Every year, the natural world surprises us with new species, each more intriguing than the last. From the vibrant depths of the ocean to the secluded corners of dense forests, these discoveries remind us of Earth’s vast biodiversity and the mysteries that remain hidden. Let’s explore eight fascinating species that have been newly identified this year.
The Neon-Tailed Gecko
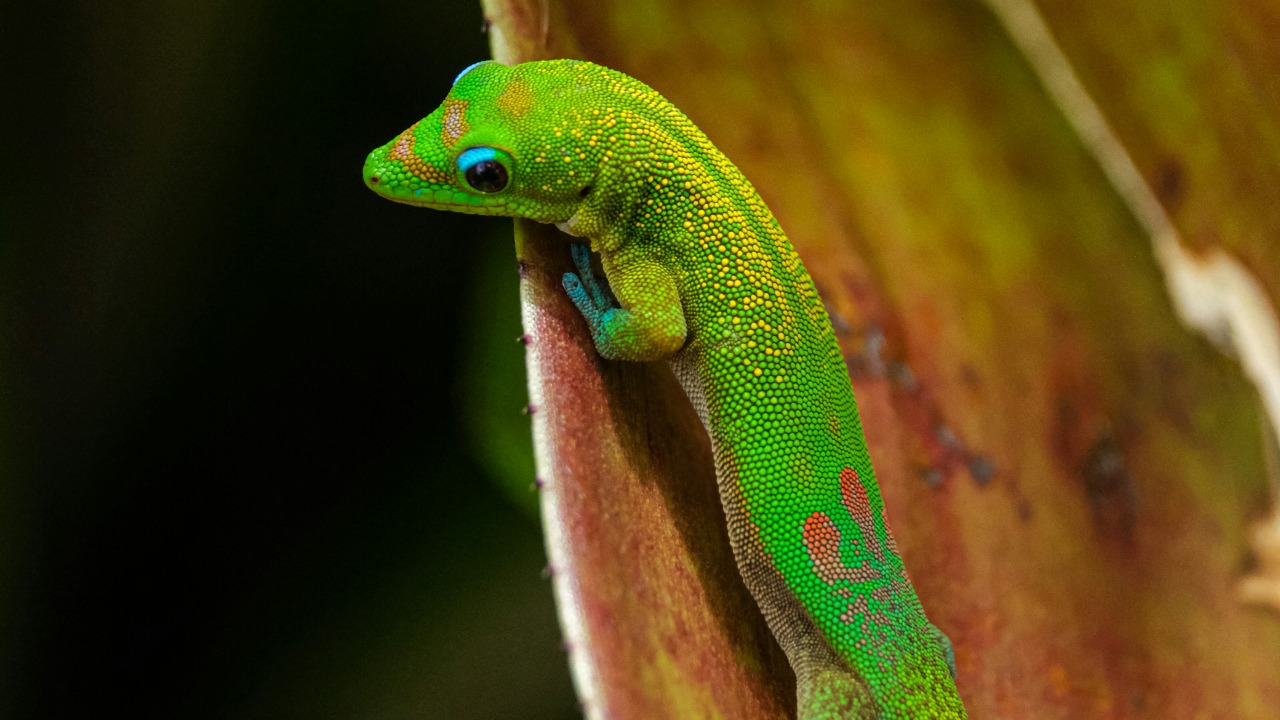

The Neon-Tailed Gecko is a stunning addition to the gecko family, found in the rainforests of Southeast Asia. Characterized by its vibrant, luminescent tail, this gecko has captivated researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Its unique tail coloration is believed to be a defense mechanism, distracting predators and allowing the gecko to escape. This fascinating adaptation highlights the complexity of evolutionary biology and the ongoing wonders of the natural world.
