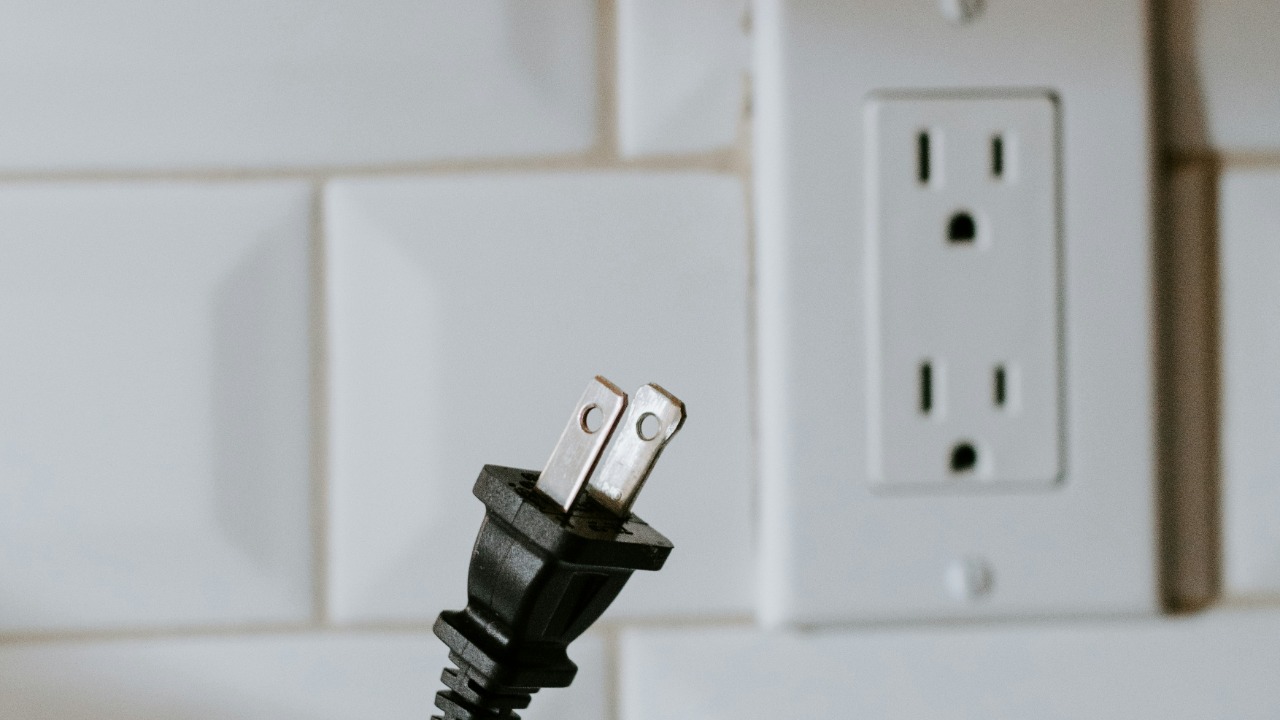

In many households, encountering different types of electrical outlets is common, especially when dealing with older appliances or homes. A frequent question arises: Can you plug a two-prong plug into a three-prong outlet? Navigating the compatibility and safety considerations of these electrical connections is crucial, as is understanding the purpose of the third prong in modern outlets.
Understanding Electrical Outlets

