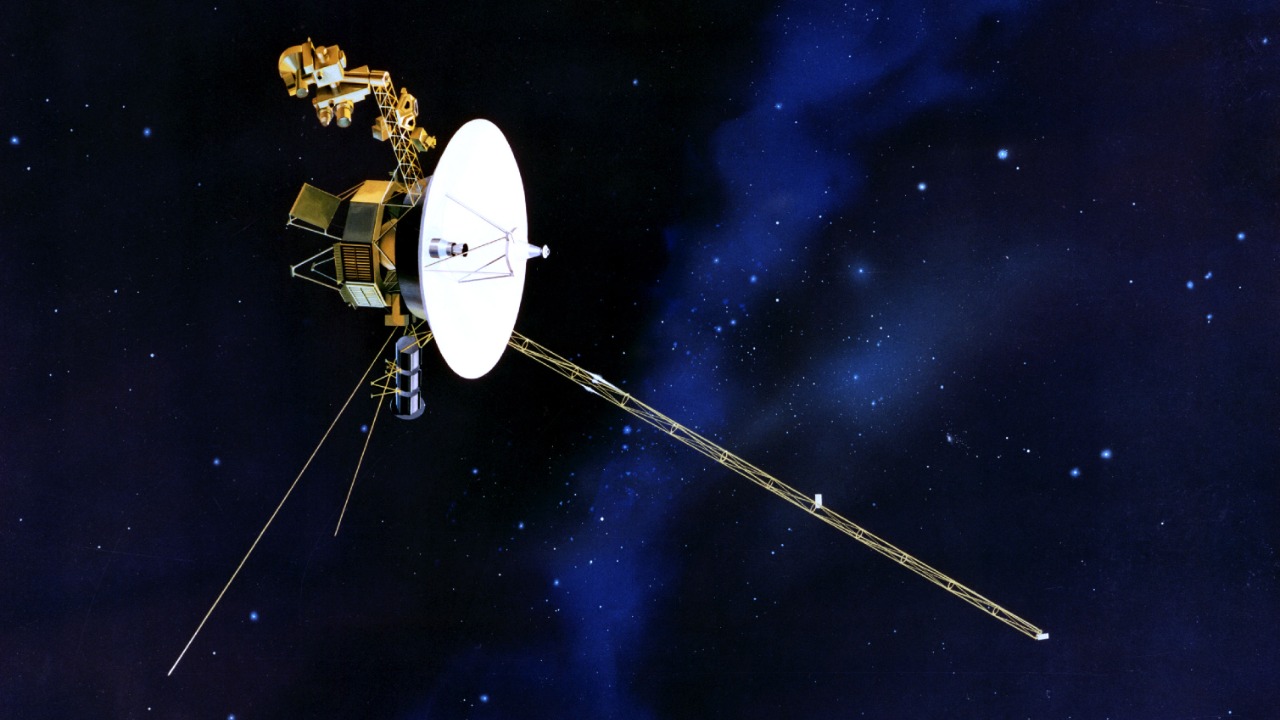

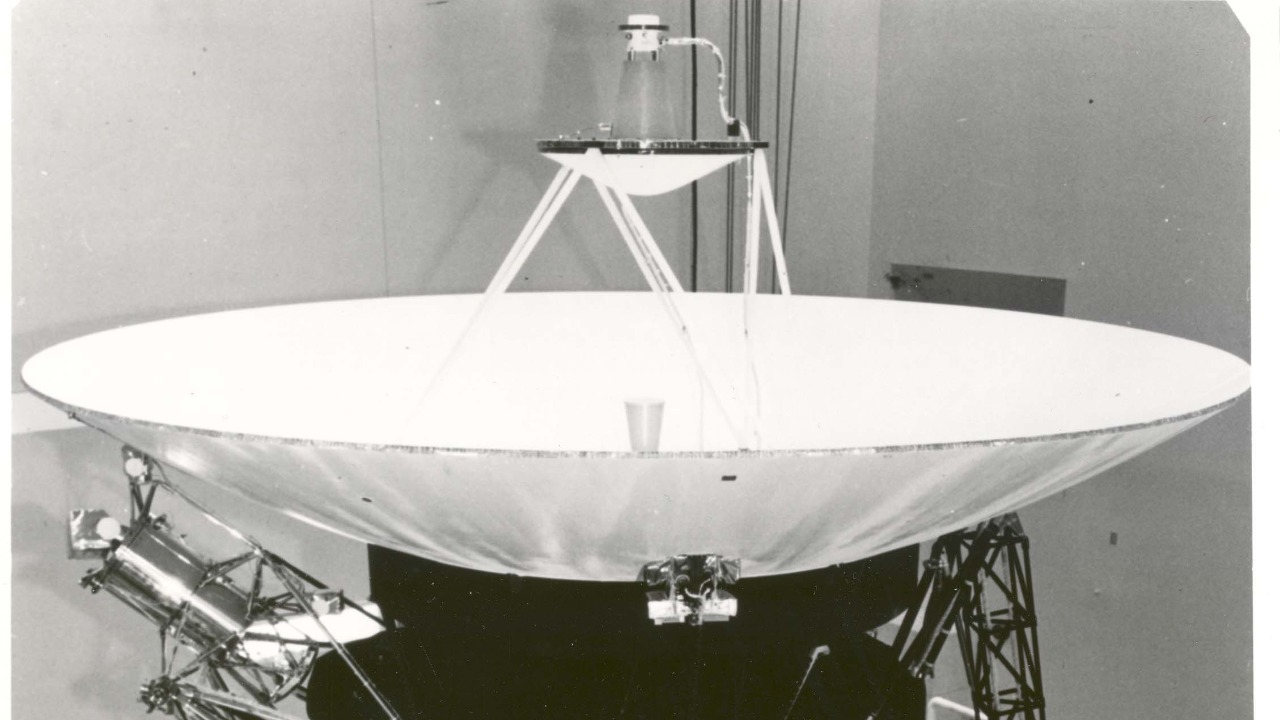
The technical challenges faced by the Voyager spacecraft in sending data from the edge of the solar system back to Earth are immense. These probes operate on technologies developed over 40 years ago, and yet they continue to function in the harsh environment of deep space. The vast distances involved mean that communication signals take over 20 hours to travel one way, requiring precise coordination and timing.
One of the pressing issues for the Voyager missions is power depletion. Both spacecraft rely on radioisotope thermoelectric generators, which are gradually losing their ability to produce adequate power. As a result, engineers must carefully manage the power supply to keep essential systems running. Despite these challenges, the Voyager missions continue to send data back to Earth, providing valuable insights into the outer reaches of our solar system.
The Future of Solar System Exploration
As the Voyager spacecraft continue their journey, NASA and other international space agencies are planning new missions to explore the edges of our solar system and beyond. These upcoming missions aim to build on the foundation laid by the Voyagers, using advanced technologies to overcome the challenges of deep space exploration. Innovations such as improved propulsion systems and miniaturized instruments are being developed to enable future spacecraft to travel further and faster.
The broader implications for humanity are significant. These missions not only enhance our scientific understanding but also inspire a sense of wonder and curiosity about our place in the universe. As we continue to push the boundaries of space exploration, we are reminded of the potential for discovery and the enduring human spirit of exploration.
The Scientific and Philosophical Impact of Discoveries
The findings from the Voyager missions have expanded our scientific knowledge, offering new insights into the structure and behavior of our solar system. By studying the unknown phenomena at the boundary of our solar system, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the galaxy and our position within it. These discoveries also invite philosophical reflections on the nature of our universe and humanity’s quest for knowledge.
Moreover, the achievements of the Voyager spacecraft serve as an inspiration for future generations of scientists, engineers, and explorers. The ongoing exploration of space encourages young minds to pursue careers in science and technology, fostering innovation and discovery. As we continue to explore the cosmos, we are reminded of the vast opportunities that lie ahead and the potential for uncovering new mysteries that await us in the universe.