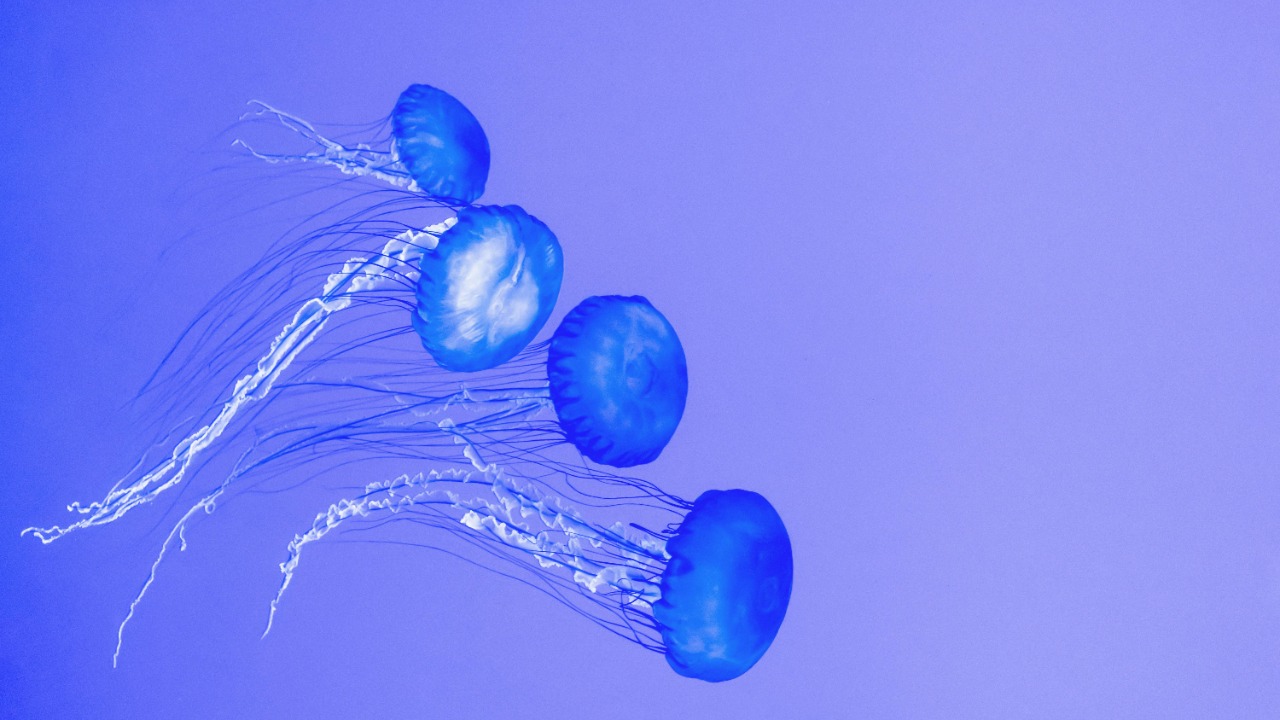
The Bioluminescent Jellyfish
Discovered in the deep waters of the Pacific Ocean, the Bioluminescent Jellyfish is a mesmerizing spectacle. Its ability to emit light not only creates a breathtaking underwater show but also serves as a tool for communication and predation. This jellyfish’s bioluminescence is a classic example of nature’s ingenuity, offering insights into marine ecosystems and the adaptive strategies of oceanic life.