Electrical outlets come in various configurations, with two-prong and three-prong outlets being the most common in residential settings. The two-prong outlets, often seen in older homes, were once the standard. These outlets provide a basic connection with a hot and neutral wire, allowing current to flow to and from appliances. In contrast, the three-prong outlets, which have become the standard in modern construction, include an additional grounding prong. This evolution in design reflects growing awareness of electrical safety and the need to protect against potential hazards.
The shift to three-prong outlets is rooted in their enhanced safety features. Unlike their two-prong counterparts, three-prong outlets have a grounding wire that prevents electrical shocks and reduces the risk of electrical fires. This grounding feature is especially important for appliances with metal exteriors, as it offers an extra layer of protection against accidental contact with live electrical parts.
The Third Prong: Grounding Explained
The grounding prong serves a critical role in electrical systems. It acts as a safety measure by providing a path for electrical current to return to the ground in the event of a short circuit or fault. This prevents the current from traveling through an unintended path, such as a person touching the appliance, thereby reducing the risk of electric shock.
There are common misconceptions about the necessity of grounding. Some people believe that grounding is an unnecessary feature, especially in areas with reliable electrical systems. However, the grounding prong is crucial in preventing potential electrical hazards, such as fires caused by stray currents. This understanding underscores the importance of using properly grounded outlets and appliances.
Plugging a Two-Prong Plug Into a Three-Prong Outlet
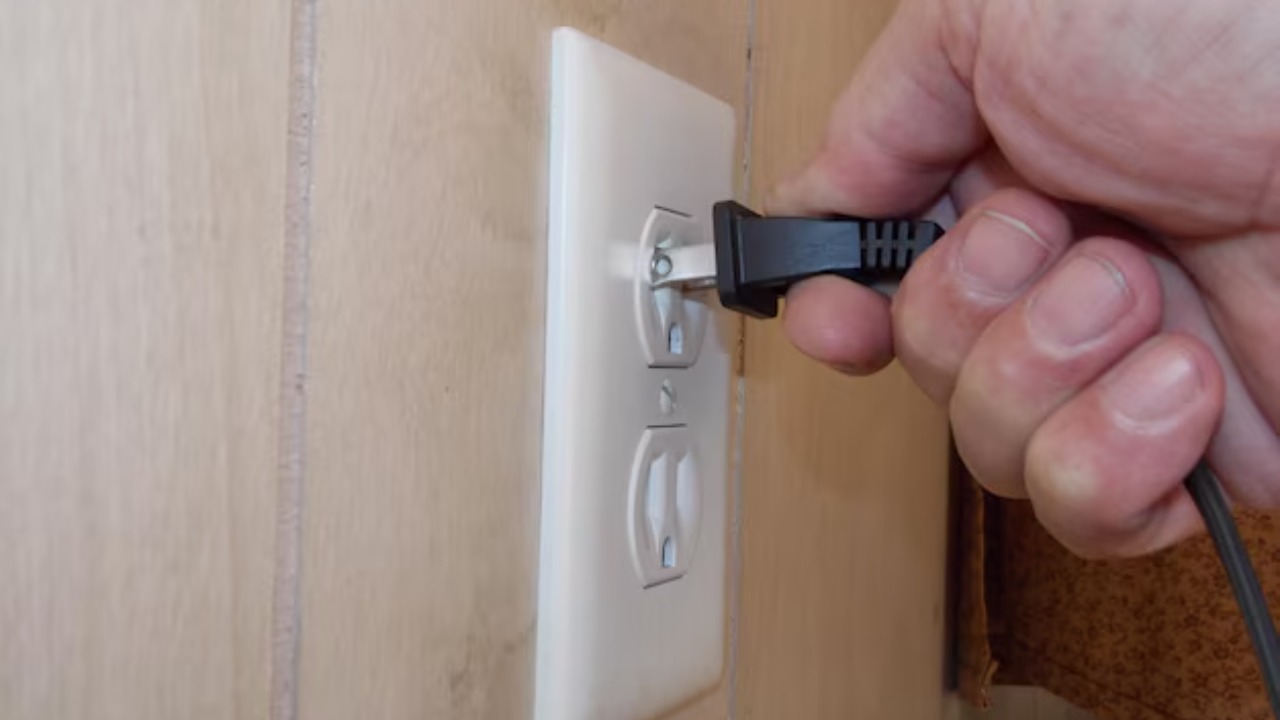

When faced with the dilemma of plugging a two-prong plug into a three-prong outlet, many turn to using adapters. These adapters allow the connection of two-prong plugs to three-prong outlets by bypassing the grounding feature. However, it’s important to note the potential risks of using adapters, as they can compromise the safety provided by the grounding system.
To ensure safety when using adapters, it’s vital to consider certain precautions. Always use adapters with a grounding connection, which involves attaching the metal tab or wire to the outlet’s center screw. Additionally, avoid modifying plugs to fit three-prong outlets, as this can lead to unsafe situations and potential electrical hazards.
Alternatives and Solutions
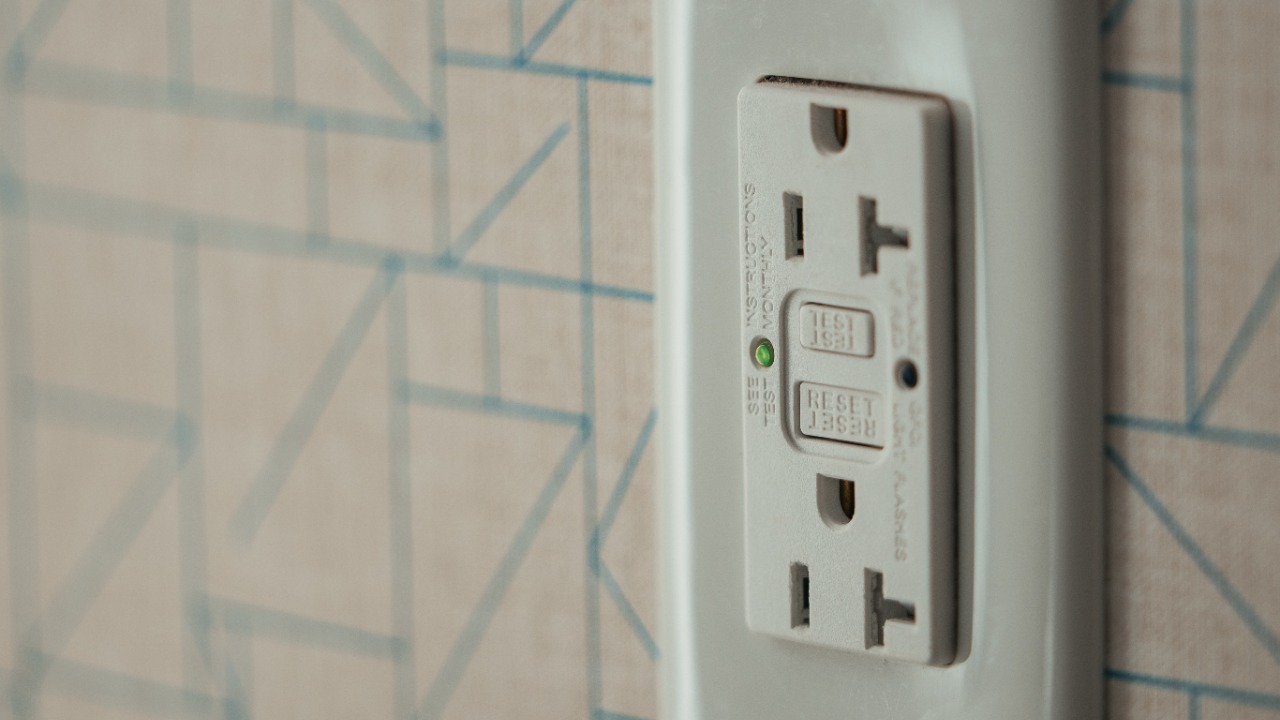

