
NASA is exploring the ambitious concept of beaming solar power from space to Earth, a revolutionary idea that could transform our energy landscape. By harnessing solar energy in space and transmitting it wirelessly to our planet, this technology promises a constant and abundant energy supply. Let’s delve into the details of NASA’s plans, the technology behind it, and the potential implications for the future of energy.
The Concept of Space-Based Solar Power

Space-based solar power involves capturing solar energy in space using large solar arrays and then transmitting it wirelessly to Earth. The technology relies on key components such as solar panels in orbit, microwave or laser transmitters, and receiving stations on the ground known as rectennas. These rectennas convert the transmitted energy into electricity, integrating it into existing power grids.
The idea of space-based solar power isn’t new. It dates back to the mid-20th century when scientists first envisioned the potential of capturing solar energy in space. Early research efforts, such as those summarized in the OSTI report, laid the groundwork for the technological advancements we see today. Key milestones include NASA’s studies in the 1970s and more recent projects that have reignited interest in this promising energy source.
One of the main advantages of collecting solar power in space is the uninterrupted exposure to sunlight, free from atmospheric interference or weather conditions. This means energy can be harvested continuously, unlike Earth-based solar panels that are limited by day-night cycles and weather variations. Consequently, space-based solar arrays can yield significantly higher energy outputs, making them an attractive option for meeting global energy demands.
NASA’s Current Initiatives and Research
NASA is currently engaged in several projects to explore the feasibility of space-based solar power. These initiatives include collaborations with other space agencies and private companies to develop and test technologies necessary for energy transmission from space. Noteworthy among these is NASA’s collaboration with international partners and private enterprises to advance the research and development of lightweight materials and efficient transmission methods.
Technological innovations play a crucial role in these projects. Advances in energy transmission methods, such as microwave and laser technologies, are key enablers. Additionally, the development of advanced robotics is essential for deploying and maintaining these solar arrays in the harsh environment of space. The use of lightweight materials further aids in reducing launch costs and improving the efficiency of space-based systems.
Funding and partnerships are vital for these initiatives. NASA receives support through government budgets, and collaborations with private enterprises and international partners are pivotal. These partnerships not only provide financial backing but also bring together a diverse set of expertise to tackle the myriad challenges associated with space-based solar power.
Challenges and Technical Obstacles

One of the primary challenges in space-based solar power is the efficient transmission of energy over long distances. Wireless energy transmission, whether through microwaves or lasers, is subject to efficiency losses. Additionally, there are safety concerns regarding the potential effects of these beams on the atmosphere, wildlife, and human health.
The financial and infrastructural challenges are also significant. Launching and maintaining solar arrays in space is costly, and the infrastructure required on Earth to receive and distribute the power adds to the expense. As highlighted in Carlos Rios’ research paper, overcoming these cost barriers is critical to the viability of space-based solar power.
Regulatory and environmental considerations further complicate the development of this technology. International agreements are necessary to manage the use of global airspace for energy transmission. Additionally, the environmental impact of continuous microwave beams needs thorough investigation to ensure the ecological balance is not disrupted.
Global Implications and Competition
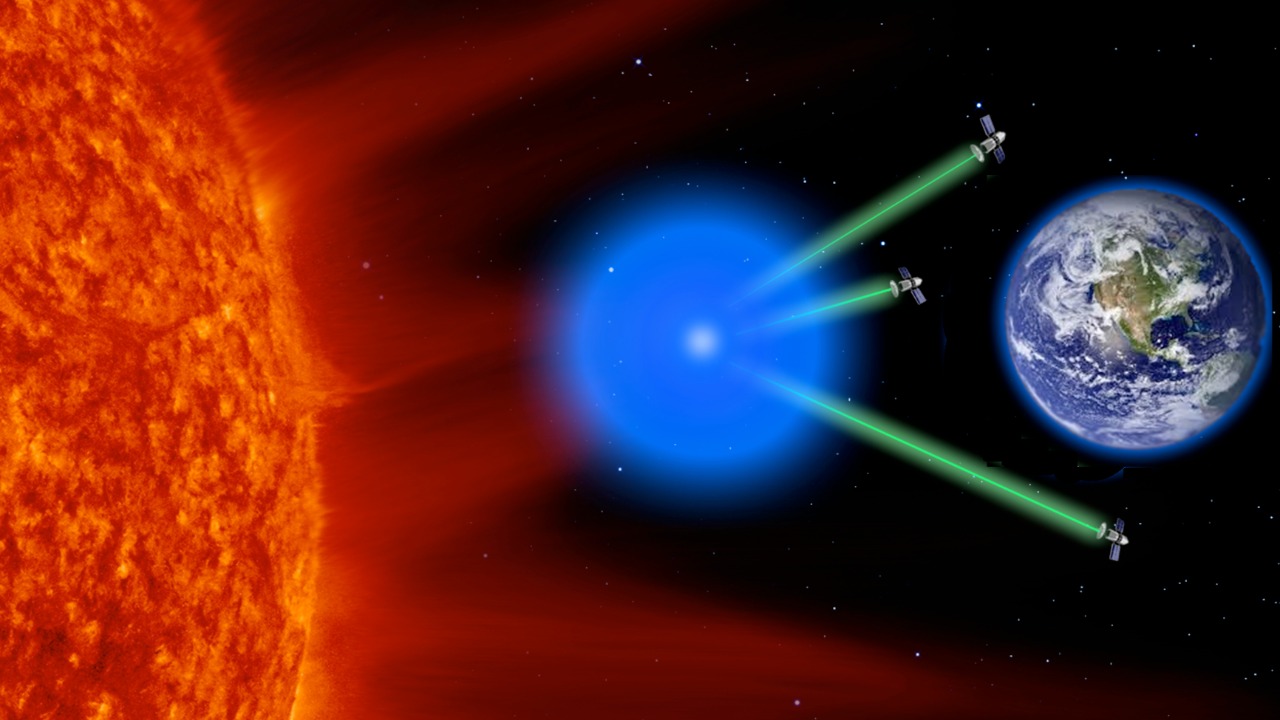
NASA is not alone in pursuing space-based solar power. Countries like China have ambitious plans to develop solar arrays in space, underscoring a global race for energy innovation. China’s projects are aimed at creating vast solar farms in orbit, capable of delivering substantial amounts of energy back to Earth. This international competition can drive rapid advancements in the field.
The economic and geopolitical impact of space-based solar power could be profound. By reducing dependence on fossil fuels, this technology has the potential to alter global energy markets and shift geopolitical power dynamics. Countries that lead in space-based solar power development might gain significant influence in the global energy landscape.
From a sustainability perspective, space-based solar power offers a promising solution to combat climate change. By providing a clean and renewable energy source, it could significantly reduce carbon emissions and help transition the world toward more sustainable energy practices. The potential of this technology in addressing global energy needs and environmental challenges cannot be overstated.
Future Prospects and Vision

The scalability and implementation timeline of space-based solar power are critical factors for its success. While experimental projects are already underway, scaling up to commercial applications will require significant advancements in technology and infrastructure. The timeline for widespread implementation depends on overcoming current challenges and securing continued investment and international cooperation.
Envisioning a future where solar power is harnessed from space, it becomes clear how transformative this technology could be. It holds the potential to meet global energy demands sustainably, contributing to a future where energy is abundant and clean. Such a shift could redefine how societies function and interact with the environment.
Public engagement and education are essential for advancing space-based solar power. Raising awareness and building support through educational initiatives and public policy advocacy will play a crucial role in the technology’s development and acceptance. By fostering a well-informed public, we can ensure that space-based solar power receives the attention and support it needs to become a reality.