The Crimson-Feathered Hummingbird
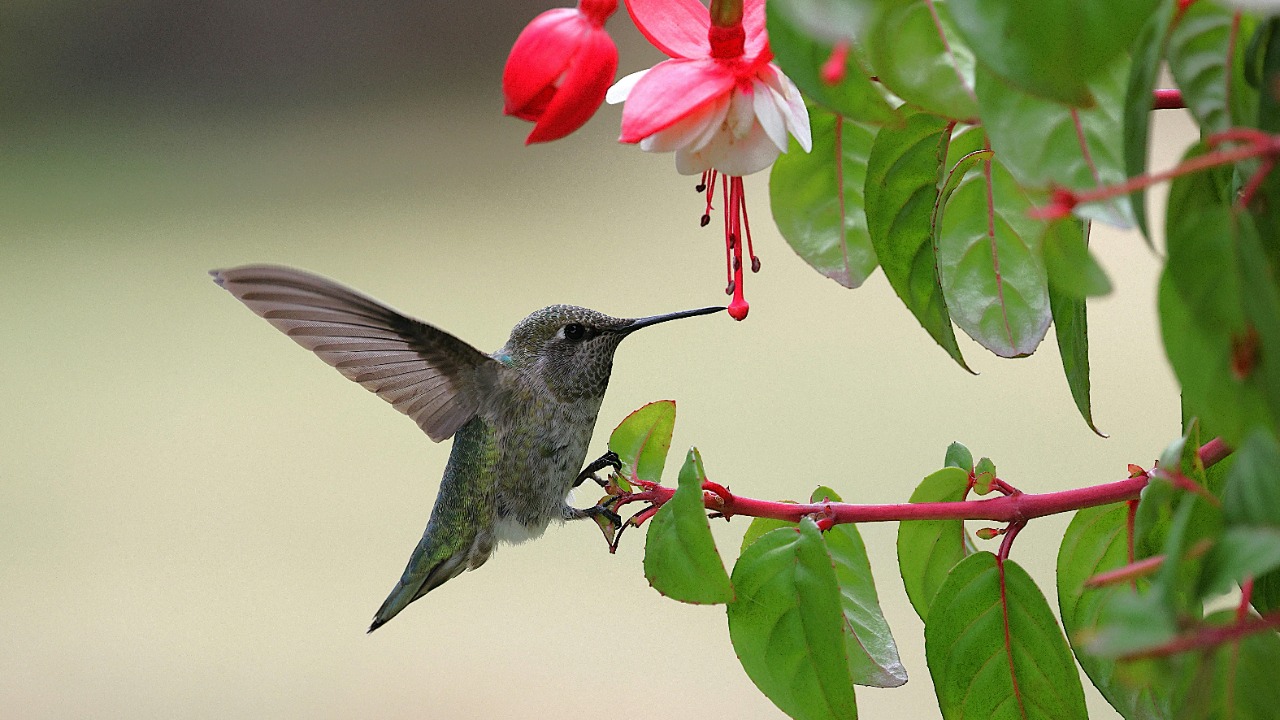

High in the Andes, the Crimson-Feathered Hummingbird darts through the air with remarkable agility. Its vibrant red plumage sets it apart from its relatives, making it a true gem of avian biodiversity. The discovery of this hummingbird contributes significantly to our understanding of ecological niches and the critical role these birds play in pollinating mountain flora.
The Glass Frog with Transparent Skin

In the cloud forests of Central America, the Glass Frog with Transparent Skin offers a unique glimpse into its inner workings. Its translucent skin allows researchers to observe its beating heart and other organs, providing valuable data on