For those living in older homes, upgrading outlets from two-prong to three-prong is a viable solution. This upgrade not only improves safety but also ensures compatibility with modern appliances. The process typically involves rewiring and may require the assistance of a licensed electrician to ensure compliance with electrical codes.
Another alternative is the use of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets. These outlets provide an additional layer of protection by detecting ground faults and interrupting the circuit to prevent electrical shocks. GFCI outlets are particularly useful in areas with high moisture levels, such as kitchens and bathrooms, where the risk of electrical shock is heightened.
Global Perspective on Electrical Outlets
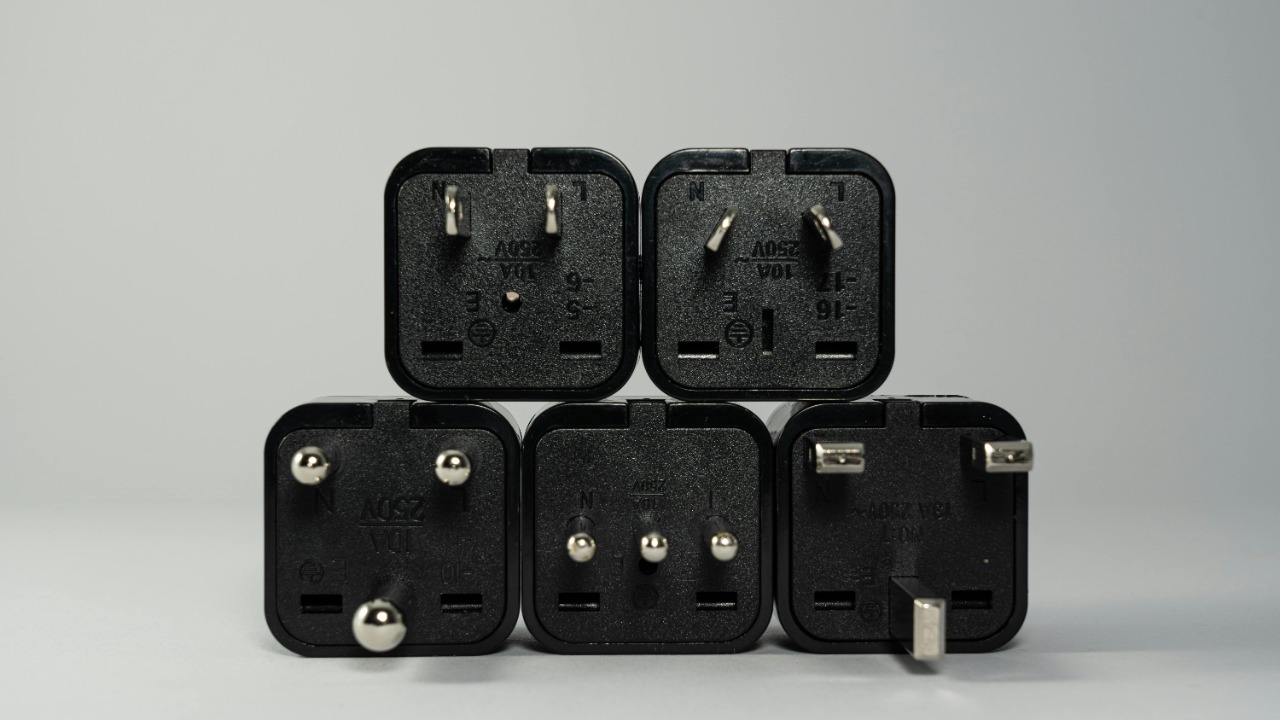

Electrical outlets and plug types vary significantly around the world, which can present challenges for travelers and those using international appliances. Different regions have different standards, and what works in one country may not be compatible in another. For instance, plug types in Europe differ from those in North America, necessitating the use of adapters and converters.
When adapting to different electrical standards, it’s crucial to use high-quality adapters and converters to ensure safety. These devices should be rated for the appropriate voltage and current to prevent overheating and potential hazards. Awareness of international electrical standards and proper use of adapters can help avoid issues when using appliances across different regions.