amphibian physiology. This discovery underscores the importance of conserving fragile habitats where such unique species thrive.
The Electric Blue Tarantula
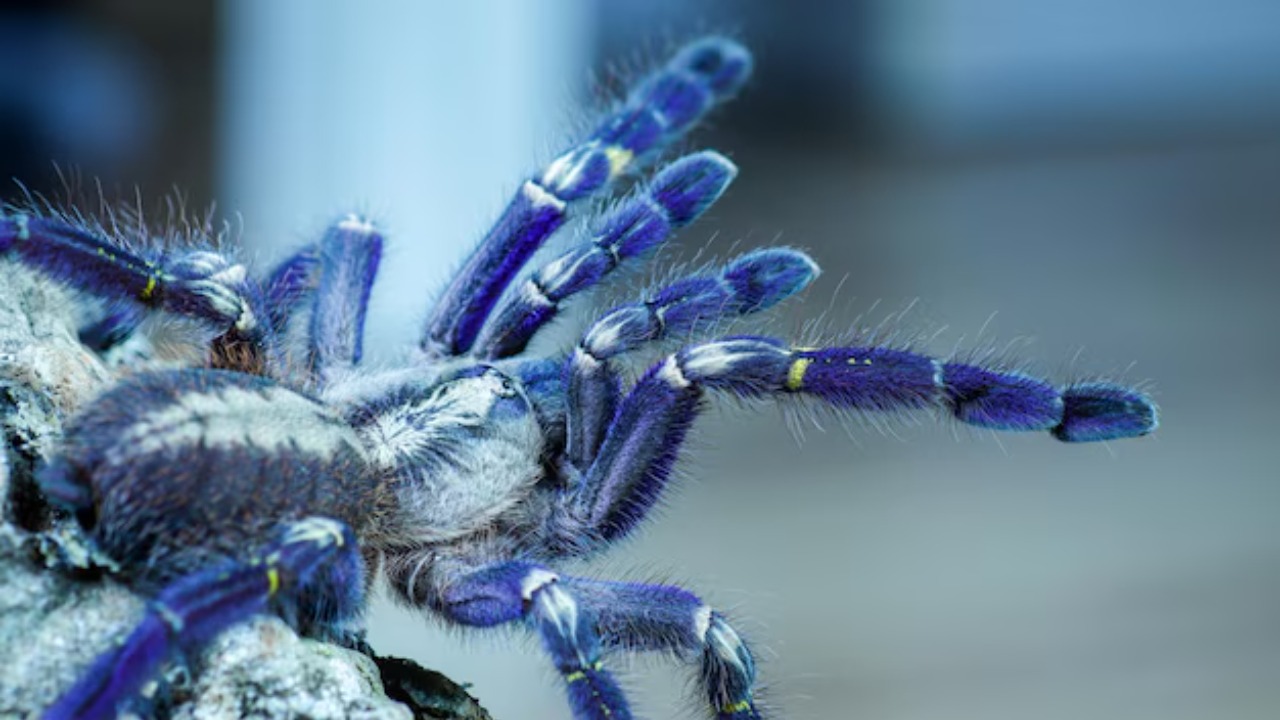

The Electric Blue Tarantula, recently found in the jungles of South America, is a dazzling arachnid with iridescent blue hairs. Its striking appearance has made it a subject of interest for arachnologists and enthusiasts alike. This tarantula’s vivid coloration is not just for show; it plays a crucial role in its survival strategies, from mating rituals to predator deterrence.
The Miniature Forest Elephant
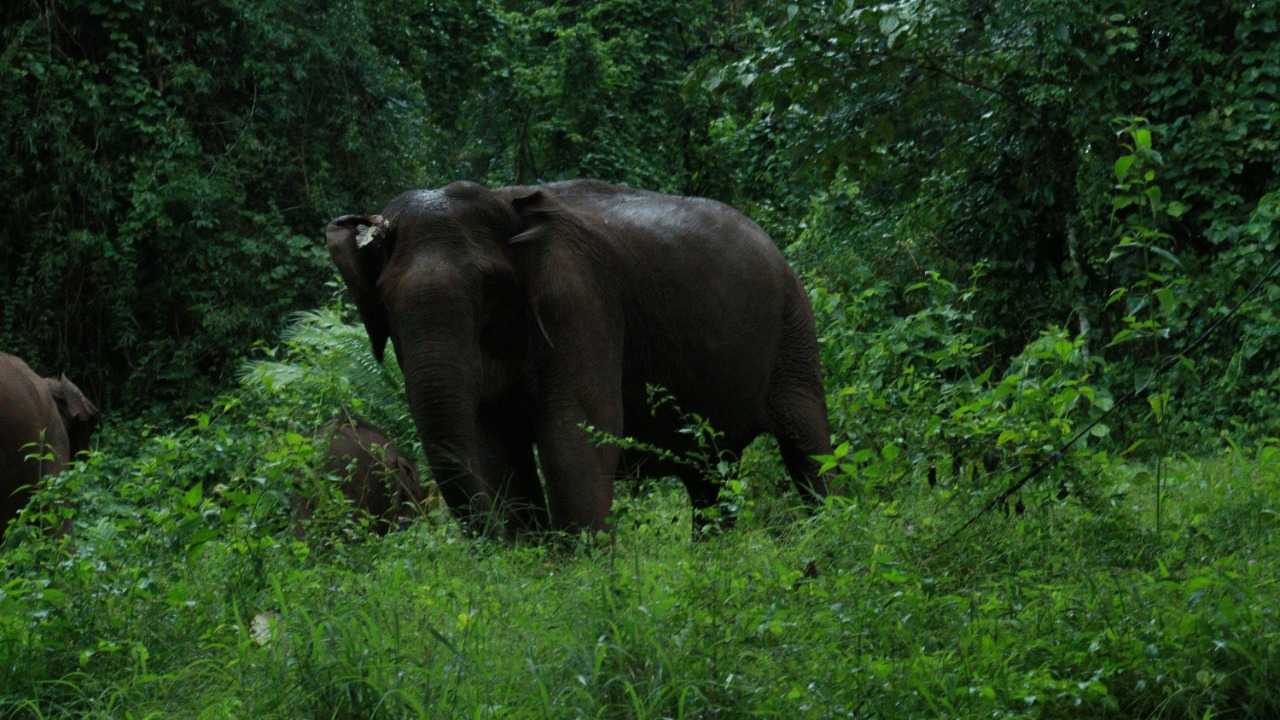

The Miniature Forest Elephant, a newly discovered subspecies in the dense rainforests of Africa, is a remarkable find for conservationists. Smaller than its savannah-dwelling relatives, this elephant is adapted to life in thick vegetation. Its discovery highlights the rich diversity of life in forest ecosystems and the need for habitat protection.
The Rainbow-Colored Sea Slug
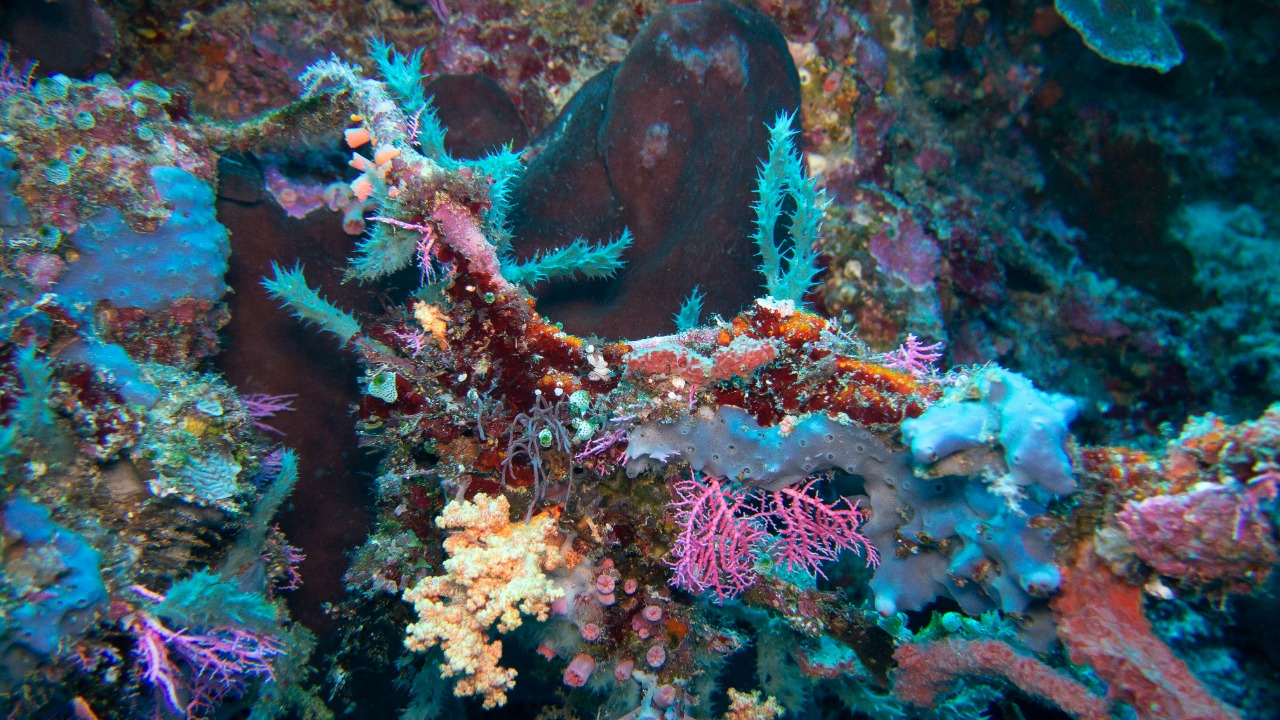

Vibrantly adorned with a spectrum of colors, the Rainbow-Colored Sea Slug is a dazzling addition to marine biodiversity. Found in the coral reefs of the Indo-Pacific, this sea slug’s brilliant hues are more than just a visual delight; they serve as a warning to potential predators of its toxicity. This discovery adds to our understanding of the complex interactions within coral reef ecosystems.
The Spotted Snow Leopard of the Himalayas
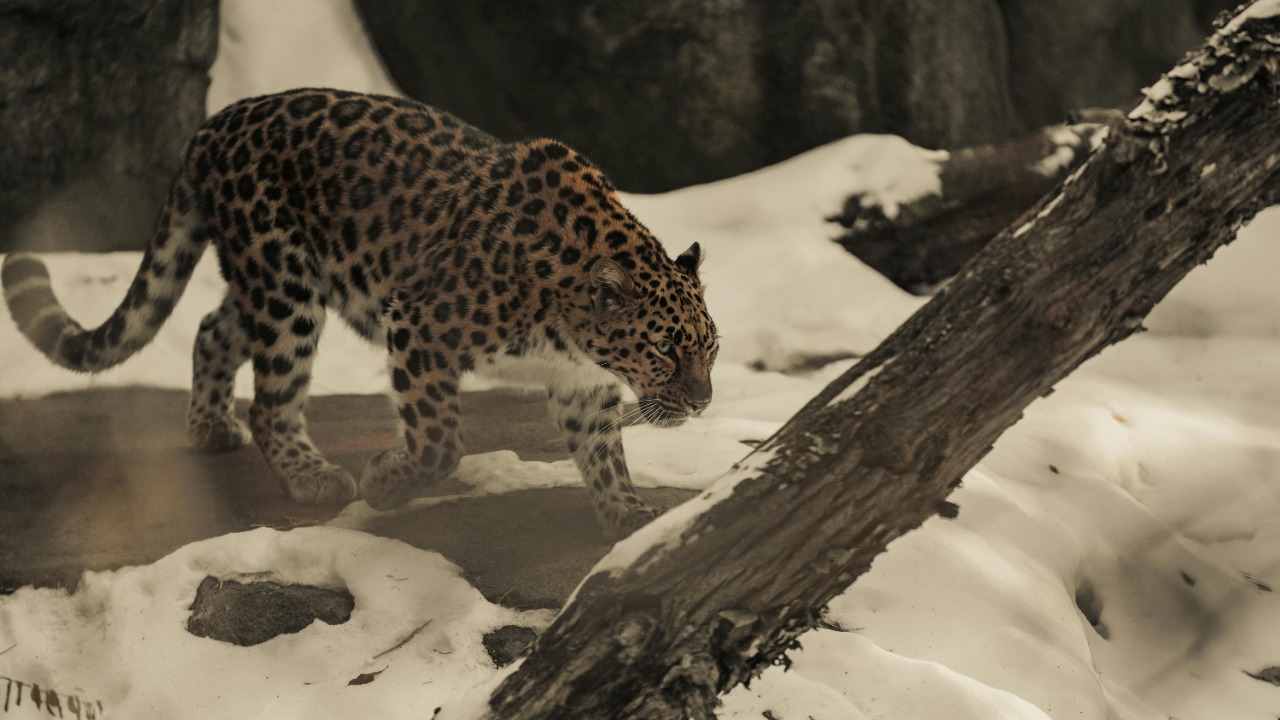

In the remote and rugged terrain of the Himalayas, the Spotted Snow Leopard has been identified as a distinct subspecies. Its unique coat pattern and adaptations to cold, high-altitude environments emphasize the incredible diversity within the snow leopard species. Understanding these differences is crucial for conservation efforts, particularly in regions facing climate change and habitat encroachment.